James, Jr. Network Engineer
Hey Adam, I've been working with different IoT protocols, and I notice TCP is everywhere. Why do we rely on it so much for IoT applications?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
TCP is like the certified mail service of the internet. While other protocols just send data hoping it arrives, TCP ensures every piece of data reaches its destination correctly and in order. This is crucial for IoT applications where data integrity is non-negotiable.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
But doesn't this reliability come with overhead? Some IoT devices have limited resources.
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
You're right. TCP does have more overhead compared to protocols like UDP. However, for critical IoT applications like industrial control systems, healthcare devices, or financial transactions, the benefits of guaranteed delivery outweigh the overhead. It's all about choosing the right tool for the job.
James, Jr. Network Engineer
So what makes TCP particularly suitable for certain IoT applications?
Adam, Sr. Network Engineer
Think of TCP as a careful courier service. It not only confirms delivery but also handles congestion on the network, retransmits lost data, and ensures everything arrives in the correct order. For IoT devices sending critical sensor data or receiving firmware updates, these features are invaluable.
In today's world, where billions of IoT devices communicate across vast networks, reliability isn't just a feature—it's a necessity. Network protocols are standardized rules or guidelines that dictate how data is transmitted and received across networks, allowing devices to communicate with one another efficiently and reliably. These protocols operate at different layers of the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, each serving a specific purpose to enable successful communication.
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) stands as one of the fundamental pillars enabling reliable communication. From industrial sensors transmitting critical data to smart devices receiving firmware updates, TCP ensures that what's sent is exactly what's received.
What is TCP or Transmission Control Protocol?
TCP or Transmission Control Protocol is a connection-oriented protocol that operates at the transport layer (Layer 4) of the OSI model. It provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of data between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Unlike its counterpart UDP, TCP prioritizes reliability over speed, making it ideal for applications where data integrity is crucial.
TCP works at the Transport Layer (Layer 4 of the network) and its TCP protocol number is 6. It ensures that data is reliably sent in the correct order between applications on different devices. It uses a technique called the transmission window protocol to manage the flow of data, starting with a default window size of 64KB (65,535 bytes), which can expand up to 1GB if needed for larger data transfers.
TCP implements flow control through a dynamic transmission window size that adjusts based on network conditions, with congestion control algorithms like Slow Start, Congestion Avoidance, Fast Retransmit, and Fast Recovery. For IoT devices, TCP maintains connection state information requiring approximately 1.5KB of memory per connection. It implements retransmission timers that typically start at 200ms and can exponentially back off up to 3 minutes. TCP protocol includes a sophisticated error detection mechanism with a 16-bit checksum field, and its header size ranges from 20 to 60 bytes, with options for features like Selective Acknowledgement (SACK) and Timestamps.
Components of TCP Protocol
TCP Segments
TCP transmits data in units called segments. Each segment is a chunk of data with a TCP header attached, which contains control information essential for managing the communication.
