Imagine a Wi-Fi network that can stretch across factory yards, farmland, or multiple city blocks connecting thousands of sensors without requiring dense access-point placement or draining device batteries.
As IoT adoption accelerates across industries, the need for wireless connectivity that combines long-range reach, efficient power usage, and dependable performance has become increasingly important. Conventional Wi-Fi standards deliver high-speed data but were never intended to support wide-area, battery-powered IoT deployments. This is where Wi-Fi HaLow (IEEE 802.11ah) becomes relevant. Engineered specifically for long-range and low-power IoT scenarios, HaLow brings better penetration, wider coverage, and improved energy efficiency. This article outlines how Wi-Fi HaLow functions, where it fits in today’s connectivity landscape, and why it is emerging as a practical choice for modern IoT networks.
What is Wi-Fi HaLow?
Wi-Fi HaLow is built on the IEEE 802.11ah specification a long-range, sub-1 GHz version of Wi-Fi designed to maintain stable connectivity in environments where distance and power constraints make traditional Wi-Fi unsuitable. It retains compatibility with IP-based networks, making it a natural fit for IoT sensors, meters, and devices that require dependable wireless links without high power consumption.
Key Characteristics of Wi-Fi HaLow
Wi-Fi HaLow addresses the core connectivity challenges common in IoT deployments extended coverage, low power operation, and the ability to support large numbers of devices within a single network. Its defining characteristics include:
Sub-Gigahertz Operation
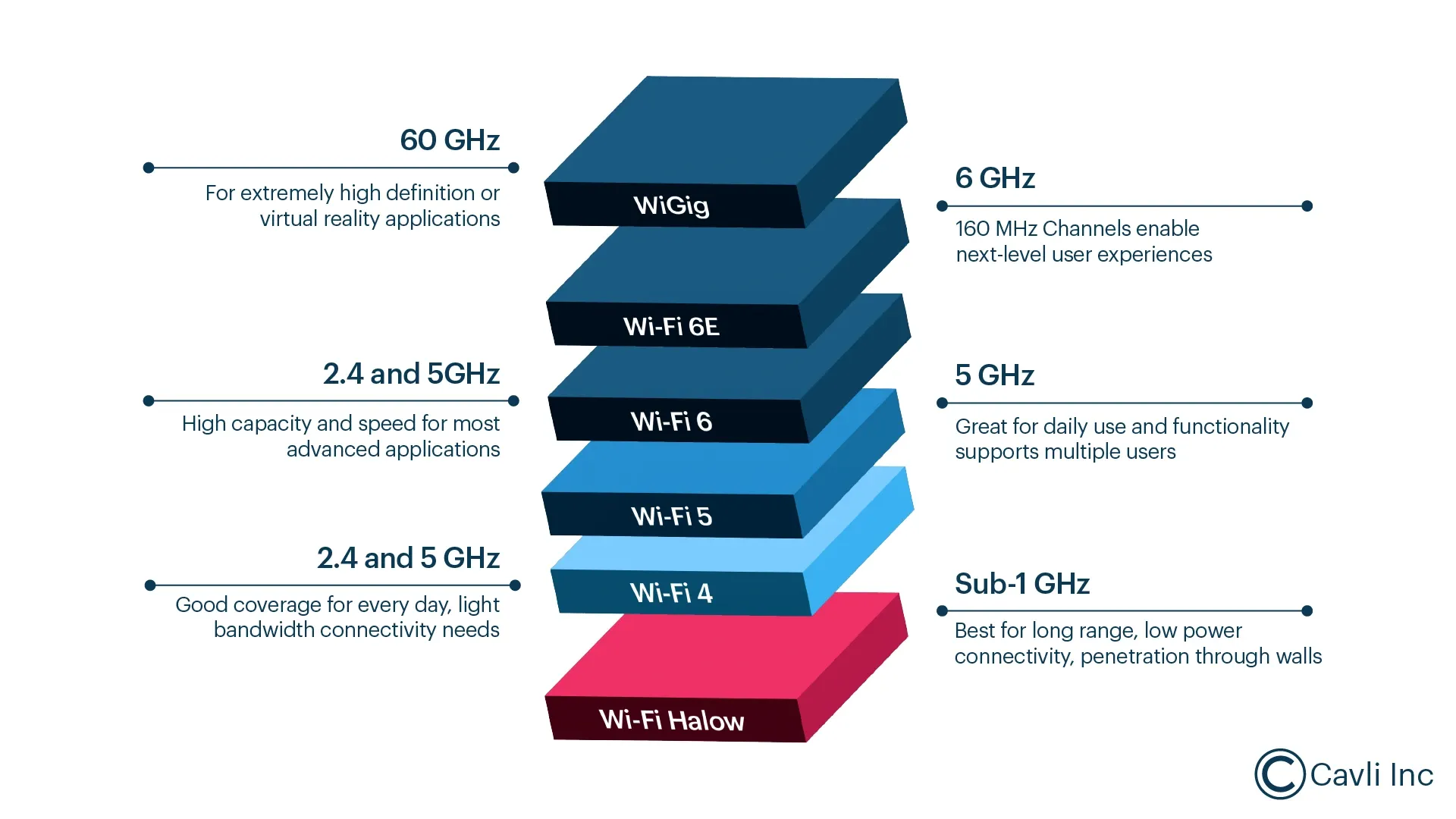
Most conventional Wi-Fi operates in the crowded 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, or 6 GHz bands, where limited propagation and high interference restrict performance in industrial or outdoor environments. Wi-Fi HaLow operates below 1 GHz, enabling signals to travel several times farther often approaching a kilometer and penetrate walls, structural barriers, and dense layouts more effectively. This makes it suitable for agriculture, industrial automation, and large-area sensor networks.
