James, Jr. Network Engineer
I'm evaluating connectivity options for our new IoT product line. Everyone talks about USB dongles, but I'm curious about how we got here. What was device connectivity like before USB?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
Ah, you're opening up quite a history book there! Before USB, we relied on the RS-232 serial interface, originally developed for teletypewriters. It operated at just 20 kilobits per second, which is about 0.0025% of today's USB 3.0 speeds. Each connection needed multiple pins, specific voltage levels, and careful wiring. It was like crafting a fine watch just to get two devices talking.
I2C
James, Jr. Network Engineer
That sounds complicated! How did the USB port change things, and why was it such a game-changer for device connectivity?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
USB was revolutionary because it simplified connectivity. Imagine going from a complex switchboard to a simple plug-and-play solution. When USB 1.0 launched in 1996, it could transfer data at 12 Mbps — about 600 times faster than RS-232. USB also introduced the concept of "hot-swapping" —connecting devices without rebooting, thereby saving hours of productive time.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
Fast forward to today, and we're looking at IoT dongles for our products. How different are they from those early USB modems?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
When cellular modems adopted USB, suddenly internet connectivity became as simple as plugging in a flash drive. This paved the way for today's IoT dongles. Modern IoT dongles are like Swiss Army knives compared to those early modems. They pack cellular connectivity, processing power, and application logic into a single plug-and-play device. They're transforming how we retrofit legacy systems with connected capabilities.
The transition from serial communication ports (like RS-232) to USB and eventually to USB-powered dongles has been a pivotal evolution in the IoT landscape. USB quickly became the standard for connecting devices to computers and other peripherals, replacing serial ports.
As IoT systems grew more complex, the need for compact, mobile, and adaptable connectivity solutions led to the creation of dongles. USB-powered dongles provided a simple and portable way to retrofit legacy systems. It incorporated wireless and wired communication technologies (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Cellular) without major device redesign. This journey is not just about hardware evolution, but about how each technological step laid the foundation for today's connected world.
The Era of RS-232 and Legacy Communication Jacks