TCP Header
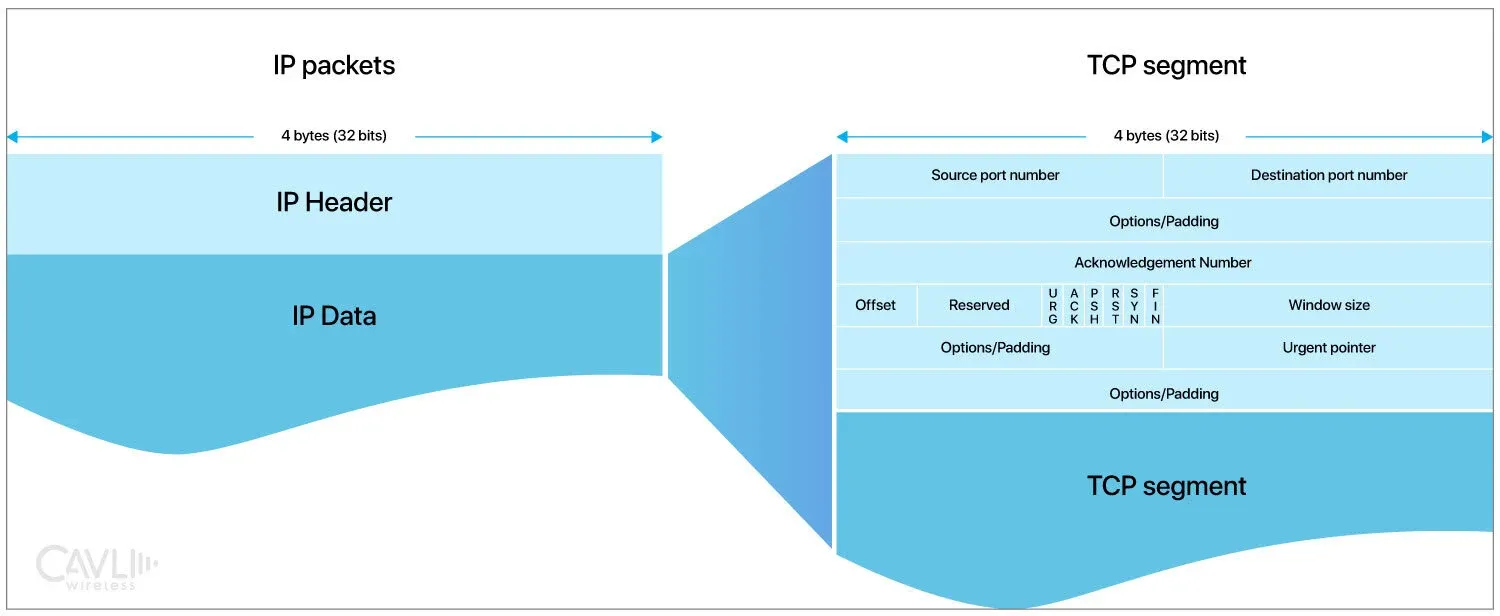
Each TCP segment includes a header with crucial fields for managing the connection. Key fields include:
Source Port and Destination Port
It identifies the application or process on the sending and receiving devices. It has a total of 65,535 possible port numbers.
Sequence Number
It identifies the first data byte in this segment. It ensures that data is reassembled in the correct order.
Acknowledgment Number
It indicates that the sender has received all data up to this number from the other side. It contains the next sequence number expected from the other side. It is valid only if the ACK flag is set.
Data Offset
Data Offset specifies the TCP header length in 32-bit words. The reserved (6 bits) are for future use and must be zero.
Control Flags
Flags (like SYN, ACK, FIN) that control the connection state, helping establish, maintain, and terminate the connection.
- URG: Urgent pointer field is significant
- ACK: Acknowledgment field is significant
- PSH: Push function
- RST: Reset the connection
- SYN: Synchronize sequence numbers
- FIN: No more data from sender
Checksum
It is used for error-checking in the TCP header, ensuring data integrity during transmission. It is a mandatory field that must be calculated.
Urgent Pointer
It identifies data that should be prioritized. It points to the sequence number of the last urgent data byte. It stands valid only if the URG flag is set.
Flow Control (Windowing)
Window size is used for flow control. It manages flow control by specifying the amount of data that can be sent before needing an acknowledgment.
It allows the sender to adjust the data rate based on the receiver's capacity. This process prevents data from overwhelming the receiving device.
Sliding Window Protocol
A specific technique TCP uses to manage data flow, sending multiple segments before requiring an acknowledgment and adjusting the window size dynamically.
Error Detection and Retransmission
TCP includes error-checking mechanisms using the checksum field in the header. If an error is detected in a received segment, TCP discards it, and the sender retransmits the missing or damaged data.
Congestion Control
TCP employs algorithms like Slow Start, Congestion Avoidance, Fast Retransmit, and Fast Recovery to manage congestion in the network, preventing excessive data transmission that could slow down or disrupt communication.
