What is APN? Understanding Access Point Names
An Access Point Name (APN) tells a mobile network how to connect your device to the internet or a private enterprise network. In IoT, the APN governs routing, DNS, NAT, and security policies—so the “right” APN choice directly affects stability, latency, and cost. This guide explains public vs private APNs, roaming behavior, and the practical checks teams should run before scaling a fleet.
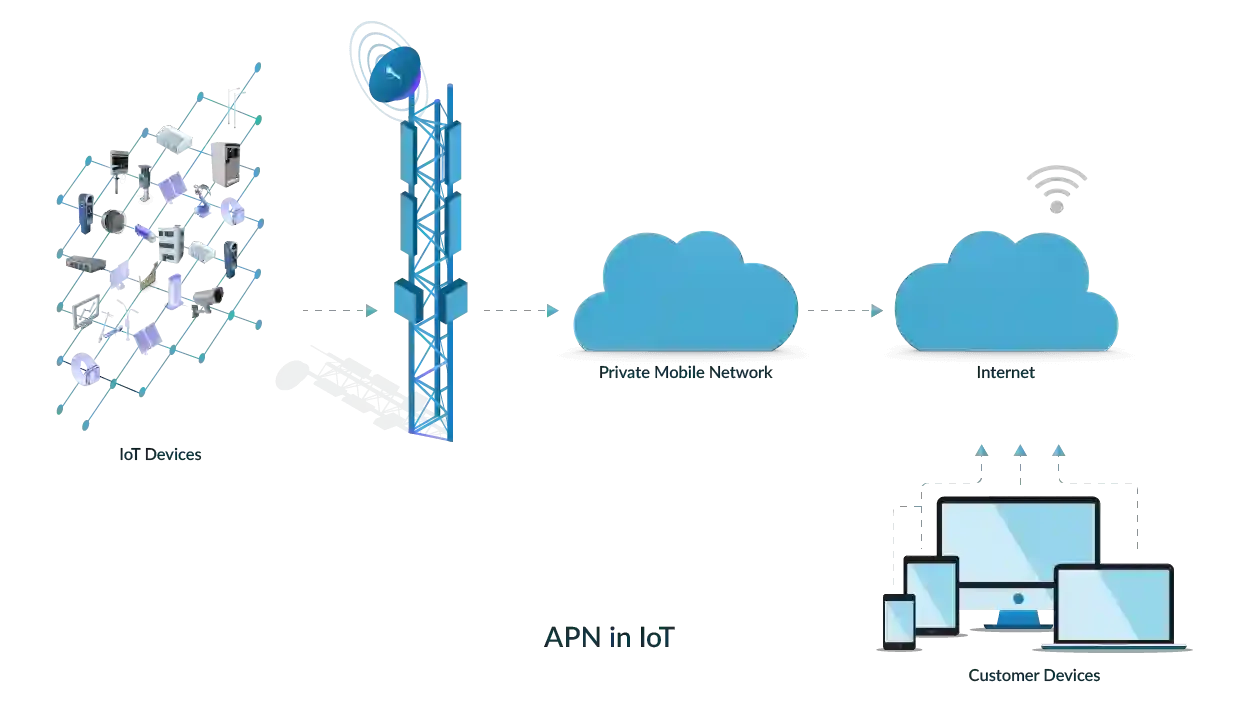
What is the Role of APN in IoT Connectivity?
Access point names serve as gateways, linking IoT devices to mobile networks for secure, efficient data transfer. According to GSMA guidelines, APNs define how a device accesses operator packet data networks under 3GPP standards (TS 23.003). An APN manages bandwidth, prioritizes traffic, and ensures reliable connections for applications like smart city infrastructure or remote health monitoring. By routing data correctly, APNs enable devices to communicate with cloud servers, supporting real-time updates and analytics.
Why Do IoT Devices Need Custom APN Settings?
IoT devices often require custom APN settings to ensure secure, optimized connectivity. Unlike default settings for smartphones, custom access point names provide tailored configurations for security (e.g., CHAP authentication) and performance (e.g., low-latency routing). For example, a smart meter may use a custom APN to securely transmit usage data, reducing risks and ensuring reliability.
How to Configure APN Settings for IoT Devices
Configuring what is apn settings ensures IoT devices connect seamlessly to mobile networks. Follow these steps to set up an access point name for IoT applications:
- Locate APN settings in the device’s network menu, typically under “Mobile Networks” or a management platform.
- Enter the APN name (e.g., iot.network), MCC, and MNC provided by your carrier.
- Set authentication to PAP or CHAP for secure access, based on your application’s needs.
- Configure apn type as dynamic IP for scalability or static IP for consistent access (e.g., for surveillance systems).
