James
Hey, I've been diving deep into our next-generation telematics project. Can you help me understand what makes telematics technology so critical in today's connected vehicles?
Adam
Absolutely! Think of a Telematics Control Unit as the communication hub of a modern vehicle. It's essentially the gateway in connected cars that enables intercommunication to the outside world, whether that's communicating with cellular networks, GPS satellites, or even other vehicles on the road. V2X, V2G, and V2V technologies are all associated with telematics systems.
James
That sounds fascinating, but how does this differ from the traditional automotive systems we've worked with before? I mean, cars have had electronic control units for decades. How does TCU technology differ from it?
Adam
Great question! Traditional ECUs were like isolated islands - they managed specific vehicle functions internally. But TCUs act as bridges connecting the vehicle to a vast digital ecosystem. With cellular IoT connectivity, a TCU can transmit real-time vehicle diagnostics to manufacturers, enable over-the-air updates, provide emergency services, and even facilitate vehicle-to-everything communication.
James
So we're essentially talking about transforming vehicles into IoT devices on wheels? That must require some serious cellular connectivity infrastructure.
Adam
Exactly! And that's where cellular connectivity becomes game-changing. With 4G LTE and 5G networks, we're seeing telematics solutions that can handle everything from basic GPS tracking to complex autonomous driving scenarios. The bandwidth and low latency of these networks are enabling use cases we couldn't even imagine a few years ago.
Opening Notes
The automotive industry has long been synonymous with innovation, but the recent shift toward connected, intelligent vehicles marks a new era in transportation. At the heart of this transformation lies telematics, a critical technology that enables cars to talk to each other (Vehicle-to-Vehicle), infrastructure (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure), and even the cloud. But what is behind this revolution?
How is the integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) and cellular connectivity reshaping vehicle telematics systems?
The integration of cellular connectivity into automotive telematics units represents more than just a technological upgrade - it is a fundamental shift toward intelligent transportation systems that can adapt, learn, and communicate in real-time.
The Evolution of Telematics Systems
What is Telematics?
Telematics refers to the integrated use of telecommunications and informatics to collect, transmit, and analyze data from remote sources, typically vehicles, fleets, or mobile assets. It combines real-time data transmission with advanced analytics to enhance decision-making, operational efficiency, and safety.
Primarily used in vehicle tracking, fleet management, and transportation, telematics systems monitor key metrics such as location, speed, fuel consumption, vehicle diagnostics, and driver behavior. Telematics technology enables businesses to optimize fleet operations, reduce costs, and improve customer service through predictive maintenance, route planning, and data-driven insights.
Telematics is a critical enabler for industries including logistics, automotive, vehicle insurance, and public transportation, facilitating advancements in autonomous driving, smart cities, and the Internet of Things (IoT).
It’s the backbone of connected car services, turning vehicles into mobile data hubs. Initially, telematics focused on basic functionalities such as GPS navigation, emergency services, and remote diagnostics. But as vehicles began to evolve, so did vehicle telematics. At the heart of this transformation lies cellular connectivity, which serves as the critical enabler for modern vehicle telematics solutions.
Imagine your car as a smartphone on wheels.
It doesn’t just track itself, but it also understands how it’s performing, communicates with other vehicles, and even carries out over-the-air updates. All of this is made possible by the integration of cellular connectivity and IoT.
Counterpoint Technology Market Research quotes that in 2024, a staggering 75% of all passenger cars sold worldwide came with embedded cellular connectivity, marking an 8% year-over-year surge. This leap showcases the growing demand for connectivity features in mass-market vehicles, rooting for seamless in-car connectivity.
Need help understanding how Cellular Connectivity can boost your Automotive Solutions?
Get in touch with us here.