Device Capacity
In dense IoT environments, traditional Wi-Fi access points can quickly become congested. Wi-Fi HaLow avoids this issue with a MAC-layer design capable of supporting up to 8,000 device connections per access point. This allows large fleets of sensors many running on batteries to operate efficiently for years without consuming excessive energy.
Extended Coverage
For IoT systems spanning large outdoor areas smart farming, distributed metering, city-wide sensing, or multi-building industrial facilities the long-range capability of Wi-Fi HaLow provides a practical advantage. Support for narrow channel widths helps maintain reliable connections over long distances, even when devices transmit small amounts of data periodically.
Mesh Networking
Wi-Fi HaLow can be deployed in mesh setups, allowing access points to interconnect and extend coverage across complex environments. This is particularly beneficial in industrial campuses or large warehouses, where coverage continuity is essential. If one access point becomes unavailable, devices can reroute through neighboring nodes, maintaining service reliability.
No Proprietary Hubs or Controllers
A major advantage of Wi-Fi HaLow is that it integrates directly with existing LAN infrastructure. It does not require proprietary coordinators, hubs, or special controllers. HaLow access points connect to standard IP networks just like traditional Wi-Fi, simplifying deployment and reducing long-term operational costs while preserving a familiar network architecture.
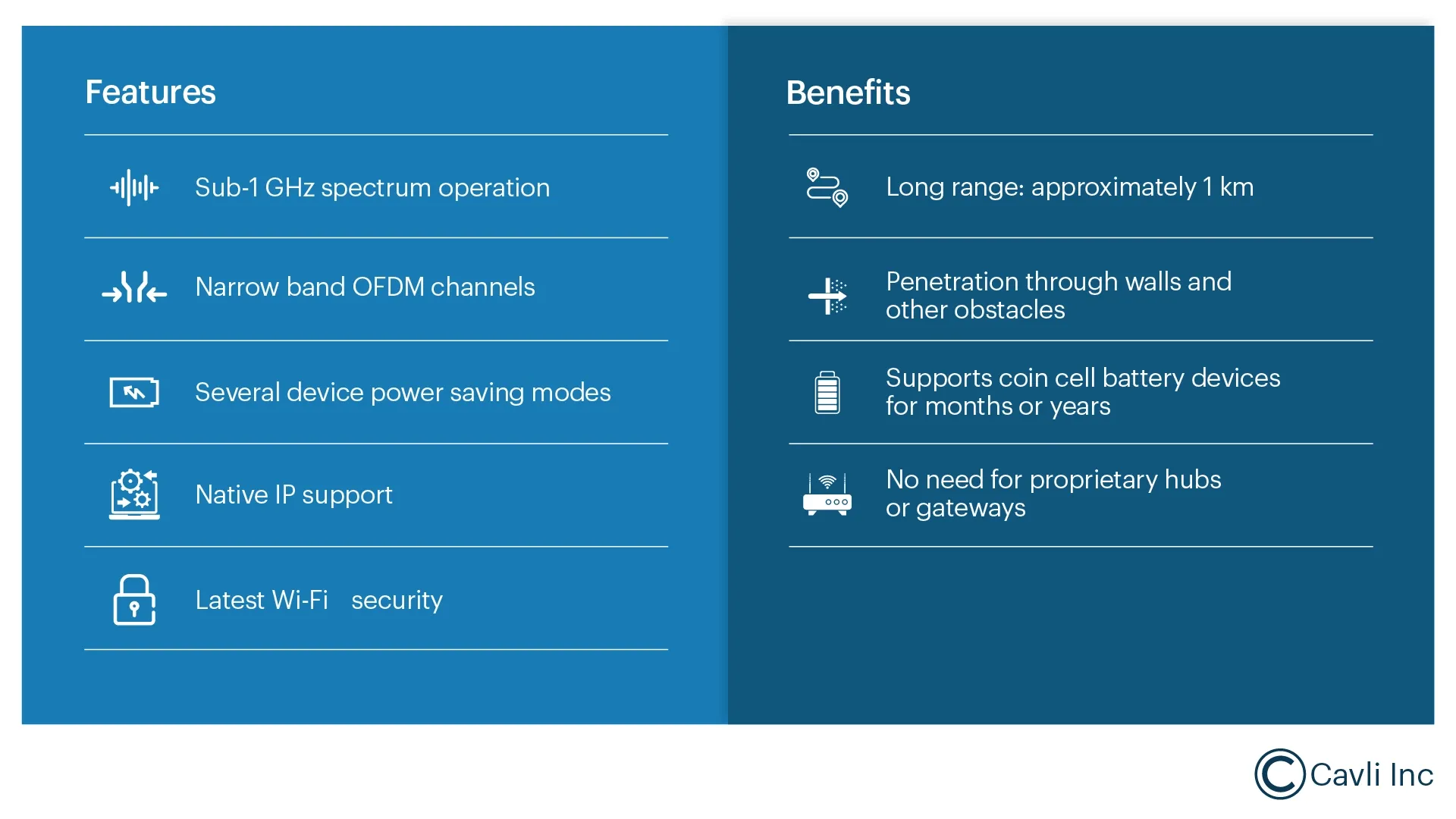
Why the Sub-1 GHz Frequency Matters in Wi-Fi HaLow
Operating in the sub-1 GHz spectrum allows Wi-Fi HaLow to avoid the congestion that affects traditional 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi networks. This lower-frequency band experiences far less interference, which is especially valuable in industrial facilities, dense urban spaces, or areas where multiple wireless systems overlap. The longer wavelength also supports wider coverage from each access point, reducing the number of APs required and lowering infrastructure complexity.