- Save settings, reboot the device, and test connectivity to confirm stability.
Using AT Commands for APN Configuration in IoT
For advanced IoT setups, AT commands configure APN settings manually. For example, use AT+CGDCONT=1,"IP","iot.network" to set the access point name. These commands define the Packet Data Protocol (PDP) context, ensuring devices connect to the correct network. Check your device’s manual for specific commands and test after configuration to verify connectivity.
Configuring APN for Global IoT Deployments
Global IoT deployments require what is apn settings that support roaming across regions. Use a management platform to input region-specific access point names, MCC, and MNC values. For example, a smart logistics tracker needs an APN to ensure seamless data transfer across countries, minimizing downtime during international operations. Explore global IoT solutions.
Best APN Settings for Secure IoT Connectivity
Secure IoT connectivity relies on optimized what is apn settings. Recommended configurations for access point names include:
| Parameter | Setting | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| APN Name | iot.network | Connects to IoT-specific network |
| Authentication | CHAP | Secures device access |
| IP Type | Dynamic/Static | Balances scalability and stability |
| MMSC | [Carrier-specific] | Enables multimedia messaging |
Benefits of Private Access Point Names for IoT Security
Private access point names enhance IoT security by routing data through dedicated networks, reducing exposure to public internet threats. As highlighted by 3GPP and GSMA working groups, enterprise APNs allow traffic isolation that strengthens endpoint authentication and minimizes attack vectors.
Private access point names enhance IoT security by routing data through dedicated networks, reducing exposure to public internet threats. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced security: Data stays within a private network, protecting sensitive information like medical records.
- Configurability: Customize IP ranges and authentication for specific IoT needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: Aggregates usage for efficient network management.
- Global coverage: Supports roaming for international IoT deployments.
Troubleshooting APN Connectivity Issues for IoT Modules
Connectivity issues in IoT devices often stem from incorrect what is apn settings. Follow these steps to troubleshoot:
- Access APN settings in the device’s network menu or management platform.
- Verify configuration by comparing settings (e.g., APN name, MCC, MNC) with carrier recommendations.
- Modify settings to update incorrect fields, such as MMSC or apn type.
- Test changes by rebooting the device and checking connectivity for stability and speed.
- Perform advanced checks by resetting to default settings or updating firmware if issues persist.
Common issues include slow speeds (due to network congestion or mismatched apn type) and intermittent access (caused by weak signals or incorrect network types). Switching to IPv6 or auto-selecting network types can resolve these.
Types of Access Point Names: Public, Private, and Static IP
Access point names come in three main apn types, each serving different needs:
Public APN
Default for general users, offering simple internet access with dynamic IPs. Ideal for basic IoT devices but less secure.
Private APN
Provides dedicated, secure connections via VPN-like gateways. Perfect for sensitive IoT applications like finance.
Private APN with Static IP
Assigns fixed IPs for stable, consistent access, ideal for IoT sensors or monitoring systems.
APN vs. VPN: Key Differences
APN, provided specifically by the mobile carrier, is the first step in establishing a connection between the mobile device and the internet. It plays a crucial role in enabling cellular connectivity for devices, including those equipped with IoT modules. Sometimes, private APN and VPN are often used interchangeably due to the assumption they have the same purpose… Virtual Private Network adds an additional layer of security by encrypting data sent over the internet. VPNs are specifically used for the exchange of private information over a public communication network. Businesses most often give employees working a VPN login remotely to access company assets. It is important to note that APN is a mandatory setting for cellular connectivity, while VPN is optional.
| APN | VPN |
|---|---|
| A gateway to let you connect to the public internet. | VPN is an additional secure layer that encrypts your internet traffic, ensuring privacy and security. |
| APN provides information required for connecting to the mobile network, enabling internet access and services. | VPN works by creating a secure virtual tunnel, encrypting data and ensuring secure access, especially for sensitive information. |
| Security depends on the carrier network. Private APN allows custom configurations, making it ideal for IoT deployments requiring dedicated and secure access. | VPN can choose the level of encryption for security, offering varying levels of privacy and control. |
| APN is mandatory for connectivity. It’s essential for accessing mobile data, MMS, and internet services. | VPN is optional but is commonly used for secure data transfer and remote access for businesses and IoT applications. |
| Use Cases: Primarily used for mobile data services and IoT connectivity, such as in smart city or IoT applications that require network access. | Use Cases: Ideal for enterprises, remote workers, and IoT applications needing encrypted connections for data security. |
| Benefits: Easy to set up and use, no encryption overhead, best for standard mobile data usage. | Benefits: High security, ideal for accessing sensitive data over public networks, essential for maintaining privacy. |
| Limitations: Limited security as it uses public internet; might not be suitable for secure IoT deployments or enterprise-level data protection. | Limitations: Additional setup and configuration required, higher cost due to encryption overhead and complex routing. |
Practical Use Cases of Access Point Names
e-Scooter Sharing
Uses private access point names for secure, real-time location tracking and user authentication.
