In our increasingly connected world, the ability to manage and monitor Internet of Things (IoT) devices from any location isn't just a luxury now—it's an essential capability for maintaining competitive advantage and operational efficiency.
You all may agree with me that we are deeply influenced by technology and it is our necessity now to manage devices from our fingertips. Thus, we are constantly innovating and learning to incorporate modern technologies into our daily lives to be productive and efficient.
Well this blog aims to explain the various facets of remote IoT device access and management. . Let’s explore how remote IoT monitoring empowers businesses with real-time insights, improved responsiveness, and better resource allocation.
The Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a vast network of connected devices that interact with each other and their environments through the internet. These devices can range from simple sensors to complex industrial tools, all designed to collect, exchange, and process data with minimal human intervention.
Importance of Remote Access
Remote IoT device access is pivotal in IoT technology as it enables users to manage devices from any location. This capability is crucial for maintaining continuous operations, especially in sectors like manufacturing, where remote IoT monitoring is a necessity to ensure production continuity and safety. Remote internet access IoT devices not only aids in operational efficiency but also reduces the need for on-site maintenance, lowers costs and minimizes disruptions.
What is Remote IoT Management?
Remote IoT management refers to the practice of monitoring, operating, and controlling Internet of Things (IoT) devices from a centralized location, without needing direct physical access to the devices. This enables us to control and have a clear visibility over IoT devices, even if they are deployed in different parts of the globe.
The main aspects of remote IoT management includes:
Device Management
It involves remote IoT device connection and management, including provisioning, configuring, and securing devices from vulnerabilities and handling OTA updates that are essential for remotely deploying firmware or software upgrades. It also manages the whole device lifecycle by accessing IoT devices from anywhere.
Monitoring and Diagnostics
It enables real-time observation of device status, performance metrics, and operational health by monitoring data traffic, battery life, and performing remote diagnostics, providing the capability to monitor an IoT device from anywhere.
Data Management
It involves collecting, processing, and managing the data generated by remote IoT devices to derive business insights and make informed decisions.
Security Management
It ensures the security of IoT devices and the data they transmit through remote IoT management of security settings, security protocols, and helps to carry out efficient remote IoT device access.
Components of Remote Monitoring Systems
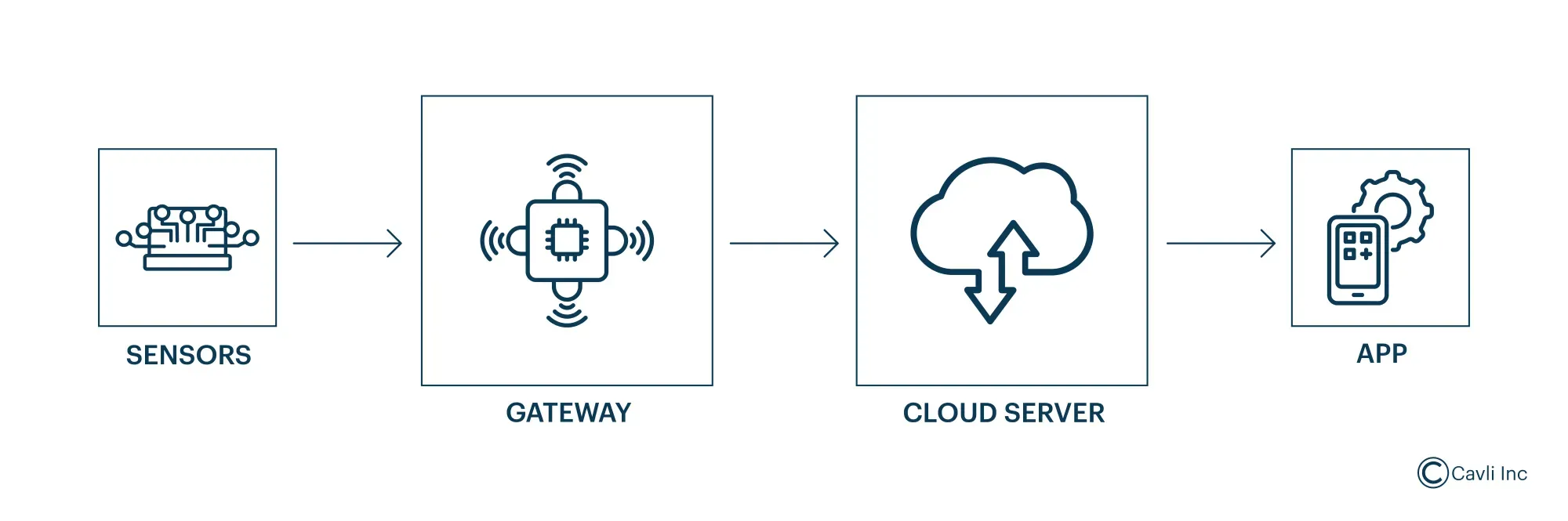
Components of remote IoT monitoring
Sensors
These are the frontline components in IoT, tasked with collecting various data such as temperature, pressure, motion, and more. Their role is crucial in remote IoT device access as they provide the raw data needed for further analytics and action.