Wi-Fi HaLow is purpose-built for IoT environments where long-range communication, support for large device fleets, and efficient power management are essential. As IoT deployments scale into the billions, HaLow’s ability to maintain stable, long-reach connections positions it as a practical connectivity option for future large-area sensor and device networks.
Infrastructure Components for Wi-Fi HaLow Connectivity
The overall infrastructure for deploying Wi-Fi HaLow resembles traditional Wi-Fi architecture, with a few advantages stemming from its extended propagation range.
Wi-Fi HaLow Access Points (APs)
- HaLow access points operate in the sub-1 GHz band, enabling much broader coverage compared to standard Wi-Fi APs. Because each AP can span larger zones, networks require fewer units, reducing installation and maintenance overhead. This is particularly beneficial in industrial yards, farms, and large commercial spaces.
IoT Devices with Wi-Fi HaLow Support
- Sensors, cameras, meters, and other IoT endpoints must support the Wi-Fi HaLow standard to connect natively with HaLow APs. With the growing adoption of 802.11ah, more device manufacturers are integrating HaLow capabilities into low-power and long-range IoT hardware, making it easier for organizations to source compatible equipment.
Integration with IP-Based Networks
- HaLow APs plug into existing IP infrastructures just like traditional Wi-Fi. This ensures seamless integration with LAN/WAN environments and allows IoT devices to transmit data to on-premises servers or cloud systems without additional gateways or proprietary controllers. Organizations with established Wi-Fi setups can extend their network to include HaLow with minimal configuration changes.
Key Considerations for Deployment of Wi-Fi HaLow
- Environmental Factors:HaLow’s ability to penetrate walls and structural barriers makes it effective in warehouses, multi-floor buildings, and urban deployments. AP placement should still account for possible interference sources or blockage points to maintain optimal performance.
- Bandwidth Requirements:While HaLow is optimized for low-data IoT traffic, it can support moderate throughput when necessary. For high-bandwidth applications like real-time video or heavy file transfers traditional Wi-Fi or cellular IoT may still be more suitable.
