James, Jr. Network Engineer
Hey Adam, I have been working on our new IoT project, and I keep seeing references to the HTTP protocol. I know that it is fundamental for the web, but how does it apply to IoT devices? Is HTTP a good fit for resource-constrained devices?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is indeed the foundation of data communication on the web. In the context of IoT, HTTP provides a standardized way for devices to communicate with servers using RESTful APIs. It is widely supported and easy to implement, which makes it a popular choice for IoT applications. However, traditional HTTP/1.1 can be verbose and not optimized for low-bandwidth or high-latency networks. That is where HTTP/2 comes into play—it introduces features like multiplexing and header compression, which can make communication more efficient for IoT devices.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
That makes sense. So, HTTP/2 can help mitigate some of the limitations of HTTP/1.1 for IoT devices. Can you explain how features like multiplexing and header compression benefit our devices, especially those with limited resources and intermittent connectivity?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
Multiplexing allows multiple requests and responses to be sent simultaneously over a single TCP connection, reducing the overhead of establishing various connections and improving throughput. Header compression with the HPACK algorithm reduces the size of HTTP headers by compressing them. It reduces power consumption and improves response times by minimizing the amount of data transmitted. These features together make HTTP/2 more suitable for IoT applications than its predecessor.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
Now, our security team insists on using HTTPS for all device communications. I understand that HTTPS is HTTP over TLS for encryption, but would not the TLS handshake add overhead that could impact performance on our IoT devices?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
You are correct that TLS adds some overhead due to the handshake process. However, security is crucial, especially when transmitting sensitive data. With TLS 1.3, the handshake process has been optimized to require fewer round trips compared to its earlier versions. Additionally, implementing TLS session resumption allows devices to reconnect without performing a full handshake each time, which saves time and reduces computational load.
What is HTTP Protocol?
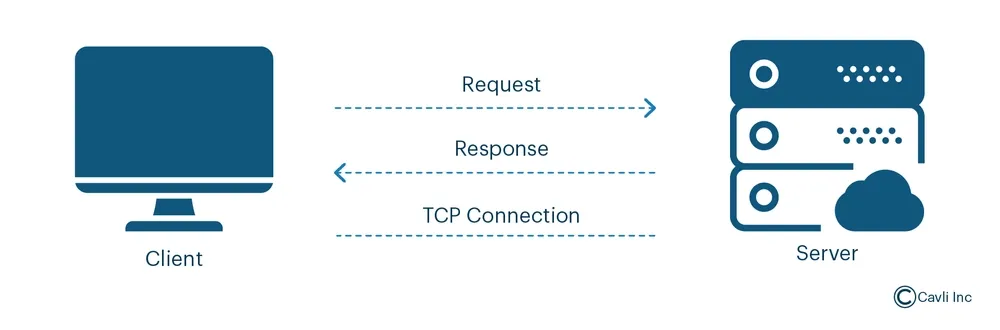
HTTP Protocol or HyperText Transfer Protocol is an application-layer protocol for transmitting hypermedia documents, such as HTML, across the Internet. It is the foundation of data communication, enabling web browsers (clients) and web servers to communicate effectively.
It enables web browsers (clients) and servers to communicate using a request-response model. In this model, a client sends an HTTP request to a server, which then returns an HTTP response containing the requested content or an error message.
HTTP is stateless, meaning each request is independent and doesn't retain information about previous interactions. It supports various methods like GET (to retrieve data) and POST (to submit data). Secure communication is facilitated through HTTPS, which incorporates encryption protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) to ensure data integrity and confidentiality during transmission.
HTTP Versions
HTTP/0.9
The first version, HTTP/0.9, released in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, was designed as a simple protocol for raw data transfer across the Internet.
Its minimalistic design supports only the GET method and operates without HTTP headers. It consists of a basic request format (GET/path/resource) and raw HTML response.
The protocol's simplicity came with significant limitations:
- No request or response headers, meaning no way to specify metadata like content type, encoding, caching, or authentication.
- Lacks support for other formats like JSON, XML, and images and only supports HTML content.
- It does not provide status codes like 404, making error handling and debugging difficult.
Despite these constraints, HTTP/0.9 played a crucial role in web history, serving as the foundation for subsequent HTTP versions.
Components of HTTP Protocol
HTTP Request Components
An HTTP request is sent by the client to request resources from the server. It consists of several parts:
Request Line
- Specifies the action the client wants the server to perform (e.g., GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- URL (Uniform Resource Locator): The address of the resource the client wants to access.