Gateways
To manage IoT devices from anywhere, the data collected is transmitted through gateways to a central system for processing. This is typically done through wired/wireless networks, which must be robust and reliable to handle potentially large volumes of data from numerous sources.
Cloud Storage and Analysis
This data is then stored in the cloud. This capability is central to remote IoT monitoring, providing the infrastructure needed to manage remote internet access IoT device data effectively. With advanced analytics and machine learning algorithms, this remote IoT device access data can be converted into meaningful insights for businesses.
Application Interface
An IoT application interface displays the data in a meaningful manner, enabling users to monitor and control connected IoT devices. It helps to visualize data, set alerts, and manage settings through a user-friendly dashboard, ensuring seamless device interaction and remote IoT device access, free of geographical constraints.
Connecting and Managing Remote IoT Devices
Effectively connecting and managing IoT devices from anywhere involves a structured approach to device setup, choosing the right connectivity options, and leveraging management tools in remote IoT monitoring.
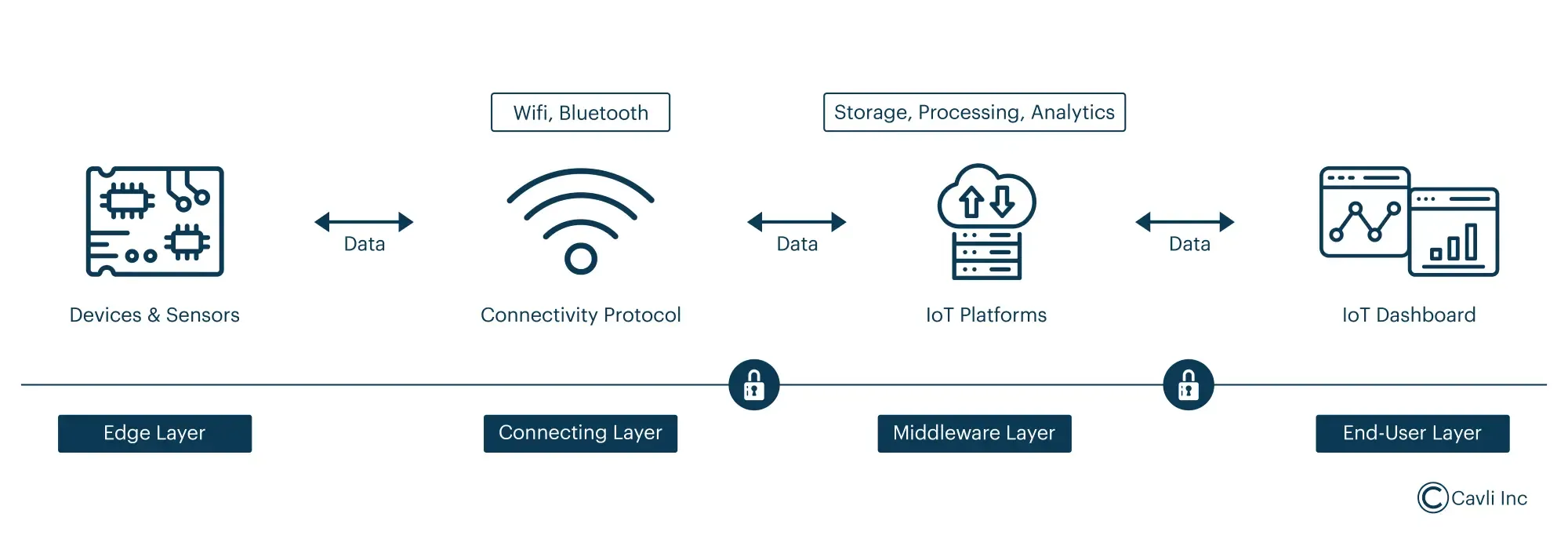
Secure data transmission through different IoT layers
Edge Layer: Device Configuration
The edge layer manages device-specific configurations and local data processing at the remote IoT device access source. Proper configuration at the edge layer is foundational for remote IoT device management.