- Compliance with Regional Frequency Bands:Sub-1 GHz frequency allocations vary by region. Organizations deploying Wi-Fi HaLow across multiple countries must ensure compliance with local regulatory requirements.
Comparison of Wi-Fi HaLow with Other LPWAN Technologies
With the number of IoT technologies available today, selecting the right connectivity layer depends on coverage needs, data requirements, cost considerations, and application type. Below is a practical comparison of Wi-Fi HaLow with established LPWAN options.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. Traditional Wi-Fi
Conventional Wi-Fi standards like Wi-Fi 5 and Wi-Fi 6 deliver high data rates but offer limited range and higher energy consumption, making them unsuitable for large, battery-powered IoT fleets. Wi-Fi HaLow’s sub-1 GHz operation allows it to reach distances up to ten times farther up to 3 km in ideal conditions while prioritizing power efficiency over throughput. This makes HaLow better aligned with sensors and devices that transmit small, periodic data packets.
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. LoRa (Long Range)
LoRa also operates in the sub-1 GHz band and offers excellent long-range performance but at very low data rates (typically 300 bps to 50 kbps). This makes LoRa effective for simple sensor telemetry but impractical for use cases requiring burst data or occasional higher throughput. Wi-Fi HaLow supports data rates up to 86.7 Mbps at close range, giving it greater flexibility for applications like surveillance or industrial automation where low latency and moderate bandwidth matter.
Ideal Applications:
- LoRa:Environmental sensing, utility meters, long-distance low-data applications
- Wi-Fi HaLow:Higher-bandwidth IoT use cases, including video, automation, and real-time monitoring
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT)
NB-IoT operates on licensed cellular spectrum and provides wide-area coverage with high reliability, but its recurring subscription costs add up in large deployments. Wi-Fi HaLow runs on unlicensed spectrum, eliminating ongoing data fees. While NB-IoT is preferred for guaranteed coverage and mission-critical monitoring, HaLow is attractive for private IoT networks where cost and local control matter.
Ideal Applications:
- NB-IoT: Healthcare monitoring, emergency systems, regulated environments
- Wi-Fi HaLow:Smart agriculture, smart buildings, city infrastructure, cost-sensitive IoT deployments
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. Zigbee and Z-Wave
Zigbee and Z-Wave are widely used in homes and small commercial environments due to their low power usage and mesh capabilities. However, their short range typically under 100 meters limits their usefulness in large-area deployments. HaLow’s sub-1 GHz penetration and extended reach allow a single AP to cover what would otherwise require numerous Zigbee or Z-Wave nodes.
Ideal Applications:
- Zigbee/Z-Wave: Home automation, small indoor networks
- Wi-Fi HaLow:Smart cities, logistics yards, industrial plants, and high-density IoT environments
Wi-Fi HaLow vs. Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
BLE is optimized for personal and short-range device communication, with typical effective distances of 50–100 meters. BLE networks also support far fewer simultaneous devices. Wi-Fi HaLow, with its multi-kilometer reach and ability to handle thousands of connections, is far better suited for industrial, agricultural, or municipal IoT systems that span large distances.
Ideal Applications:
- BLE: Wearables, indoor smart home devices, proximity-based applications
- Wi-Fi HaLow: Wide-area sensor networks, industrial automation, outdoor IoT deployments
| Attribute | Wi-Fi HaLow | LoRa | NB-IoT | Zigbee | BLE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | Sub-1 GHz | Sub-1 GHz | Licensed spectrum | 2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz |
| Range | Up to 3 km | Up to 10 km | Up to 10 km | Up to 100 m | Up to 100 m |
| Data Rate | Up to 86.7 Mbps | 300 bps - 50 kbps | 20 kbps - 127 kbps | Up to 250 kbps | 125 kbps - 2 Mbps |
| Device Capacity | 8,000 per AP | Limited by topology | Limited by network design | 65,000+ in mesh | Limited by topology |
| Ideal Use Cases | Smart cities | Environmental monitoring | Healthcare, emergency systems | Home automation | Wearable devices, smart home |
Limitations of Wi-Fi HaLow Compared to Cellular IoT
While Wi-Fi HaLow brings long-range, low-power connectivity to local IoT networks, it still carries several limitations when stacked against cellular technologies like NB-IoT, LTE-M, LTE, and 5G.