- HTTP Version: Specifies the version of the HTTP protocol used (e.g., HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2).
Request Headers
These HTTP request headers provide additional information about the request or the client. Common request headers include:
- User-Agent: Describes the client software making the request (e.g., browser, mobile app).
- Accept: Specifies the media types the client is ready to accept in the response (e.g., text/html, application/json).
- Authorization: Provides credentials for authentication (e.g., bearer token, basic auth).
- Host: Specifies the domain name of the server (necessary in HTTP/1.1 and above).
- Content-Type: Describes the format of the data being sent in the body (e.g., application/json, application/x-www-form-urlencoded).
HTTP Messages
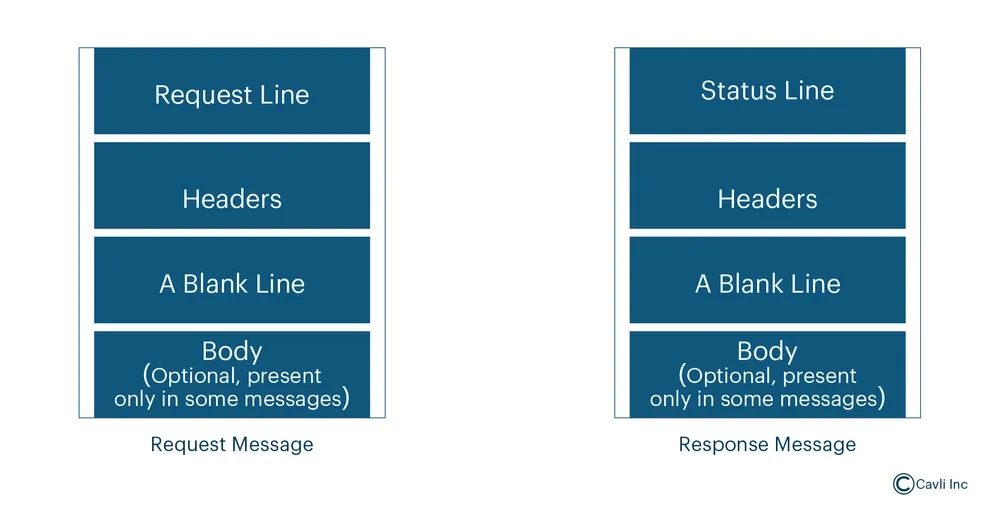
HTTP communication works based on the exchange of structured messages between the client and server. There are two types of messages:
- Request Messages: Sent from the client to the server to initiate an action.
- Response Messages: Sent from the server back to the client containing the results.
Key Differences Between HTTP Requests and HTTP Responses
| Aspect | HTTP Request | HTTP Response |
|---|---|---|
| Initiated By | Client (e.g., browser, app, or user agent) | Server |
| Purpose | To request a resource or action from the server | To deliver the requested resource or action result |
| Status | No status code; the request itself defines the action | Includes a status code (e.g., 200 OK, 404 Not Found) |
| Method | Includes the HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, etc.) | Not applicable; the response is determined by the server's action |
| Headers | Provide information about the request (e.g., Accept, Authorization) | Provide information about the response (e.g., Content-Type, Set-Cookie) |
| Body | May contain data (e.g., JSON, form data) for methods like POST or PUT | May contain the requested data (e.g., HTML, JSON) or an error message |
Structure of HTTP Messages
Start Line: Indicates the nature of the message.
Request Line (for requests): Contains the HTTP method, Request URI, and HTTP version (e.g., GET /index.html HTTP/1.1).
Status Line (for responses): It contains the HTTP version, status code, and reason phrase (e.g., HTTP/1.1 200 OK).
Headers: Key-value pairs providing additional information about the request or response (e.g., Content-Type: text/html).
Blank Line: A mandatory empty line indicating the end of the header section.
Message Body: Optional part containing the data to be transmitted (e.g., HTML content, JSON data).
HTTP Methods
HTTP methods define the action to be performed on the identified resource. Common methods include:
- GET: Retrieves data from the server.
- POST: Sends data to the server to create a new resource.
- PUT: Updates an existing resource with new data.
- DELETE: Removes a resource from the server.
- HEAD: Same as GET but only retrieves the headers.
- OPTIONS: Describes the communication options for the target resource.