Sequence Numbers and Acknowledgments
Sequence Numbers ensure that data is received in the correct order, even if segments arrive out of order. Acknowledgment Numbers inform the sender of successful data receipt, allowing reliable data transfer.
Timers
TCP uses various timers to manage operations, such as:
- Retransmission Timer: It determines when to retransmit a segment if no acknowledgment is received.
- Persistence Timer: It prevents a deadlock when the receiver's window size is zero.
- Keepalive Timer: It checks if the connection is still active.
- Time-Wait Timer: It ensures all segments have been received after a connection closes.
These components work together to make TCP a robust, reliable protocol that can handle complex communication needs over diverse network conditions, ensuring the data arrives in order and intact.
Working of TCP Protocol
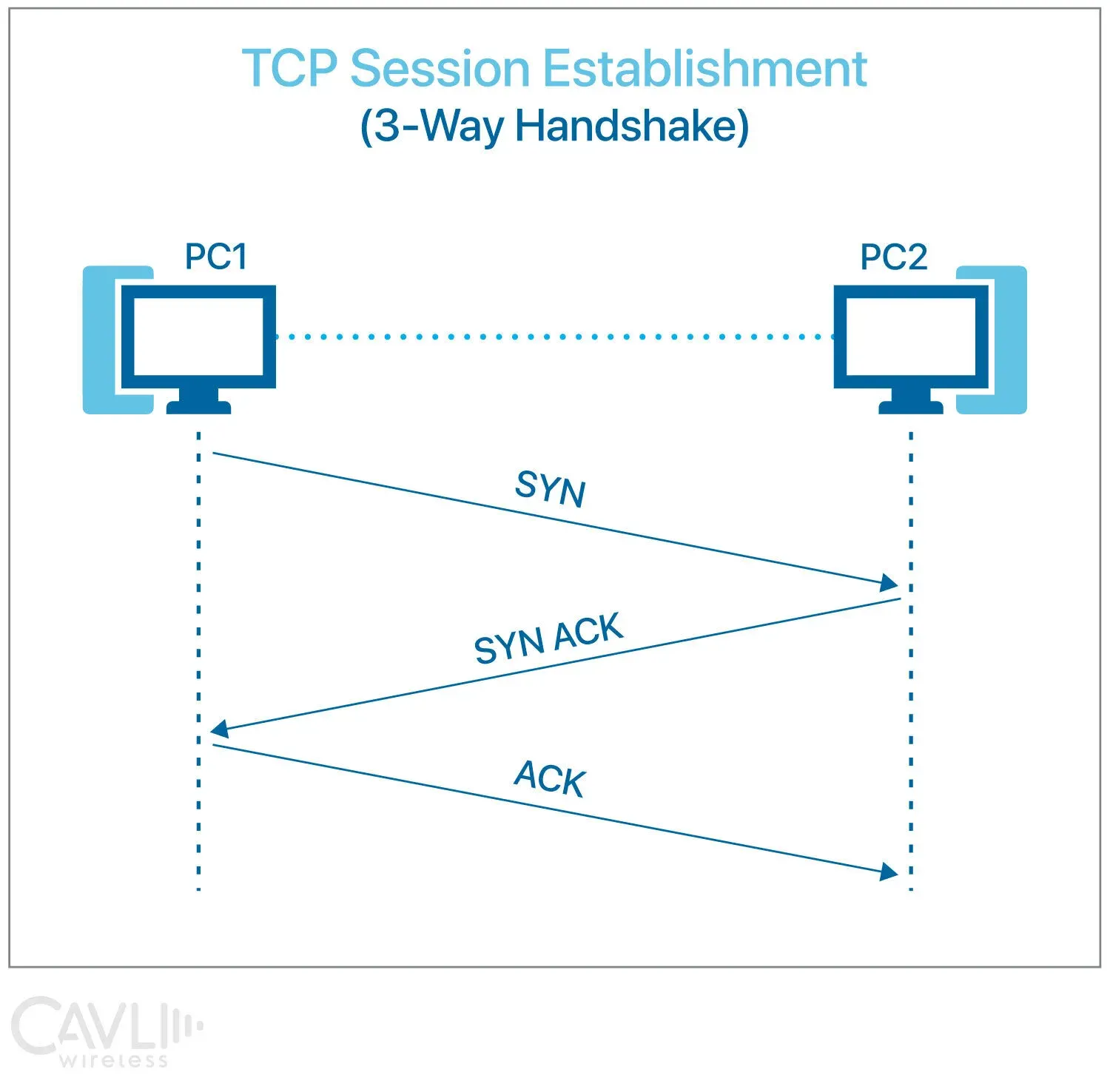
TCP uses a three-way TCP handshake to establish a connection between two devices. This involves:
Connection Establishment (Three-Way Handshake)
Step 1: SYN (Synchronize)
The client sends a SYN packet to the server to initiate a connection.