Before the USB port debuted, communication interfaces were often large, cumbersome, and specialized. RS-232 is one of the earliest standards for serial communication, used in the 1970s and ’80s for connecting computers to peripheral devices such as modems. With its distinct 9 or 25-pin connector, RS-232 was functional but limiting.
Its limited speed, typically 115,200 bps, became a bottleneck for data-intensive devices like printers, scanners, and digital cameras. Other legacy communication jacks, such as parallel ports, VGA, and PS/2 connectors, also had a similar story. While they served their purpose, they became outdated as the demand for data speeds, simplicity, and versatility grew.
In 1996, a consortium of technology companies such as Intel, Microsoft, and IBM introduced the Universal Serial Bus (USB). The goal was to create a universal, easy-to-use interface to replace the cables and connectors for peripherals, such as printers, cameras, and storage devices.
The introduction of USB brought several advantages: higher data transfer speeds, plug-and-play functionality, and the ability to power devices through the same connection.
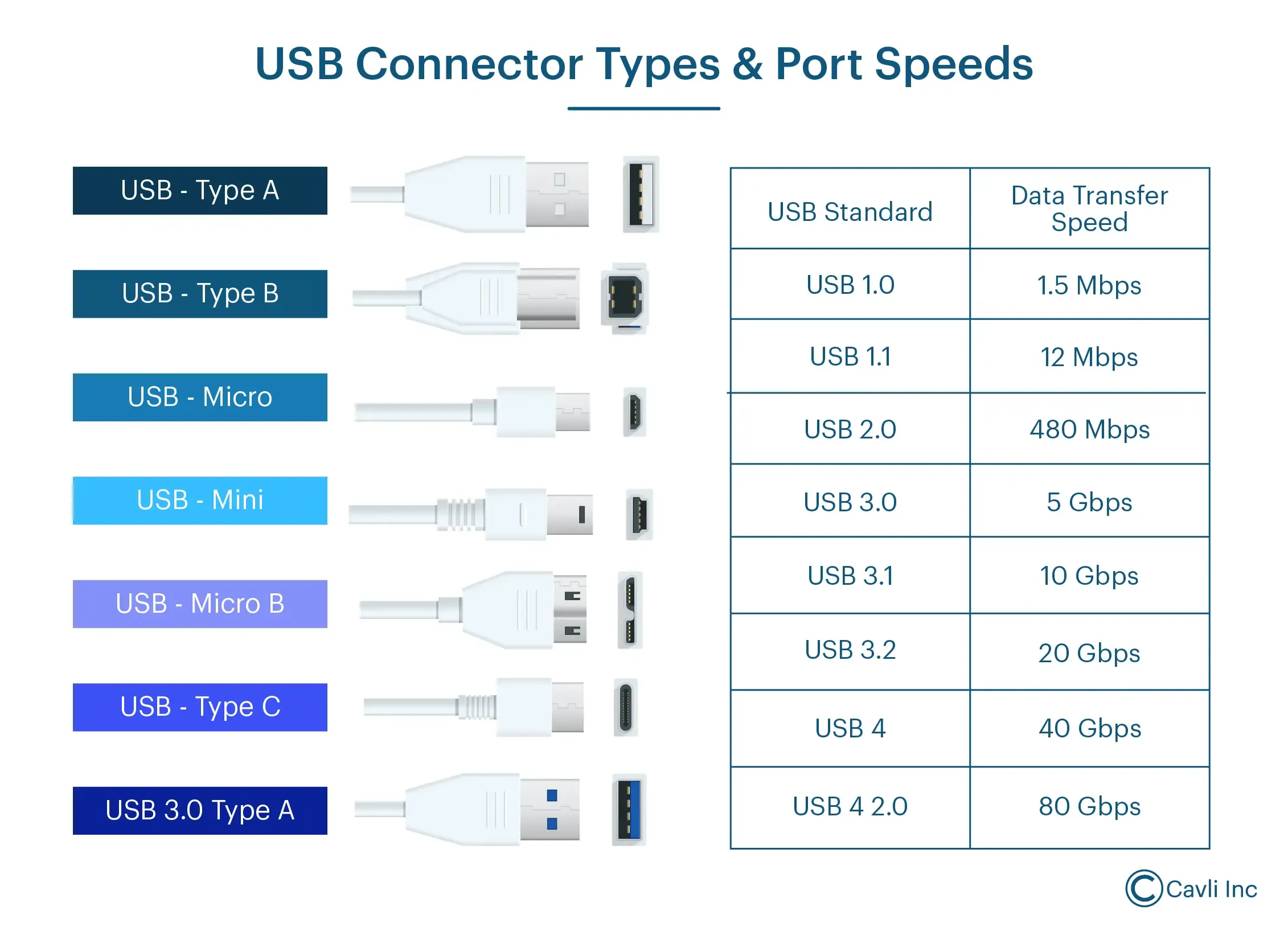
The USB port's design was compact, and its ability to transmit data and power through a single cable made it an instant hit. This flexibility allowed the USB standard to grow rapidly.
Soon, USB ports appeared on every device — from desktop computers to laptops, gaming consoles, and even smartphones. For the first time, we had a single connector that could handle different devices.
USB 1.1 introduced data transfer speeds of 12 Mbps (100x faster than RS-232). Later versions like USB 2.0 (480 Mbps), USB 3.0 (5 Gbps), and USB 3.1/3.2 (up to 20 Gbps) offered even better performance. It paved the way for high-bandwidth applications like video streaming and fast file transfers.
How Did USB Ports Supersede Serial Communication Ports?
Plug-and-Play Simplicity
- USB has plug-and-play functionality. The USB devices can connect with the operating system automatically, recognizing the device and installing the necessary drivers. This user-friendly feature made USB superior, especially for the general consumer market.
Connectivity and Flexibility
- USB offers hub functionality, allowing multiple devices to connect through a single port using a USB hub. USB supports up to 127 devices on a single host (depending on the version), which was a massive leap from the one-to-one connection typical of RS-232.
Power Delivery
- The USB port supplies power—typically 5V—directly to connected devices, a capability that revolutionized portable devices. They could now be charged or powered through a single cable, which became critical for the growth of mobile devices, USB-based storage, and IoT devices.
- USB Power Delivery (PD) extended the power capabilities to 20V at 100W in USB-C, allowing even high-power devices like laptops to be charged over USB.