- PATCH: Applies partial modifications to a resource.
- CONNECT: Establishes a tunnel to the server identified by a given URI.
- TRACE: Performs a message loop-back test along the path to the target resource.
HTTP Status Codes and Reason Phrases
When a server responds to a client request, it includes a status code and a reason phrase indicating the outcome:
| Code | Category | Description | Common Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1xx | Informational | Informational responses — The request was received, and the process is ongoing. | Indicates that the server is processing the request. |
| 100 | Continue | The server has received the request headers, and the client should proceed to send the request body. | Used in long requests, like file uploads. |
| 101 | Switching Protocols | The server is switching protocols as per the client's request (e.g., switching to WebSocket). | Used in protocol upgrades, like from HTTP to WebSocket. |
| 2xx | Success | Successful responses — The request was successfully received, understood, and accepted. | Indicates that the request was processed correctly. |
| 200 | OK | The request was successful, and the server has returned the requested data. | Standard response for a successful HTTP request. |
| 201 | Created | The request was successful, and a new resource was created. | Often used after a successful POST request. |
| 202 | Accepted | The request has been accepted for processing, but the processing is not yet complete. | For asynchronous tasks like queuing a job. |
| 204 | No Content | The server successfully processed the request, but there is no content to return. | Used for PUT or DELETE operations. |
| 3xx | Redirection | Redirection responses — The client must take additional action to complete the request. | Indicates that the client must make another request to fulfill the original request. |
| 300 | Multiple Choices | There are multiple options for the resource, and the client should choose one. | Rarely used. |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | The resource has been permanently moved to a new URL. | Used in permanent URL redirects. |
| 302 | Found | The resource is temporarily located at a different URL. | Used in temporary URL redirects (often for URL shortening). |
| 303 | See Other | The client should perform a GET request to another URL. | Typically used after a POST or PUT request to redirect to another resource. |
| 304 | Not Modified | The resource has not been modified since the last request. | Used in caching to check if the cached resource is still valid. |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | The resource is temporarily located at a different URL (similar to 302 but preserved method). | Used when a temporary redirect is needed while maintaining the HTTP method. |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | The resource has permanently moved to a new URL (similar to 301 but preserved method). | Used for permanent redirects while preserving the HTTP method. |
| 4xx | Client Errors | Client error responses — The request contains bad syntax or cannot be fulfilled. | Indicates that there was a problem with the request sent by the client. |
| 400 | Bad Request | The server could not understand the request due to invalid syntax. | Invalid requests due to incorrect parameters, missing data, etc. |
| 401 | Unauthorized | The request lacks valid authentication credentials. | Used for authentication failure (e.g., missing or invalid API keys). |
| 402 | Payment Required | Reserved for future use, though it is not commonly used. | Originally meant for payment-required errors (e.g., subscription issues). |
| 403 | Forbidden | The server understands the request, but the client does not have permission to access the resource. | For authorization issues (e.g., attempting to access a restricted page). |
| 404 | Not Found | The server could not find the requested resource. | Most common error for non-existent URLs. |
| 405 | Method Not Allowed | The HTTP method used is not supported for the resource. | Used when a client tries to access a resource using an unsupported HTTP method (e.g., POST on a read-only resource). |
| 406 | Not Acceptable | The server cannot produce a response that meets the criteria set by the client (via Accept headers). | Usually occurs when the requested content type is not available. |
| 407 | Proxy Authentication Required | The client must authenticate with a proxy server. | Used when a proxy requires authentication. |