Telematics Solutions: Features and Innovations Shaping the Future
Vehicle telematics has evolved far beyond GPS tracking. Today's connected telematics solutions encompass a comprehensive ecosystem of services including real-time diagnostics, predictive maintenance, emergency response, infotainment, and even autonomous driving capabilities. The evolution of telematics systems has been driven primarily by advances in cellular IoT technology, which provides the reliable, high-speed connectivity that modern automotive applications demand.
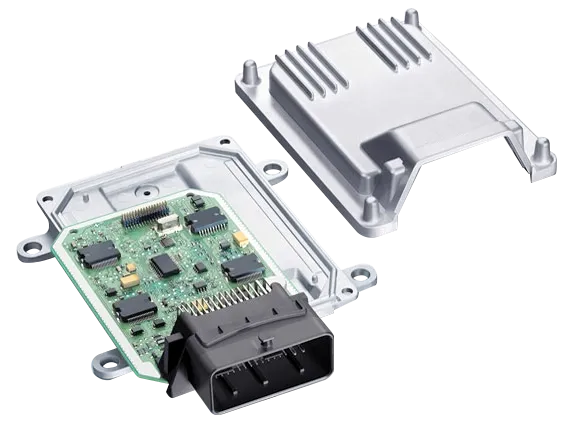
What is a Telematics Control Unit? Understanding the Brain of Vehicle Telematics
A Telematics Control Unit (TCU) serves as the central nervous system for all connectivity-related functions in a modern vehicle. This sophisticated piece of hardware acts as the primary interface between the vehicle's internal systems and external networks, enabling seamless communication through cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS technologies.
What are the Functions of Telematics Control Units (TCUs)?
The Telematics Control Unit (TCU) is like the brain of your vehicle’s connectivity system. It processes and routes data between the car’s internal systems and the outside world. Think of it as a translator, making sure everything inside the car—whether it’s the engine, safety system, or infotainment unit—can communicate with external networks.
A TCU is responsible for handling multiple functions:
- Connectivity Management: It connects your car to cellular networks (like 4G and 5G), enabling services like live traffic updates, weather forecasting, and even remote control features.
- Real-Time Diagnostics: It allows mechanics to monitor your car’s health and receive real-time alerts for potential issues, like engine malfunctions or tire pressure drops.
- Over-the-Air Updates: Seamless software updates that can add new features, fix bugs, and enhance security without requiring a dealer visit.
- Emergency Response: In case of a crash, TCUs can automatically notify emergency responders with eCall systems and provide them with precise location data.
- Infotainment & Connectivity: It integrates all your media needs, from navigation to streaming music and in-car internet access.
- Telematics Fleet Management: Comprehensive tracking and management capabilities for commercial vehicle operators.
Core Components of a TCU
A Telematics Control Unit (TCU) is a key component in connected vehicles, combining an MCU for real-time control and an application processor for running software like diagnostics and OTA updates. It includes a cellular modem (2G–5G) for wide-area communication, a GPS/GNSS receiver for location tracking, and antenna systems for cellular, GNSS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and V2X. Security modules (HSM/TPM) ensure encrypted communication and secure key storage. Integrated IMU/MEMS sensors provide vehicle motion data, supporting dead reckoning when GPS is weak. The TCU connects to other vehicle systems via CAN, LIN, and Ethernet, and supports cloud connectivity for remote monitoring, updates, and fleet services.