It begins with defining device parameters that align with operational requirements, such as data sampling rates, communication protocols, and power management settings. Additionally, each device should have a unique identifier to facilitate easy tracking and management within the network, enhancing remote IoT device access.
Connecting Layer: Connectivity Options
The connecting layer ensures seamless communication between IoT devices and the network using appropriate connectivity technologies. Selecting the right connectivity technology is crucial for ensuring reliable remote IoT device connection capabilities. It involves setting up a robust network infrastructure that can support the connectivity requirements of various IoT devices.
The connecting layer forms the backbone of IoT infrastructure by ensuring seamless communication between devices and networks through diverse connectivity technologies. Selecting the right connectivity option is crucial as it directly impacts system reliability, performance, and scalability.
Wired connectivity options provide the most stable and secure foundation for IoT deployments. Industrial Ethernet supports speeds up to 1Gbps and offers deterministic communication essential for factory automation and critical infrastructure. Standard Ethernet (10/100/1000BASE-T) delivers reliable, high-speed connectivity for fixed installations where consistent performance is crucial.
Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) technology excels in short-range applications requiring high throughput, reaching speeds up to 9.6 Gbps with Wi-Fi 6. This makes it perfect for indoor deployments like smart buildings and local sensor networks. However, implementers must carefully consider interference management and robust security protocols to ensure reliable operation.
For wide-area deployments, cellular networks provide extensive coverage through advanced technologies. LTE-M offers speeds up to 1 Mbps and enhanced building penetration, while NB-IoT is specifically designed low-bandwidth IoT applications requiring extended battery life. These cellular options are ideal for mobile assets and geographically dispersed devices requiring reliable connectivity. LPWAN solutions add another dimension to IoT connectivity by offering exceptional long-range communication capabilities, reaching up to 15km in urban areas with minimal power consumption. This makes them perfect for battery-operated sensors and actuators in applications like smart agriculture, urban monitoring, and utility metering.
Middleware Layer: Managing Devices
The middleware layer provides centralized management, data processing, and integration services for managing remote IoT devices from anywhere in the world.
- Middleware software tools such as device management platforms enable the monitoring, updating, and managing of IoT devices from anywhere. They also process data, storage, and its analytics for constructing data-based decisions, enhancing the capability to manage remote IoT devices from anywhere.
- Firmware Updates: Middleware helps keep device firmware up-to-date, which is essential for security and functionality. Remote management tools support automated or scheduled firmware updates, ensuring devices operate efficiently and securely without manual intervention.
- Troubleshooting: Remote diagnostics can identify and resolve issues without physical access to the device. These tools perform tasks such as rebooting devices, logging error reports, and updating settings to rectify common operational problems, which is crucial for maintaining remote IoT device access.
End-User Layer: User Interaction and Control
The end-user layer offers user interfaces and tools for monitoring, controlling, and analyzing IoT device data. It enables users to analyze data collected from IoT devices, generating reports that can help in decision-making and improving operational efficiencies.
This layer is vital for businesses looking to use IoT devices from anywhere, providing the tools needed to manage remote IoT device access effectively.
How to Use IoT Device from Anywhere: Setting Up Remote Access
Security Measures
Security is a major concern when it comes to remote access. Ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted between IoT devices and control centers is crucial.