Backward Compatibility
- Despite the rapid evolution of USB ports from USB 1.0 to USB 3.x, it remained backward compatible with earlier versions. For example, a USB 2.0 device would still work on a USB 3.0 port (though at USB 2.0 speeds). It ensures a smooth transition for users upgrading their devices without being forced to discard older peripherals.
Universal Adoption Across Industries
- USB ports became the universal port for consumer electronics, including computers, smartphones, gaming consoles, IoT devices, and more. Their ubiquity helped them overtake serial ports and become the standard across both consumer and industrial products.
The Rise of Net Setters: Cellular Connectivity at Your Fingertips

In the early 2000s, a new phenomenon began to take shape: the net setter, a USB device that provided internet connectivity. They were used to connect laptops and desktops to the internet via 3G or 4G networks, especially in areas where traditional broadband infrastructure was lacking. Netsetters revolutionized mobile connectivity, transforming any laptop or computer into a mobile internet device. As the mobile networks evolved, so did these devices, stepping up from the initial 3G models to the more advanced 4G LTE versions. This adoption of USB-based cellular modems was a game changer, laying the groundwork for more sophisticated connectivity solutions.
Dongles: A New Era of Portable Connectivity
The next phase in this journey came with the rise of dongles. Though they share the same plug-and-play functionality as USB devices, dongles are distinct in their ability to add specific functionalities to a device, often serving as a bridge between different connectivity standards.
Consider this: the first USB cellular modems from the early 2000s required external drivers, consumed over 500mA of power, and supported only 2G networks at 384 Kbps.
They have also shrunk from the size of a deck of cards to smaller than a thumb drive while adding multi-core processors, encryption engines, and edge computing capabilities.
What is particularly revolutionary is their power efficiency.
Modern dongles use just 1/10th the power per bit transferred compared to their previous generations. Some advanced models even incorporate energy harvesting technologies to extend battery life in remote deployments by up to 400%.
Whether Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, or even specialized IoT applications, dongles allow users to extend their device capabilities without an entire system overhaul.
Dongles became necessary as IoT devices began to proliferate across various industries. Manufacturers were no longer limited to making standalone devices; they were now designing systems that could integrate into bigger networks and be powerful enough to retrofit existing devices to meet growing IoT ecosystem needs.
Dongles and IoT: The Retrofit Solution for Legacy Applications

The most compelling use case for dongles emerged within the world of IoT. With the explosion of connected devices, many manufacturers faced the dilemma: How could they cost-effectively retrofit their existing products with the latest communication technologies, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or 4G/5G?
Dongles provided an elegant solution. Instead of re-engineering entire product lines, companies could integrate these compact, plug-and-play devices into their existing systems. For example, a legacy factory machine could be upgraded with a Wi-Fi dongle, allowing it to communicate with the cloud and contribute to an efficient factory environment without a complete redesign.
Incorporating wireless communication to almost all devices without extensive hardware changes has been the key advantage in the IoT space. Dongles have allowed companies to innovate quickly, ensuring even conventional systems can be integrated into modern IoT networks.
Why Does a Dongle Matter in Modernizing the World?
Dongles have emerged as transformative tools for modernizing legacy systems by providing instant connectivity through effortless retrofitting. Instead of completely replacing existing hardware, dongles allow older devices and equipment to integrate into the digital age. Dongles upgrade devices by simply plugging into a USB or specialized port, enabling remote access, real-time monitoring, and advanced IoT functionalities without a significant infrastructure overhaul. This ease of retrofitting accelerates digital transformation, significantly reducing costs, time, and complexity for industries seeking rapid modernization.
Steps Involved in Retrofitting Applications with Dongles
Assessment and Planning
Evaluate the existing application:
Understand the type of hardware you are working with (e.g., electromechanical or electronic meters) and its compatibility with retrofitting options.
Define retrofitting goals:
Identify what features you want to add, such as remote reading, real-time data monitoring, or smart grid integration.
Determine connectivity requirements:
Decide which network (cellular, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, NB-IoT, LoRa, etc.) is most suitable for your needs based on range, power requirements, and data throughput.
Choosing the IoT Module/Dongle
Select a suitable IoT dongle:
Choose a cellular or low-power IoT form factor (preferably a dongle, as it is a retrofitting scenario) that can be attached to the existing meter. This module will handle communication between the meter and the cloud or central system.
- Example: An NB-IoT module or cellular LTE module for wide-area connectivity, or Wi-Fi if working within a local network.