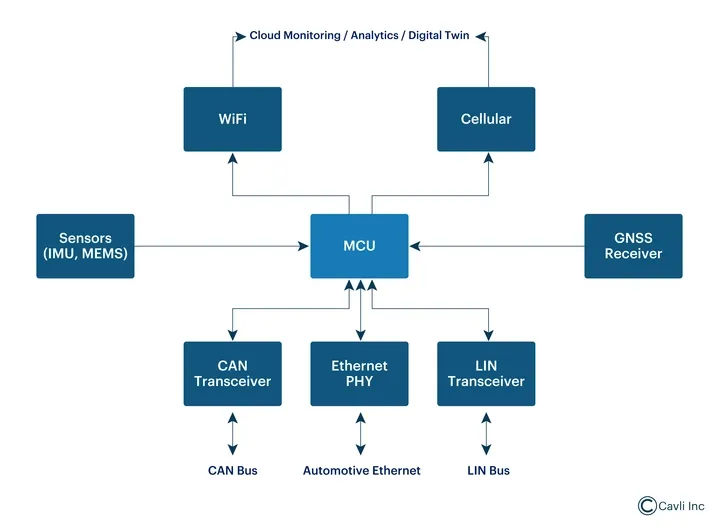
MCU (Microcontroller Unit)
The MCU serves as the central hub, handling all the critical communication and data processing tasks. It acts as the core unit that interfaces with all the other components in the TCU, coordinating and processing data from sensors, communication modules, and vehicle systems.
Cellular Modem
The heart of connectivity, supporting various cellular standards from 2G/3G legacy networks to cutting-edge 5G technology. Modern TCUs typically include multi-band, multi-mode modems or IoT modules that can automatically switch between different network types based on availability and application requirements.
Curious which Cavli IoT Modules can power your Telematics Vehicle Tracking Solutions?
Don’t miss out. Get in touch with us here.
GPS/GNSS Receiver
The GNSS receiver provides precise location data essential for navigation, fleet telematics, emergency services, and location-based applications. Advanced TCUs support multiple satellite constellations, including GPS, GLONASS, Galileo, and BeiDou, to provide enhanced accuracy.
To discover more about the role of global satellite navigation in Telematic Devices –Download eBook now
Application Processor
It is a powerful computing unit that manages data processing, protocol handling, and communication with various vehicle systems. This processor runs the embedded telematics software that orchestrates all functions of the telematics device.
Antenna Systems
The antennas manage different communication needs such as cellular (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), GPS, and other short- and long-range wireless communications. Its design ensures that signal quality is maintained even in the challenging radio frequency (RF) environment of a vehicle, where interference can be significant.
Security Module
It is critical for protecting sensitive data and ensuring secure communication. Modern TCUs incorporate hardware security modules (HSMs) and trusted platform modules (TPMs) to safeguard against cyber threats.
Sensors (IMU, MEMS)
The sensors, including Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) and Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS), collect data on the vehicle's movement, orientation, and other critical parameters. These sensors contribute to the system’s ability to track vehicle dynamics and improve the overall performance of telematics applications.
Communication Interfaces: CAN, LIN, Ethernet
- CAN Transceiver: The CAN Bus facilitates communication between various vehicle ECUs (Electronic Control Units) for internal vehicle diagnostics and operation.
- Ethernet PHY: Provides connectivity for automotive Ethernet, enabling high-speed data transmission within the vehicle’s internal network.
- LIN Transceiver: The LIN Bus facilitates communication with lower-speed peripherals like window motors, seat controllers, and lighting systems within the vehicle.
Cloud/Configuration
The cloud connection allows the TCU to interact with remote servers for data storage, configuration management, and over-the-air updates. This makes it possible to remotely configure, update, and monitor telematics devices in real-time.