Implementing strong encryption protocols, using Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and installing firewalls are fundamental steps in securing IoT networks.
Protocols for Device Management and Communication
Effective remote management of IoT devices relies on robust protocols that ensure secure and efficient communication and control. These protocols serve as the backbone for the operations of IoT systems, providing essential functionalities such as device configuration, command execution, and firmware updates. The key protocols include:
- MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): A lightweight messaging protocol designed for limited device resources and low-bandwidth, high-latency networks typical in IoT scenarios. It supports asynchronous communication and is ideal for real-time data exchange between remote IoT devices and the management server.
- CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): A web transfer protocol for use with constrained nodes and networks in the remote IoT management. CoAP is designed to easily translate to HTTP for simplified integration with the web while also meeting specialized requirements such as multicast support, very low overhead, and simplicity.
- LWM2M (Lightweight Machine to Machine): A protocol from the Open Mobile Alliance built for remote IoT device management and service enablement. It defines the communication between remote IoT devices and a central management server, focusing on the transfer of service and management information.
- Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS): It enables secure communication between remote IoT devices and remote IoT device management servers. It is designed to operate over datagram protocols such as UDP (User Datagram Protocol), ensuring privacy and data integrity. This makes it particularly suitable for IoT applications, where resources are constrained, and low latency communication is crucial.
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol): SNMP is used for remote IoT monitoring because of its widespread support across many platforms. It allows administrators to remotely configure devices and monitor their status.
Using these protocols in remote IoT monitoring can efficiently manage and control IoT devices, ensuring timely updates, consistent performance, and quick responsiveness to operational commands.
Security Considerations for Remote IoT Access
As IoT networks grow in complexity and scale, ensuring the security of remote IoT device access becomes paramount. The interconnected nature of remote IoT devices makes them vulnerable to various security threats.
Security risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, and even the hijacking of device control. Each point of interaction—from device sensors to communication networks—presents a potential entry point for security threats.
There are certain preventive measures we take up to fix these vulnerabilities in IoT network.
Authentication
Implementing strong authentication mechanisms is key here. This includes using multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized users can access remote IoT devices.
Implement secure boot processes to ensure remote IoT devices work using only trusted and authenticated firmware and software.
Data Encryption
All data transmitted between remote IoT devices and remote IoT management platforms should implement end-to-end encryption to secure data and prevent interception by unauthorized parties throughout its journey.
Using robust encryption protocols like TLS/SSL for device communications ensures that data remains confidential and integral.
Access Control
Implementing Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to restrict access to the remote IoT devices and IoT device management systems based on user roles, ensuring that only authorized personnel have access to critical functions.
Implement Least Privilege Principle to ensure that users and remote IoT devices have the minimum level of access necessary to perform their functions, reducing the potential impact of a security breach.
According to Statista reports, there will be over 29 billion IoT devices by 2030. As connected IoT devices increase, researchers have also discovered new threats like Ransomware for IoT (R4IoT), targeting weak or poorly maintained IoT devices to get access and install ransomware to disrupt business operations.
Data Integrity
For message integrity checks, use cryptographic hash functions and message authentication codes (MACs) to verify the integrity of messages exchanged between IoT devices and servers, ensuring data has not been altered.
Employ digital signatures to provide non-repudiation and assure the authenticity and integrity of transmitted data.
Regular Audits
Conducting regular security audits and assessments helps identify and address vulnerabilities within the IoT ecosystem.
Maintain detailed audit logs of all access and communication events, providing a traceable history that can be used for forensic analysis and compliance purposes.
Physical Security
Deploy tamper-evident hardware and sensors to detect and respond to physical attempts to compromise remote IoT device management.
Use hardware security modules (HSMs) and trusted platform modules (TPMs) to store cryptographic keys to secure hardware components and perform sensitive operations securely.
Benefits of Remote Management of IoT Devices
Remote IoT device management offers significant benefits that transform operational capabilities across various sectors.
Remote Monitoring and Insights
The statistics from the market research report on “Global Remote Patient Monitoring Statistics 2023” states that in 2020, 23 million patients utilized technologies and services for remote patient monitoring. By 2025, this number is expected to rise to 70.6 million patients in the US, nearly 26.2% of the population.