| 408 | Request Timeout | The client did not produce a request within the time the server was prepared to wait. | Often caused by network issues or slow client requests. |
| 409 | Conflict | The request could not be completed due to a conflict with the current state of the resource. | Used in situations like version control or when editing a resource simultaneously. |
| 410 | Gone | The resource requested is no longer available and will not be available again. | Used for permanently deleted resources (e.g., deprecated content). |
| 411 | Length Required | The server refuses to process the request without a valid Content-Length header. | Used in requests that need a specified content length. |
| 412 | Precondition Failed | The server does not meet one of the preconditions set by the client. | Usually happens with conditional requests (like If-Match). |
| 413 | Payload Too Large | The request is larger than the server is willing or able to process. | Used when uploading a file that is too large. |
| 414 | URI Too Long | The URI provided in the request is too long for the server to process. | Common with overly long URLs or query parameters. |
| 415 | Unsupported Media Type | The media type of the request is not supported by the server. | Used when the server cannot process a request with a given content type. |
| 416 | Range Not Satisfiable | The client asked for a portion of the resources that is outside of the available range. | Typically used for partial downloads. |
| 417 | Expectation Failed | The server cannot meet the requirements specified in the Expect header of the request. | Rare, but can happen with specific client expectations (e.g., Expect: 100-continue). |
| 5xx | Server Errors | Server error responses — The server failed to fulfill a valid request. | Indicates that the server failed to process a valid request. |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | The server encountered an unexpected condition that prevented it from fulfilling the request. | Generic error message for unexpected server failures. |
| 501 | Not Implemented | The server does not support the functionality required to fulfill the request. | Used when the server doesn’t recognize a method or feature. |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | The server, while acting as a gateway or proxy, received an invalid response from an upstream server. | Common with issues in reverse proxies or load balancers. |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | The server is currently unable to handle the request due to temporary overloading or maintenance. | Common during server downtime or heavy traffic. |
| 504 | Gateway Timeout | The server, while acting as a gateway or proxy, did not receive a timely response from an upstream server. | Common with timeouts in reverse proxy setups. |
| 505 | HTTP Version Not Supported | The server does not support the HTTP protocol version used in the request. | Used when the HTTP version is not supported by the server. |
What does HTTP Caching mean?
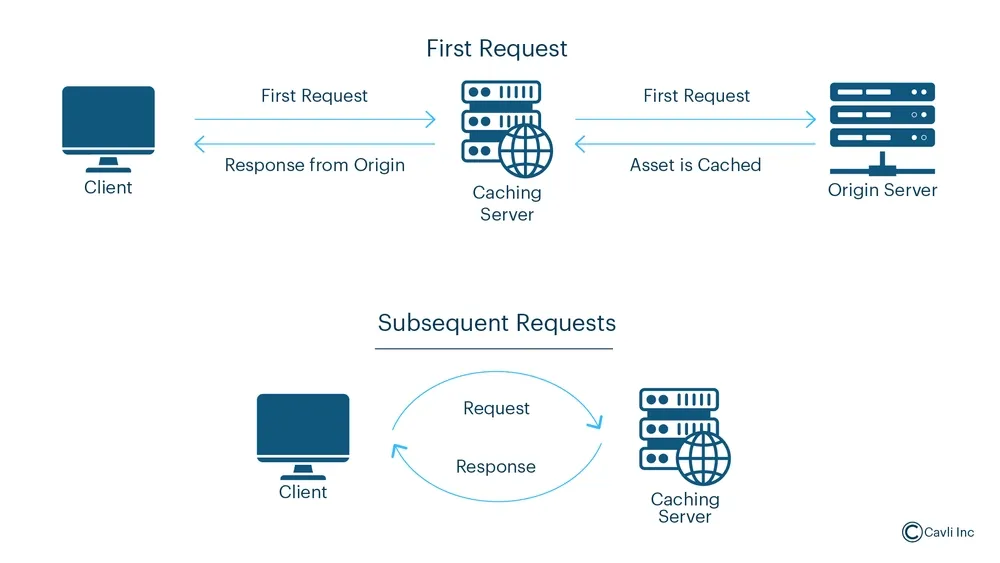
HTTP caching is a mechanism that stores copies of responses from a web server (such as HTML pages, images, or JSON data) so that subsequent requests for the same resources can be served more quickly without having to re-fetch them from the server.
This process is typically managed using HTTP headers that control how and when content should be cached, either on the client side (in a browser or application) or at intermediate locations (like proxies or Content Delivery Networks).
HTTP caching works by saving a "cached" version of the content, which is then reused for future requests, rather than fetching the data from the server again. There are several types of HTTP caching, including:
- Browser cache: Stores resources locally in the user's browser.
- Proxy cache: Used by servers or CDNs to cache resources on behalf of many users.
- Server-side cache: Can store content in memory to speed up responses for repeated requests.
HTTP caching offers several key benefits:
- Reduces repeated requests for the same resources.
- Improves performance by serving cached content quickly.
- Reduces server load.
- Enhances user experience.
- Improves scalability.
HTTP vs HTTPS
HTTPS Protocol
HTTPS encrypts the data transmitted between the client and server using SSL/TLS protocols. It ensures that sensitive information (like passwords, payment details, etc.) is protected from eavesdropping.