Mobile Payment Terminals
Employs private access point names to secure transaction data.
Electric Vehicle Charging Stations
Combines public and private access point names for payment processing and system logs.
What is APN Settings? Key Components Explained
These are configurations that ensure your device connects to the mobile network. Key components include:
APN Name
The gateway to the network (e.g., wholesale for general use).
APN Type
Includes Generic (internet), Supl (GPS), MMS (messaging), or Wap (mobile web).
MMSC
Manages multimedia messaging services.
Proxy
Controls access via a proxy server for security.
Securing Mobile Networks with APN Protocols
Access point names enhance security through:
Encryption
Protects data privacy during transmission for APNs.
Authentication (PAP/CHAP)
Verifies device identity for secure access.
Monitoring
Regular updates to APN settings prevent unauthorized access.
Dynamic vs. Static IP Allocation
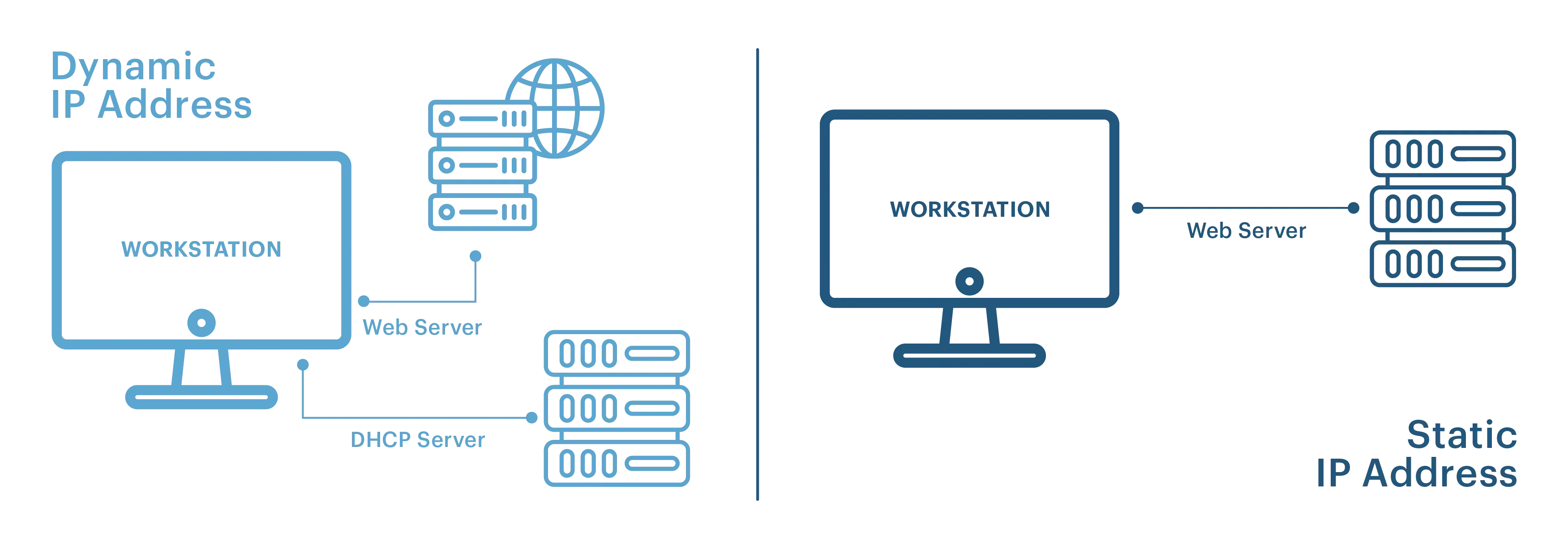
Dynamic IP
Automatically assigned, scalable for many devices, enhances security by changing IPs.
Static IP
Fixed for consistent access, ideal for IoT sensors or surveillance systems.
Do I Need a Private APN for IoT?
Private access point names offer:
- Control: Customize firewall rules and IP ranges.
- Security: Keep data off the public internet.
- P2P Connectivity: Enable secure device-to-device communication.
They’re ideal for IoT deployments needing high security and reliability.
Conclusion
Access point names are the backbone of mobile and IoT connectivity, enabling secure, reliable data transfer. Whether you’re setting up a smartphone or an IoT system, understanding what is apn, apn type, and what is apn settings ensures optimal performance. Explore more about IoT network solutions to enhance your connectivity experience.