- Sets SYN flag = 1
- Chooses initial sequence number (ISN) x
Step 2: SYN-ACK (Synchronize-Acknowledge)
The server responds with a SYN-ACK packet, acknowledging the request.
- Sets both SYN and ACK flags
- Chooses its own ISN y
- Acknowledges the client's sequence number
Step 3: ACK (Acknowledge)
The client replies with an ACK packet to confirm the connection.
- Client acknowledges the server's sequence number
Connection established successfully.
Connection Termination (Four-Way Handshake)
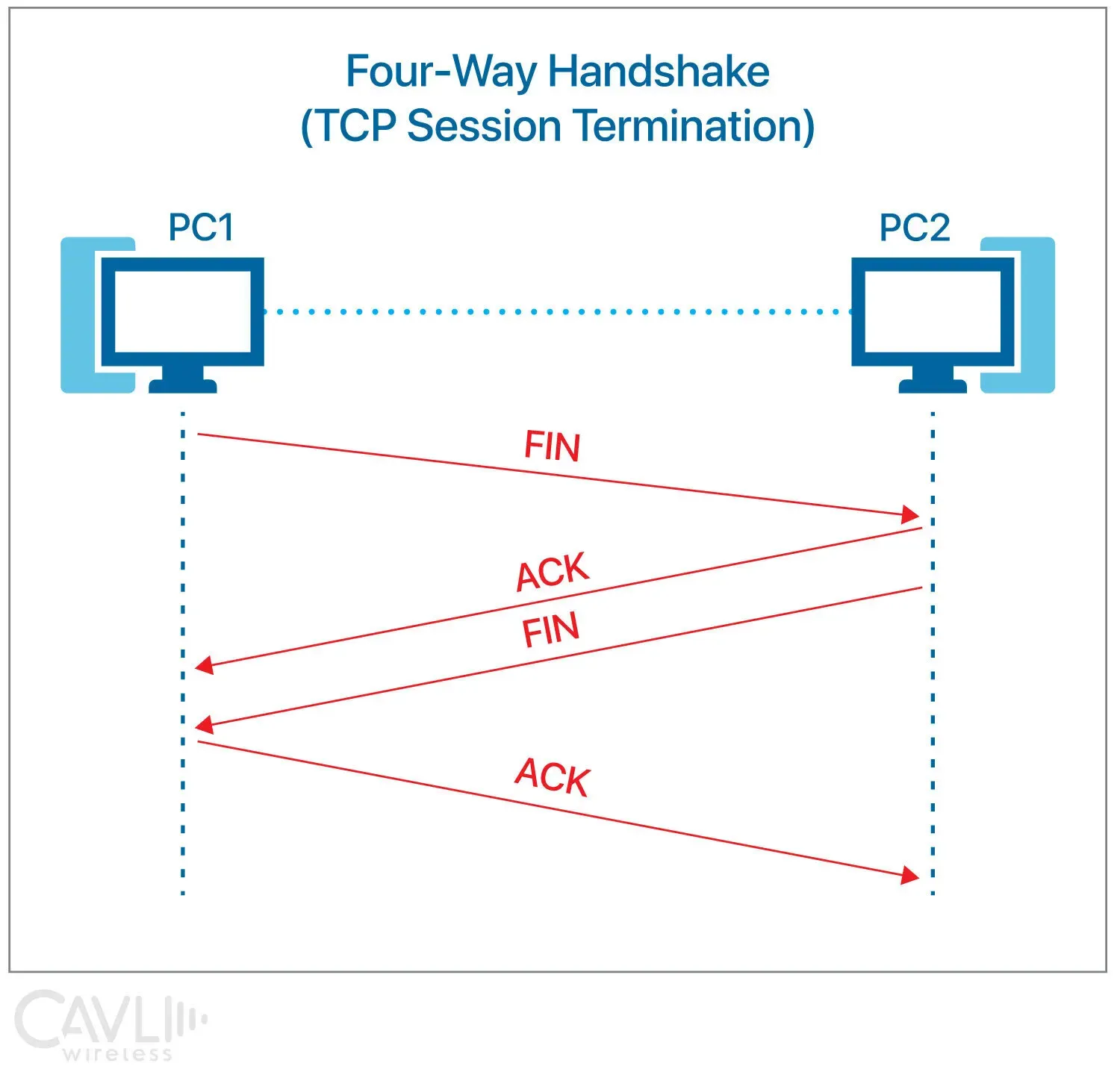
TCP uses a four-step process to terminate a connection, ensuring both sides have agreed to end the communication. This is called the four-way TCP handshake.
Step 1: Initial FIN
The device that wants to terminate the connection sends the first FIN packet.
- State Change: Client → FIN-WAIT-1
Step 2: First ACK
The server acknowledges the client's FIN packet.
- State Change:
- Server → CLOSE-WAIT
- Client → FIN-WAIT-2
Step 3: Server FIN
The server sends its own FIN to the client.
- State Change: Server → LAST-ACK
Step 4: Final ACK
The client acknowledges the server's FIN and sends an ACK packet to complete the termination process.