Coverage & Range
Wi-Fi HaLow typically covers up to 1 km and depends on locally installed access points. In comparison, cellular networks such as NB-IoT, LTE, and 5G provide nationwide and even global coverage, making them better suited for deployments that need wide-area connectivity without additional on-site infrastructure.
Scalability & Device Density
While a HaLow access point can support more than 8,000 devices, this capacity is still tied to localized deployments. Cellular networks are engineered to manage far larger device densities across each cell, which is why they remain the preferred option for smart-city grids, utilities, and industrial IoT systems with thousands of distributed endpoints.
Mobility & Roaming
Wi-Fi HaLow works best for stationary or slow-moving assets and requires device handovers between access points. Cellular connectivity offers seamless mobility across towers and regions, making it the natural choice for fleet management, logistics, and other applications where devices constantly move.
Power Consumption & Battery Life
HaLow is energy-efficient for Wi-Fi-class communication, but ultra-low-power technologies such as NB-IoT and LTE-M extend battery life significantly further. This advantage becomes critical in use cases like remote meters and sensors that operate for years on a single battery.
Infrastructure & Deployment Costs
A HaLow-based network requires dedicated access points to be deployed and maintained. Cellular IoT, by contrast, leverages the operator’s existing infrastructure, reducing both installation effort and long-term maintenance overhead for large-scale rollouts.
Security & Network Reliability
Wi-Fi HaLow inherits the same security model used in traditional Wi-Fi, which can be more susceptible to interference and localized attacks. Cellular networks provide SIM-based authentication and carrier-grade security layers, offering stronger end-to-end protection for critical applications.
Latency & Data Rate
Wi-Fi HaLow offers moderate data rates (Mbps) with slightly higher latency than 5G. Cellular IoT varies: NB-IoT is optimized for low-data applications, while 5G offers ultra-low latency (~1 ms) for real-time applications like autonomous driving.
Advantages of Wi-Fi HaLow for IoT
As IoT ecosystems grow, the challenge of supporting thousands of distributed devices across large areas becomes more pronounced. Wi-Fi HaLow addresses many of these scalability and efficiency limitations and brings several advantages that make it well suited for high-density, wide-area IoT deployments.
Reduced Infrastructure Costs
Wi-Fi HaLow’s extended range enables coverage across applications like smart lighting, environmental sensors, or warehouse-wide asset tracking without relying on dense clusters of repeaters or large numbers of access points. This simplifies deployment and lowers infrastructure costs, especially when scaling across large indoor or outdoor spaces.
Power Efficiency for Long-Term Operation
IoT devices often operate on tight power budgets and may be installed in areas where frequent maintenance is unrealistic. Wi-Fi HaLow’s Target Wake Time (TWT) allows devices to spend most of their lifetime in low-power sleep states and wake only when scheduled to transmit or receive data.
Restricted Access Window (RAW) further reduces contention by assigning specific communication periods, minimizing unnecessary power draw. Together, these features allow sensors, meters, and remote nodes to remain operational for months or years on the same battery, making HaLow suitable for hard-to-reach or maintenance-limited environments.
Increased Device Connections
A single Wi-Fi HaLow access point can connect up to 8,000 devices, enabling dense IoT networks without overloading the system. In a smart city scenario, one AP can support environmental monitors, street infrastructure, public safety devices, and parking systems all within the same coverage zone. This high device capacity makes HaLow a strong fit for scalable IoT rollouts.
Reduced Interference for Reliable Connectivity
Operating in the sub-1 GHz band allows Wi-Fi HaLow to avoid the congestion that affects 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz environments. Industrial facilities, urban centers, and shared spaces often experience RF noise that disrupts traditional Wi-Fi performance. HaLow’s lower-frequency operation provides more stable links and maintains reliable data transfer even in dense or interference-heavy locations.
Enhanced Security for IoT Applications
Security remains a priority in IoT networks, particularly where sensitive or operational data is involved. Wi-Fi HaLow integrates WPA3, offering stronger encryption and better protection against modern threats. This ensures a secure baseline for IoT deployments in industrial, municipal, and commercial environments.
Wi-Fi HaLow and IoT Applications
Industrial IoT (IIoT) Applications
Wi-Fi HaLow is well suited for industrial spaces that require reliable, long-range, low-power connectivity.
Use Cases:
Asset Tracking:
- Monitor equipment, tools, and materials across warehouses or production areas.
- Improve accuracy and reduce losses by integrating location and sensor data.
Predictive Maintenance:
- Link condition-monitoring sensors to machinery to watch temperature, vibration, or component health.