Similarly, in various industries, IoT devices provide real-time remote monitoring, offering decision-makers insights into operational processes, device health, and other data that can lead to improved business strategies and proactive management.
Security Enhancements
Global Platform, the organization for secure digital services and devices, has introduced a new protocol called “Secure Channel Protocol.” This protocol leverages the lightweight and efficient nature of the CoAP standard, ensuring that IoT device chains adhere to cybersecurity rules, manage updates and patches, and comply with energy-saving regulations.
It features sophisticated security enhancements that protect against unauthorized access and cyber threats. Regular updates and patches can be applied remotely to ensure that security measures are always up to date.
Cost Reduction
The Siemens Survey “The True Cost of Downtime 2022” reveals that Fortune Global 500 industrial organizations lose nearly $1.5 trillion a year due to unplanned downtime.
With predictive maintenance as a proposed solution, the need for on-site visits is minimized, and unplanned downtimes in businesses can be eliminated. This significantly reduces the costs associated with device maintenance and downtime in remote IoT device management.
Scalability
The latest Statista Report “Number of IoT Connections Worldwide 2022-2033” indicates that the number of IoT devices worldwide is forecasted to grow nearly double from 15.9 billion in 2023 to an impressive 32.1 billion by 2030.
Remote management solutions enable organizations to scale their operations quickly. As the number of devices increases, remote IoT management can still be maintained without a corresponding increase in staffing or physical resources.
Common Use Cases
The application of remote IoT access spans multiple industries, showcasing its versatility and impact.
For example, in agriculture, farmers utilize IoT solutions to monitor crop and soil conditions remotely, making informed decisions about irrigation and pesticide use.
In healthcare, remote IoT device management provides continuous patient data to medical professionals, enhancing the quality of care and patient outcomes.
Smart cities integrate IoT devices to streamline everything from traffic management to waste control, improving urban living conditions.
These examples highlight how remote access to IoT devices is revolutionizing traditional practices and driving innovation across various domains.
Advanced Technologies for Remote IoT Management
Artificial Intelligence
AI is revolutionizing remote IoT management by providing smart analytics and decision-making capabilities. Through machine learning algorithms, AI can predict device failures, automate maintenance schedules, and optimize resource allocation.
For example, AI can analyze historical data from sensors to predict when a machine is likely to fail, enabling preemptive maintenance that minimizes downtime and extends the equipment's life.
Edge Computing
Edge Computing refers to data processing that is carried out at or near the source of the data, rather than relying on a central data center. This reduces latency and bandwidth use, enhancing data processing.
By processing data locally, decisions can be made faster, which is crucial for applications requiring real-time analytics, such as autonomous vehicles.
Cloud Services
Cloud services provide scalable and flexible resources for IoT management, offering a range of tools for storing, processing, and analyzing huge volumes of IoT data. They also offer sophisticated tools for managing device firmware updates, security patches, and configuration changes, all from a centralized platform.
Blockchain for IoT Security
Blockchain technology is increasingly being considered for IoT to provide a secure, decentralized platform for IoT networks. It can offer tamper-proof data management, enhance transparency, and facilitate secure, automated transactions between devices without the need for centralized authority.
Integration of AR/VR
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are set to transform remote IoT management by allowing users to interact with IoT systems in a simulated environment. This can be particularly useful for training, maintenance, and management tasks that require a high level of precision and understanding of complex systems.
Cavli Cellular IoT Modules Supporting Remote IoT Management












Closing Notes:
The capabilities of remote management and monitoring of IoT devices are not only transforming industries but are also setting the stage for future technological advancements. The potential for future growth and innovation in remote IoT management is immense. As technologies such as AI, 5G, and edge computing evolve, they will continue to enrich the IoT landscape, making devices smarter and more connected. The challenge and opportunity for businesses lie in staying ahead of these trends, ensuring robust security measures, and continuously seeking ways to integrate these advancements into their operations to streamline and manage remote management of IoT devices.