Working of Connected Telematics Systems
Telematics systems in modern vehicles are sophisticated ecosystems that integrate multiple technologies to collect, process, and transmit vehicle data to cloud platforms. These systems capture real-time data through sensors, process it using embedded algorithms for diagnostics and performance analysis, and securely transmit it via cellular or satellite networks to cloud services for remote monitoring, analytics, and over-the-air updates, enabling applications like fleet management and predictive maintenance. Here is the step-by-step breakdown that explains how these systems work:
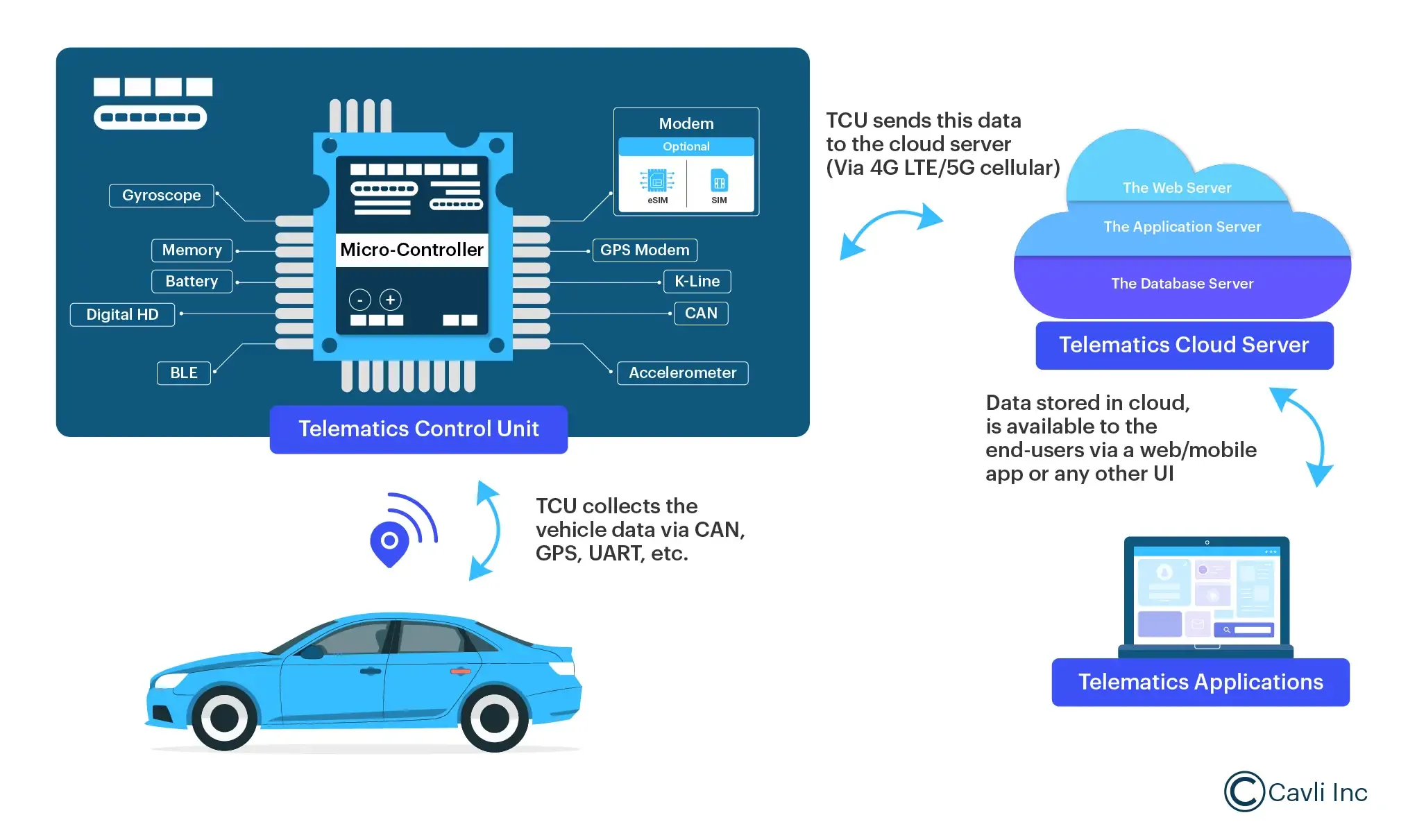
Data Collection by Telematics Control Unit (TCU)
The TCU serves as the core of the telematics system, collecting a wide array of data from the vehicle’s internal systems. These include sensors, Electronic Control Units (ECUs), GPS systems, and communication interfaces like Controller Area Network (CAN), Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART), and others. The TCU gathers essential information such as:
- Engine performance metrics (e.g., RPM, temperature, fuel consumption)
- Safety system status (e.g., airbag readiness, brake performance)
- Environmental data (e.g., GPS location, weather conditions)
- User behavior patterns (e.g., driving habits, route preferences)
ECUs are embedded with microprocessors and software that control specific vehicle functions, ensuring smooth operation, safety, and efficiency. Each ECU manages a particular aspect of the vehicle's performance or operation, from engine management to advanced safety features.