- Detect early signs of failure to minimize downtime and maintain equipment reliability.
Worker Safety:
- Use wearables and sensor nodes to detect environmental hazards or unsafe conditions.
- Improve safety compliance and emergency response capabilities.
Smart Agriculture & Environmental Monitoring
HaLow’s extended range makes it suitable for agriculture and remote environmental deployments.
Use Cases:
Crop Monitoring:
- Place soil and climate sensors across fields to capture moisture, nutrient levels, and other parameters.
- Support data-driven irrigation and resource management.
Livestock Tracking:
- Use HaLow-enabled tags to monitor movement, location, and health metrics.
- Enhance farm visibility and automate livestock management tasks.
Climate & Weather Monitoring:
- Deploy long-range sensing units to track temperature, humidity, rainfall, or wind.
- Enable better forecasting and operational planning.
Smart Cities & Infrastructure
Wi-Fi HaLow supports large-scale municipal deployments where range and device density matter.
Use Cases:
Traffic Management:
- Connect sensors and smart cameras to optimize traffic flows and monitor road conditions.
- Enable responsive systems for congestion control and alerts.
Public Safety & Security:
- Deploy long-range surveillance, access systems, and emergency alert devices.
- Improve real-time situational awareness across urban areas.
Utility Management:
- Use HaLow for remote monitoring of streetlights, water infrastructure, and power equipment.
- Increase operational efficiency and reduce energy usage.
Smart Homes & Building Automation
Wi-Fi HaLow can enhance automation, energy optimization, and security across residential and commercial environments.
Use Cases:
Energy Management:
- Connect smart thermostats, HVAC equipment, and lighting systems to reduce power usage.
- Enable remote access and control of home appliances and connected devices.
Security & Surveillance:
- Integrate smart locks, cameras, alarms, and motion sensors over a long-range, low-power network.
- Extend coverage throughout large properties without relying on dense infrastructure.
Smart Appliances & IoT Devices:
- Enable wireless control of appliances such as refrigerators and washing machines.
- Support more responsive and reliable automation across connected household devices.
Healthcare & Medical IoT
Wi-Fi HaLow delivers secure, stable connectivity for medical environments and remote healthcare applications.
Use Cases:
Patient Monitoring:
- Connect wearable vitals monitors, glucose sensors, and ECG devices for continuous tracking.
- Support timely alerts and intervention workflows for medical teams.
Medical Equipment Connectivity:
- Enable smooth data transfer between medical equipment such as ventilators or diagnostic systems and hospital networks.
- Improve equipment uptime and streamline data flow for diagnostics.
Elderly & Assisted Living:
- Power fall-detection devices, emergency alert systems, and health-monitoring wearables.
- Support remote supervision of seniors or patients with chronic conditions.
Retail & Smart Warehousing
Retail and logistics operations can leverage Wi-Fi HaLow to strengthen automation, visibility, and real-time decision-making.
Use Cases:
Inventory & Supply Chain Tracking:
- Use sensors and RFID-based systems to track goods across warehouses and distribution hubs.
- Improve stock accuracy, minimize losses, and streamline workflows.
Smart Checkout & POS Systems:
- Support mobile payments, self-checkout kiosks, and automated customer service tools.
- Reduce wait times and enhance customer interaction experiences.
In-store analytics & Digital Signage:
- Monitor customer flows and behavior to optimize store layouts and merchandising.
- Enable real-time updates to digital signage and promotional displays.
Closing Notes
Wi-Fi HaLow (IEEE 802.11ah) is a long-range, low-power Wi-Fi standard built specifically for IoT deployments that demand wider coverage and better energy efficiency than conventional Wi-Fi can provide. Operating in the sub-1 GHz band, it offers strong penetration through obstacles, extended range of up to 1 km, and support for thousands of connected devices on a single access point making it highly suitable for smart buildings, agriculture, industrial sites, and large-scale IoT environments.
However, Wi-Fi HaLow does not offer the mobility, seamless roaming, or broad geographic coverage provided by NB-IoT, LTE, and 5G. Because HaLow depends on locally deployed access points, it is cost-effective for private, localized IoT networks but not designed for applications requiring wide-area mobility. While HaLow excels in dense, localized IoT installations, technologies like NB-IoT and LTE-M continue to be better suited for low-power applications that require regional or global reach. Selecting the right connectivity option ultimately depends on factors such as required range, power efficiency, scalability, and security to ensure that IoT deployments remain robust and future-ready.