- State Change:
- Client → TIME-WAIT
- Server → CLOSED
Once this process is complete, both devices have successfully terminated the connection, ensuring all data has been received and that both sides are in agreement to close the communication.
Breaking down the TCP/IP Protocol Stack and the IoT Layers
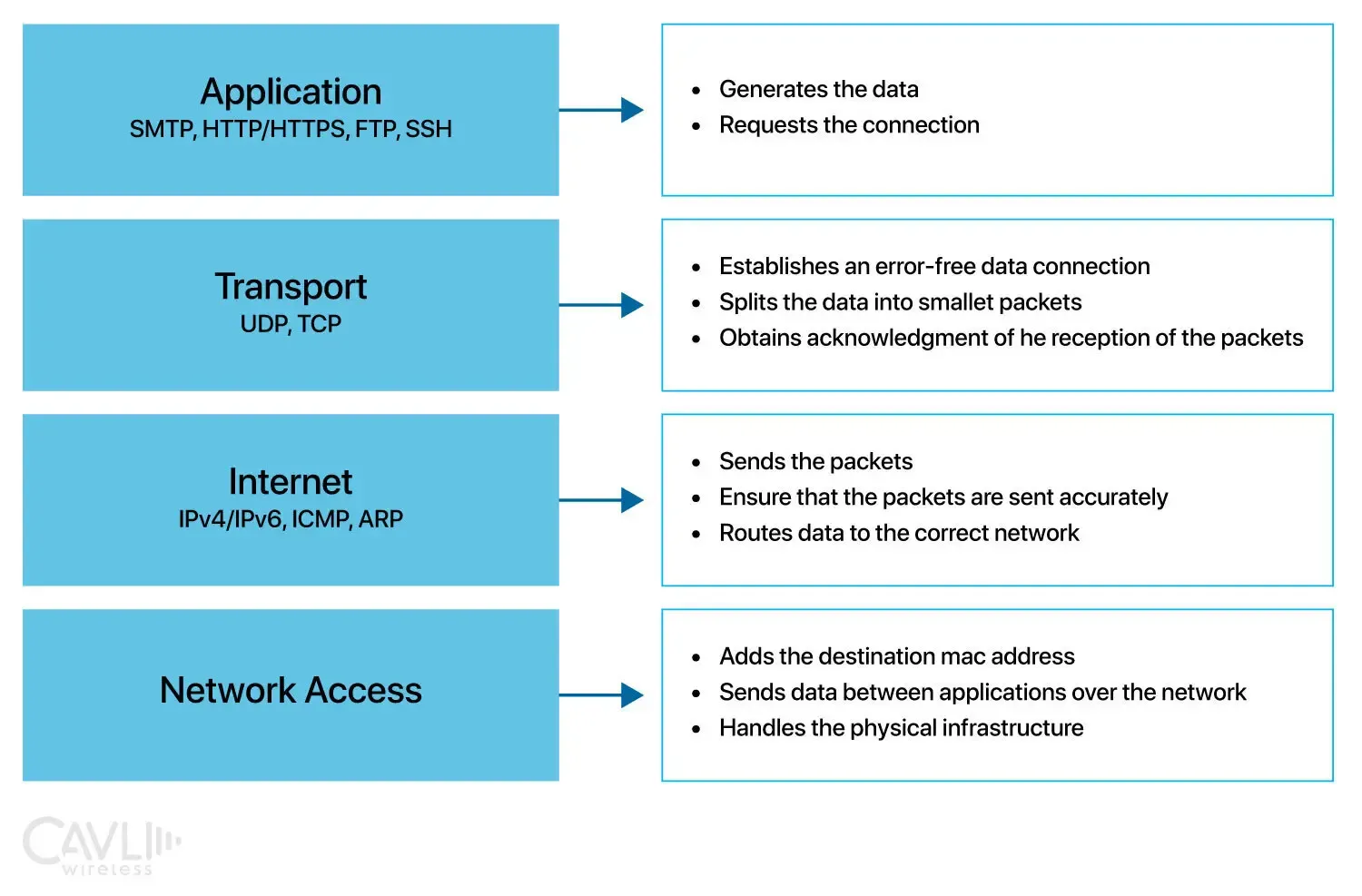
Application Layer
This is the topmost layer that directly interacts with end-user applications and processes. In IoT contexts, this layer handles protocols like MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) alongside traditional protocols shown in the image (HTTP/HTTPS, FTP, SSH). For IoT devices, this layer is crucial as it generates sensor data, handles device commands, and manages application-level security. MQTT is particularly important for IoT as it's designed for low-bandwidth, high-latency networks common in IoT deployments.
Transport Layer
The transport layer ensures reliable data transmission between IoT devices and servers. TCP provides reliable, ordered delivery with error checking, while UDP offers faster, connectionless communication preferred for real-time IoT applications like environmental sensors or streaming devices. This layer segments larger data into smaller packets and manages flow control, which is crucial for resource-constrained IoT devices that might not handle large data streams efficiently.
Internet Layer
It is also known as the network layer. It handles routing of packets across networks using IPv4/IPv6 protocols. For IoT devices, IPv6 is particularly important due to its larger address space, allowing billions of devices to have unique addresses. ICMP helps in network diagnostics and error reporting, while ARP resolves IP addresses to physical MAC addresses. This layer ensures packets reach their correct destination across different networks, essential for distributed IoT systems.
Network Access Layer
This bottom layer manages the physical transmission of data and hardware-level interactions. It handles MAC addressing, which is crucial for identifying individual IoT devices on a network. This network layer deals with various physical transmission technologies common in IoT like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, or cellular networks. It's responsible for the actual bits-and-bytes transmission over the physical medium.