HTTPS uses digital certificates to verify the server's identity. It ensures that the client is communicating with the legitimate server and not an imposter (which helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks).
HTTPS guarantees data integrity, ensuring no data alteration occurs during its transmission and preventing data tampering and corruption.
Role of HTTPS in IoT Security
HTTPS is crucial for securing IoT devices, as it ensures:
- Protection of sensitive data.
- Protection from MITM attacks.
- Secure firmware updates.
- Protection of credentials and configurations.
- Securing API communications.
Closing Notes
The HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is a fundamental protocol that enables communication between clients (such as web browsers) and servers over the Internet. It facilitates the transfer of data like web pages, images, and other resources through a request-response model. HTTP is simple and efficient, supporting various methods such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE for different types of interactions.
However, HTTP Protocol is stateless and does not provide built-in security features. Despite these limitations, HTTP remains essential for web browsing and communication, especially in non-sensitive contexts. Understanding HTTP is crucial for developing web applications, troubleshooting network issues, and optimizing server-client communication.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes Related to this Edition of Wireless By Design
The Internet Café
Imagine HTTP as an internet café where customers (clients) come in, request to use a computer (make an HTTP request), and get to use it for a short period. Once their time is up, they log off and leave. Every new customer starts fresh with their request, and the café does not remember past customers or their activity (stateless). The server (the café) gives them what they need temporarily and then resets, ready for the next customer.

The Movie Rental Service
Think of the HTTP Protocol as a movie rental service. You go to a rental shop (client), ask for a specific movie (request), and the clerk (server) retrieves it for you and hands it over (response). After you watch the movie, you return it and ask for a different one (new request). The clerk does not keep track of previous rentals; each request is treated as a new one, and the process starts fresh every time (stateless).

The Auctioneer’s Call
Think of the HTTP Protocol as a movie rental service. You go to a rental shop (client), ask for a specific movie (request), and the clerk (server) retrieves it for you and hands it over (response). After you watch the movie, you return it and ask for a different one (new request). The clerk does not keep track of previous rentals; each request is treated as a new one, and the process starts fresh every time (stateless).
Go Beyond and Explore
What is an HTTP Flood DDoS Attack?
- Rate Limiting: Limiting the number of requests a single IP or user can make within a specific time frame helps mitigate excessive traffic.
- CAPTCHA: Implementing CAPTCHA challenges can help differentiate between human users and malicious bots attempting to overwhelm the server.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): A WAF can help filter out malicious traffic by analyzing HTTP requests and blocking suspicious patterns.
- Load Balancing: Distributing the incoming traffic across multiple servers can reduce the impact on any single server.
- Bot Detection: Using bot-detection tools and services to identify and block traffic originating from known botnets.
- Traffic Analysis and Filtering: Analyzing the incoming traffic for unusual patterns (e.g., excessive requests from a single IP or geographic location) can help detect and mitigate the attack early.
What is HTTP Proxy?
- Function: It forwards HTTP requests from a client to the destination server and returns the response to the client.
- It can perform actions like security filtering, logging, content modification, anonymity, or load balancing.
- In some cases, a proxy can cache content to improve performance (this is where caching comes into play). Types of HTTP Proxies:
- Forward Proxy: The client knows about the proxy and sends all requests to it (often used for accessing restricted content, anonymity, or content filtering).
- Reverse Proxy: The proxy sits in front of the server, and clients are unaware of its existence. It handles incoming requests on behalf of the server, providing benefits like load balancing or SSL termination.
What is the difference between HTTP, SMTP, and FTP?
HTTP Protocol or HyperText Transfer Protocol, is used for transferring web pages and resources between clients and servers. It operates on port 80 (HTTP) or 443 (HTTPS) and is stateless, meaning each request is independent. Used by web browsers to load websites.
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is used for sending and relaying emails between servers. It operates on port 25 (default) and is session-based. SMTP is primarily used by email clients like Gmail or Outlook to send messages.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is used for transferring files between clients and servers. It operates on port 21 for control and dynamic ports for data transfer. FTP allows users to upload/download files and is commonly used for managing files on remote servers.
- Key Differences:
- Purpose: HTTP for web pages, SMTP for email, FTP for file transfer.
- Port: HTTP (80), SMTP (25), FTP (21).
- Security: HTTP is insecure, SMTP can be insecure, FTP is insecure by default (unless FTPS/SFTP is used).