In essence, an ECU receives data from sensors, processes it based on programmed algorithms, and then sends commands to actuators to control various systems and components within the vehicle.
Local Data Processing
Once the data is collected, the TCU performs local processing using edge computing. It filters, prioritizes, and stores the data locally before transmitting it to the next phase. It ensures critical data, such as safety alerts or performance anomalies, is processed immediately. Real-time safety algorithms also run in the background to detect and act on safety threats. For example, in a predicted case of collision, TCU can alert the driver or activate emergency systems.
Secure Data Transmission
Once data is processed locally, it is transmitted via cellular networks (such as 5G, 4G LTE, and 3G) to a central cloud server. The telematics device utilizes end-to-end encryption protocols to ensure that the data is transmitted securely.
It is crucial to protect sensitive telematics data from unauthorized access. Priority queuing systems prioritize critical messages, such as safety alerts or emergency notifications, to ensure they receive prompt attention. Adaptive compression algorithms reduce the size of telematics data before transmission, enabling efficient transfer over cellular networks, especially in regions with limited bandwidth.
Cloud Analytics and Predictive Analysis
Once the data reaches the telematics cloud server, advanced analytics engines process the data. This data analysis can provide valuable insights into the vehicle’s performance, predict potential maintenance issues, and optimize route planning in telematics fleet management.
Cellular IoT Connectivity in Telematics Vehicle Tracking
Cellular IoT is transforming vehicles from simple transportation machines into intelligent, connected devices. Cellular connectivity is pivotal in telematics vehicle tracking, enabling high-speed 4G/5G data transfer for real-time map updates and video streaming. It supports predictive maintenance by transmitting sensor data to the cloud, enhances safety through V2V and V2I communication, and underpins autonomous driving with reliable data exchange. Additionally, it facilitates over-the-air software updates, optimizes fleet management with real-time tracking and analytics, and improves navigation by dynamically adjusting routes based on traffic, weather, and driving patterns, boosting efficiency and safety. Let's break it down.
- High-Speed Data Transfer: With 4G and 5G networks, telematics systems can handle massive amounts of data in real-time, enabling a more dynamic driving experience. Whether it is updating maps or streaming video, cellular IoT ensures seamless connectivity.
- Improved Vehicle Performance: Telematics systems can monitor vehicle health, predict maintenance needs, and even schedule repairs automatically. By collecting data from vehicle sensors and sending it to the cloud, IoT enables predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and extending the vehicle's overall lifespan.
- Enhanced Safety Features: The integration of IoT and cellular connectivity allows for vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication. This means telematics-enabled vehicles can share real-time information about road conditions, hazards, and traffic, making the driving experience safer and more efficient.
- Autonomous Driving: Cellular IoT is the foundation of autonomous vehicles. High-speed connectivity ensures that these vehicles can communicate with each other and with smart infrastructure in real-time, enabling complex telematics data transmission for autonomous driving.
- Real-Time Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Cellular IoT enables over-the-air updates for vehicle telematics software and firmware. Manufacturers can remotely push updates, bug fixes, or new features directly to telematics software without requiring a service visit. It improves vehicle functionality and ensures that vehicles remain up-to-date with the latest technologies and security patches.
To understand how Firmware Over-The-Air technology works, check out this PFB blog on Firmware Updation now! Read Blog
- Telematics Fleet Management and Optimization: Cellular IoT plays a crucial role in fleet telematics. It allows fleet operators to track vehicles in real-time, monitor driver behavior, optimize routes, and improve fuel efficiency. With real-time data analytics, managers can make informed decisions about maintenance, vehicle usage, and scheduling, ensuring better operational efficiency with a telematics device.