IoT Security with TCP/IP Protocol
IoT security across the TCP/IP layers requires a comprehensive, multi-layered approach that addresses vulnerabilities at each level. The following sections break down security measures at each layer:
Application Layer
At the application layer, security measures focus on ensuring secure communication and access control. Key measures include:
- Implementing TLS/SSL encryption for HTTPS communications
- Utilizing OAuth and JWT tokens for robust authentication
- Ensuring API security through proper access control measures
- Maintaining data encryption to protect sensitive information
Transport Layer
Moving down to the Transport Layer, security implementations are critical to ensure the security of communication channels. These include:
- Using TLS for securing communication channels
- Implementing stringent port security measures
- Protection against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks
- End-to-end traffic encryption to prevent interception
Internet Layer
The Internet Layer incorporates security protocols and measures to secure network-level communications, such as:
- Implementing IPSec protocols for secure communication
- Deploying firewalls for traffic filtering
- Network segmentation to isolate critical systems
- Packet filtering to prevent unauthorized access
Network Access Layer
At the Network Access Layer, security measures focus on controlling access to devices and ensuring secure network connections:
- MAC address filtering to control device access
- Implementing WPA3 for secure Wi-Fi connections
- Physical security measures to protect hardware infrastructure
- Network access control mechanisms to restrict unauthorized devices
This multi-layered security approach, often referred to as "defense in depth," is crucial for IoT systems. These systems typically operate in resource-constrained environments and face unique challenges in implementing comprehensive security measures.
Key Differences Between TCP and IP Protocols
The Internet Protocol (IP)
The Internet Protocol (IP) is a core networking protocol that serves as the foundation for data communication across the internet. It ensures that data packets can find their way from one device to another across vast networks of interconnected computers and routers.
When data needs to be transmitted, IP breaks it down into smaller packets for efficient delivery. Each packet is treated independently and follows a "best effort" delivery approach, meaning there's no guarantee of reliable delivery or that packets will arrive in order. This is why IP is often paired with other protocols like TCP, which handle the reliability aspect of data transmission.
At its heart, IP performs two crucial functions: addressing and routing.Every device connected to a network is assigned a unique IP address. These addresses come in two main versions: the older IPv4 which uses a 32-bit format (like 192.168.1.1), and the newer IPv6 which uses a 128-bit format.
IPv4
IPv4 addresses use a 32-bit format, divided into four octets (8 bits each) separated by dots. Each octet can range from 0 to 255, creating addresses like 192.168.1.1.
IPv6
IPv6 addresses are significantly longer, represented as eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons, such as
2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
IPv4 addresses are typically configured manually or via DHCP but on the other hand, IPv6 introduces more sophisticated features like auto-configuration.
Devices can automatically generate their IPv6 addresses using their MAC addresses and network prefixes, making network administration more streamlined.
| Aspect | TCP | IP |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Transmission Control Protocol | Internet Protocol |
| OSI Layer | Transport Layer (Layer 4) | Network Layer (Layer 3) |
| Function | Ensures reliable, ordered, error-checked delivery of data | Provides addressing and routing for packets across networks |
| Connection Type | Connection-oriented | Connectionless |
| Reliability | Reliable (uses acknowledgment and retransmission) | Not reliable; does not guarantee delivery |
| Flow Control | Yes | No |
| Error Checking | Yes, checks for errors and retransmits if needed | Limited error detection, no correction |
| Data Transmission | Stream-based | Packet-based |
| Speed | Slower than UDP due to error checking and handshakes | N/A |
| Header Size | 20 bytes | 20-60 bytes |
| Use Cases | Web browsing, email, file transfers | Routing and addressing of packets across networks |
| Common Port Numbers | 80 (HTTP), 443 (HTTPS), 25 (SMTP), 110 (POP3) | N/A |
| State Management | Maintains state, manages sessions | Stateless |
Where and When to Use TCP Protocol?
Financial Transactions
It is mandatory for banking applications due to guaranteed delivery.