Power management:
Ensure the module has an efficient power management system, especially if the meter is battery-powered or located in areas with limited power.
Physical Retrofitting and Installation
Install the communication module:
Attach the IoT dongle or module to the meter. It involves:
Connecting the module to the meter's existing data interface:
(e.g., pulse output, RS-485, or Modbus).
Integrating the module with the meter's power supply:
Ensure proper antenna installation:
If the module uses cellular or wireless communication, install the antenna for optimal signal reception.
Data Integration and Configuration
Interface with existing metering data:
Set up communication between the IoT module and the meter's data collection system.
If the meter has a pulse output or other data ports:
Configure the module to read the output and transmit the data to a cloud platform or central server.
Software configuration:
Configure the IoT module to communicate with the chosen network (e.g., set up APN settings for cellular connections).
Data storage and cloud integration:
Set up the cloud platform or central server to receive data from the meter. It includes:
Configuring IoT platform settings:
For monitoring, alerting, and data visualization.
Testing and Calibration
Test the system:
Ensure the module communicates correctly with the cloud system and transmits accurate meter readings.
Calibrate the system:
Make sure that the readings from the meter match the expected values, ensuring proper data accuracy.
Deployment and Monitoring
Deploy across multiple meters:
Once the first retrofit is successful, deploy the solution across other meters.
Monitor remotely:
Use the cloud or IoT platform to monitor meter performance, collect real-time data, and set up alerts for abnormal usage or faults.
Maintenance and Support
Software updates:
Regularly update the firmware on the IoT module to improve functionality and ensure security.
Physical maintenance:
Periodically check the physical components (e.g., module, antenna, power supply) to ensure everything is functioning optimally.
For example, these are the steps involved in smart-connecting existing metering solutions with dongle connectivity.
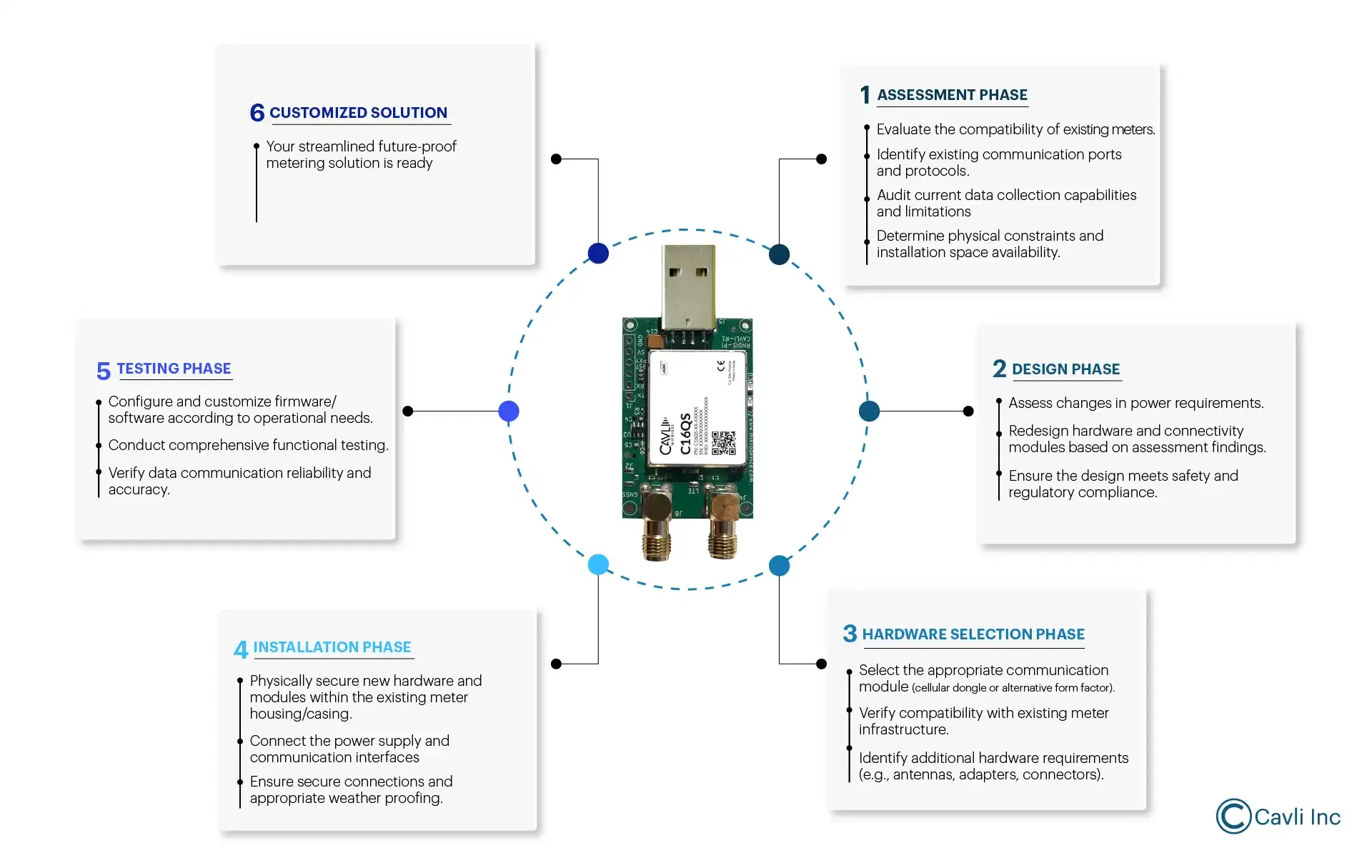
To learn more about retrofitting your metering applications, download our latest white paper on Smart Metering Solutions.
The Competitive Edge: What are the Advantages of the Dongle Form Factor in IoT Applications
1. Retrofitting Legacy Equipment
- Suppose you have industrial machines or legacy equipment built before the IoT era that lack modern communication capabilities. A dongle integrates Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or Cellular connectivity (3G/4G/5G) options without modifying the machine's internal architecture. It allows the equipment to transmit data to cloud platforms for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Example Use Case:
- Smart Factory: Attaching a cellular dongle to legacy PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) enables real-time data collection and analytics, transforming traditional manufacturing lines into smart factories without a complete overhaul.
2. Rapid Prototyping and Development
- Suppose you are developing a new IoT application and have to test different connectivity solutions without committing to a specific communication module. Using a dongle allows switching between connectivity options like LTE, NB-IoT, or Cat-M1 by simply swapping the dongle, enabling rapid prototyping and flexibility during development.
Example Use Case:
- IoT Startup Development: An IoT startup can use various LTE or NB-IoT dongles to test their prototype across multiple network carriers and regions without redesigning the entire hardware. Also, when working indoors or in lab environments, startups can skip the SIM setup and use Wi-Fi dongles to prototype their IoT applications.
3. Geographic Expansion and Roaming
- You are expanding your IoT solution to new markets that require different network compatibilities. A dongle with multi-band and multi-network capabilities can provide global connectivity, allowing devices to operate in various regions or countries without hardware modifications.
Example Use Case:
- Asset Tracking Solution: A global asset tracking solution can utilize a multi-network LTE dongle to enable seamless tracking of goods across international borders, adapting to different cellular networks in real-time.
4. Temporary Connectivity Requirements
- You need temporary connectivity for testing, events, or remote locations where permanent infrastructure is not available or practical. A plug-and-play dongle can provide instant internet connectivity, enabling devices to communicate without relying on Wi-Fi or fixed-line broadband.
Example Use Case:
- Pop-Up Events or Remote Monitoring: Using a cellular dongle to provide temporary internet access for IoT devices deployed at events, construction sites, or remote agricultural fields.
5. Adding New Features to Existing Products
- You want to add new functionalities, such as GPS tracking or Bluetooth communication, to an existing product without redesigning the hardware. A dongle can provide these additional features through its plug-and-play capability, extending the product’s lifecycle and feature set.
Example Use Case:
- Fleet Management: Retrofitting existing vehicles with GPS-enabled cellular dongles to enable fleet tracking and telematics data collection.
- Healthcare Devices: Integrating a pre-certified LTE dongle into medical devices ensures compliance with regulations while enabling remote monitoring and data transmission.
6. Modular Design and Future Proofing
- You want to future-proof your IoT product by making it modular and adaptable to evolving communication technologies. A dongle-based approach allows you to easily upgrade connectivity as new cellular technologies (e.g., 5G or 6G) become available, ensuring your product remains relevant.