- Real-time Navigation and Route Optimization As the vehicle moves, telematics systems continuously provide updated navigation routes based on real-time data such as traffic and road conditions. It allows drivers to adjust their routes dynamically for more efficient travel. It also suggests optimal routes based on traffic conditions, weather, and past driving patterns, improving fuel efficiency and travel time.
V2X: The Future of Vehicle Communication
As part of the next generation of telematics control units, V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication is a critical component of connected vehicles. This communication extends beyond V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle) and includes:
- V2I (Vehicle-to-Infrastructure): It allows vehicles to communicate with traffic signals, road signs, and even smart cities to optimize traffic flow.
- V2P (Vehicle-to-Pedestrian): This technology ensures safety for pedestrians by warning drivers about pedestrians in the vehicle’s path.
- V2G (Vehicle-to-Grid): In V2G communication, EVs can have a 2-way communication with electrical grids, drawing power from the grid (charging) and supplying power back to the grid (discharging) to manage energy flow and improve grid stability.
4G vs 5G Telematics Technology
4G telematics has laid the foundation for connected vehicle solutions, offering reliable and cost-effective communication with global coverage. It enables essential services such as GPS tracking, remote diagnostics, and emergency calling, making it ideal for applications that require moderate bandwidth and latency. However, it faces limitations in real-time applications, high-density environments, and data-intensive services, with higher latency and congestion affecting performance in urban areas.
4G/5G Automotive Telematics Control Units Market size was valued at USD 9.3 billion in 2023 and is estimated to register a CAGR of over 19% between 2024 and 2032. – Global Market Insights
The role of 5G telematics represents a significant upgrade, providing ultra-low latency, higher speeds, and the ability to support a massive number of connected devices. With capabilities such as Ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communication (URLLC), Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), and Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC), 5G enables transformative advancements in autonomous driving, Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication, and immersive infotainment experiences. While deployment challenges remain, 5G will be the backbone of next-generation connected vehicle ecosystems, enabling real-time sensor fusion, safety enhancements, and advanced connectivity features.
Closing Notes
The role of cellular connectivity in automotive telematics solutions has evolved from a luxury feature to an essential component of modern vehicles. The journey from traditional, isolated automotive systems to today's connected telematics solutions represents more than technological advancement - it signifies a paradigm shift toward intelligent, adaptive transportation systems. With telematics devices serving as the digital gateway between vehicles and the broader connectivity ecosystem, we're witnessing the emergence of vehicles as sophisticated IoT devices capable of learning, communicating, and evolving. The convergence of artificial intelligence, edge computing, and advanced cellular networks will create telematics solutions that are more intelligent, secure, and capable than ever before. As Cavli Wireless continues to pioneer innovative cellular IoT solutions, we remain committed to enabling the next generation of connected vehicle experiences that make transportation safer and more efficient.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes related to this edition of Wireless By Design
Digital Translator of Your Car
A Telematics Device acts like a skilled translator, ensuring the user understands the car's internal systems and can communicate seamlessly with the outside world, enabling seamless telematics data transfer in the connected vehicle ecosystem.
The Chess Grandmaster of Vehicle Intelligence
Think of your Telematics control unit as an automotive grandmaster; it calculates optimal routes, predicts maintenance needs, manages entertainment systems, and coordinates emergency responses - all while thinking several "moves" ahead to ensure you never get checkmated by traffic, breakdowns, or connectivity issues.

The Master Chef of Data Fusion
The Telematics control module operates like a Master chef, expertly combining raw resources (sensor data, GPS signals, cellular connections) into a perfectly orchestrated connected experience. Just as a master chef understands each ingredient, TCU knows exactly when to prioritize safety data, blend entertainment with navigation, and provide predictive maintenance alerts at the right moment.