Web Applications
It is essential for HTTP/HTTPS traffic requiring reliable data transfer.
Enterprise Software
It is critical for business applications requiring data integrity.
File Transfers
It is ideal for large file transfers requiring accuracy.
When to Consider Alternatives Protocol Stack for IoT Applications?
Real-time Gaming
TCP's acknowledgment system adds a latency overhead of 50-200ms delay. Head-of-Line Blocking makes older packets to block newer, more relevant ones. The handshake adds startup delay causing inefficiencies in connection management.
The best alternative in this scenario is UDP with a custom reliability layer. It offers a typical performance gain and lower latency.
Live Streaming
TCP can be problematic due to retransmission delays that can cause buffer underruns. Retransmissions can also waste bandwidth affecting the efficient bandwidth management. Buffering affects user experience and can result in a degraded quality experience.
Instead of TCP, using RTP (Real-time Transport Protocol) and QUIC (Quick UDP Internet Connections) typically reduces buffering in live sports broadcasts and video conferencing applications.
IoT Sensor Devices
TCP is often overkill with header overhead of about 20 bytes TCP vs 8 bytes UDP. Many IoT devices, such as sensors or wearable devices, run on limited power. TCP’s extra processing and communication steps drain power more quickly, which is especially critical for devices that need to run for extended periods on a single battery charge.
CoAP and MQTT are specifically designed for constrained environments (like IoT devices and sensor networks). With increased bandwidth efficiency, these protocols help reduce network congestion. By lowering the amount of data transmitted, they reduce the need for constant connections, entering into low-power or "sleep" modes more often, extending their battery life.
Closing Notes:
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) stands as a masterpiece of network engineering, demonstrating remarkable longevity and adaptability in the ever-evolving landscape of internet technologies. Since its inception, it has served as the cornerstone of reliable data transmission across networks, powering everything from simple web browsing to complex cloud computing operations.
Its sophisticated mechanisms for connection management, flow control, and error handling have set the standard for reliable communication protocols. Despite the emergence of newer protocols and technologies, TCP's fundamental principles continue to influence modern network design. Its ability to provide guaranteed, ordered data delivery while adapting to varying network conditions makes it indispensable in today's digital infrastructure.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes Related to this Edition of Wireless By Design
TCP as a Phone Call
TCP works like a phone call: it starts by establishing a connection, with each side confirming they’re ready to communicate. During the "conversation," both sides send and receive data, making sure each part is clear and in the right order, just like taking turns speaking and listening. If any message is missed or unclear, it’s repeated to keep everything accurate. Finally, when the exchange is complete, both sides say goodbye, ensuring that the connection closes cleanly and each side knows the conversation has ended. This ensures reliable, ordered communication.

TCP as a Book Club
TCP works like a book club where everyone reads in sync. Members agree to start reading together, then after each chapter, they check in to confirm they’re ready to move forward. If someone falls behind or skips a chapter, they go back to catch up so the group stays on the same page. Faster readers wait for others, adjusting the pace so no one is left behind. When the book is finished, everyone confirms they’re done, officially ending the session. This keeps the reading experience smooth, reliable, and orderly—just like TCP manages data transmission.

TCP as Postal Service
TCP works like sending packages to a friend. First, you agree to communicate, like saying “hello” to each other. Then, you send a few packages at a time, and your friend confirms each one as it arrives. If any packages are missing or damaged, you resend them until they’re all received in the right order. Each package is numbered to keep things organized, and when everything has been delivered, you both confirm the conversation is over and stop. This process ensures all information arrives completely, accurately, and in the correct order.
Go Beyond and Explore
Why is TCP often preferred in critical IoT applications?
TCP ensures reliable, ordered, and error-checked data delivery, which is essential for IoT use cases like industrial automation, healthcare monitoring, and financial transactions. Its features, such as retransmission of lost packets, congestion control, and sequence numbering, make it indispensable for applications where data integrity is non-negotiable.