Example Use Case:
- Smart Meters: Deploying smart energy meters with USB ports that can accommodate different dongles allows utility companies to upgrade connectivity standards without replacing the entire meter.
From RS-232 to USB, and from netsetters to IoT dongles, the evolution of communication interfaces is a testament to how innovation continues to shape our connected world. Each step in this progression has resulted in better, faster, and more flexible connectivity solutions. The dongle, with its compact form and versatile functionality, represents the apex of this journey, enabling IoT applications to thrive in the changing trends.
Dongles are versatile, cost-effective, and practical solutions for adding or upgrading connectivity in IoT applications. They enable rapid prototyping, international scalability, enhanced security, and future-proofing, all while minimizing hardware redesigns. By leveraging dongles, OEMs, ODMs, and engineers can quickly adapt to changing market demands and connectivity requirements, driving innovation and sustaining competitive advantages.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes Related to this Edition of Wireless By Design
The Old Radio to the Streaming Service
The USB is like an old radio. To listen to your favorite music, you need to be close to the radio and tune into a specific frequency (port). It’s simple but not very flexible, and you need physical intervention at times. The dongle is like a music streaming service. You can listen to your favorite tracks from anywhere—whether at home, on the move, or anywhere there’s internet access. You don’t need to tune into a specific frequency; instead, your device connects wirelessly to any available network (platform) and you get instant access to the data (music).
The Letter Carrier to the Express Drone Service
USB is the traditional letter carrier—a person who walks to deliver a letter. The letter carriers are reliable, but they are limited by their route, weather, and physical distance, making it slow. The dongle is like an express delivery drone—fast, flexible, and capable of reaching almost anywhere. A dongle, just like a drone, can ensure fast delivery and retrofit your applications with limited system overhaul.
The Chalkboard Classroom to Online Learning Platforms
The USB port is like a traditional classroom. It’s effective for knowledge transfer (communication), but it has physical constraints. We have to be present in the classroom just like ‘wired connections’. The dongle is like an online learning platform. Connect to the existing classroom from anywhere, with no need to be physically present in the classroom. It gives you access to the classes (data) wherever you are, making it more flexible and accessible.
Go Beyond and Explore
What is the difference between a USB and USB-C?
Why use an IoT Dongle to retrofit traditional applications?
- Communication with the Cloud/Network: The IoT dongle connects the meter to a network (such as cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or other IoT communication protocols like NB-IoT or LoRa) to transmit usage data to the cloud or a central server. This provides real-time access to meter data, eliminating the need for manual readings.
- Compatibility with Legacy Systems: IoT dongles are designed to be easily added to existing static meters, allowing them to "talk" to newer smart grid systems without replacing the entire meter infrastructure.
- Remote Management: IoT dongles enable remote configuration, firmware updates, and data retrieval, which is essential for the effective monitoring and management of meters in various locations.
- Cost-Effective: Instead of replacing the entire meter, retrofitting with an IoT dongle is a more cost-effective solution, as it adds smart capabilities to existing meters.
- Common examples of IoT dongles used in retrofitting applications: These include cellular IoT dongles that support 4G or 5G connectivity, Wi-Fi dongles for local area connectivity, and low-power technologies like NB-IoT (Narrowband IoT) — particularly suited for metering systems due to their extended range and low power consumption.
What are the factors to consider when choosing a dongle form factor for IoT applications?
When choosing a dongle form factor for IoT applications, several key factors should be considered:
- Size and Portability: Smaller dongles are more portable but might limit connectivity options or power. Larger dongles can offer more features but may not be as easy to integrate into compact devices.
- Power Consumption: Low-power dongles are ideal for battery-powered or remote applications, but small form factors may struggle with power efficiency.
- Connectivity: The dongle must support the required communication protocols (e.g., cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) for the IoT application. Multi-protocol dongles might be larger or more expensive.
- Durability: For industrial or outdoor use, the dongle must be rugged and have adequate protection (e.g., IP ratings) for harsh conditions.
- Data Throughput: Consider the dongle’s data handling capabilities; smaller dongles might limit speed or volume, affecting applications that need real-time analytics.
- Security: Choose a dongle with sufficient encryption and authentication features, especially for sensitive IoT data.
- Cost: Smaller, simpler dongles may be cheaper but might lack advanced features; consider future scalability and system cost.