James, Jr. Automotive Engineer
Hey James, isn't FTP the oldest protocol still used in the networking domain?
Adam, Sr. Connected Vehicle Engineer
Yes it is. FTP, or File Transfer Protocol, is still vital for transferring large files securely. It’s been around since the 1970s and remains as a strong solution in networking.
James, Jr. Automotive Engineer
Really? How does this affect network security, especially with firewalls?
Adam, Sr. Connected Vehicle Engineer
FTP uses multiple ports, configuring firewalls can be tricky. In active mode, the server tries to establish a connection back to the client, which firewalls might block. Passive mode helps by having the client initiate all connections, but you still need to open a range of ports on the server side, which can be a security concern.
James, Jr. Automotive Engineer
But what about security? I’ve heard FTP isn’t very secure and I'm curious how FTP handles authentication?
Adam, Sr. Connected Vehicle Engineer
That’s a valid concern! Traditional FTP isn’t encrypted. Traditional FTP authentication involves sending your username and password in plain text over the network, which isn't secure. This means anyone intercepting the traffic could potentially steal your credentials. For secure authentication, you'd want to use protocols like SFTP or FTPS that encrypt the login information during data transfer.
This conversation had only scratched the surface, igniting a curiosity about how data transfer protocols operate in today's interconnected world. In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands out as a revolutionary force, connecting countless devices and enabling smarter interactions. But how do these IoT devices securely and efficiently share data across networks?
FTP is the foundational protocol that facilitates massive data transfers—even in the age of cloud computing and advanced IoT ecosystems. In this blog understand the mechanics of FTP, explore its role in modern technology, and discover how it continues to be relevant in securing and optimizing data exchange in our increasingly connected world.
What Is FTP?
FTP, which stands for File Transfer Protocol, is a widely-used network protocol designed to transfer files securely and efficiently between clients and servers over TCP/IP networks such as the Internet or private intranets. Despite newer data transfer technologies emerging, FTP remains an essential protocol for reliable file management and data exchange across various devices and industries. This article explores what FTP is, how the file transfer protocol works, and why it continues to be important for secure and efficient file transfers.
FTP Protocol
In real-world IoT applications, FTP enables seamless data transfers, such as automatically uploading data from industrial IoT sensors to centralized databases for real-time monitoring or software updates on remote devices. FTP’s adaptability across systems makes it indispensable in IoT, enabling smooth interoperability, efficient data handling, and streamlined updates—opening numerous possibilities for IoT-driven innovation in industries from healthcare to logistics.
History and Evolution of FTP Protocol
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) was developed in the early 1970s, long before the modern Internet was established. FTP became a cornerstone protocol, enabling researchers and academics to transfer large datasets and collaborate remotely. Since then, FTP has continuously evolved alongside network technologies, remaining a foundational file transfer method. The original specification for FTP was published as RFC 114 in 1971. Over the decades, FTP has evolved, adapting to the changing landscape of network technologies while retaining its core functionality.
With the advent of the TCP/IP protocol suite in the early 1980s, FTP was updated to operate over TCP (Transmission Control Protocol), enhancing reliability and performance for file transfers.
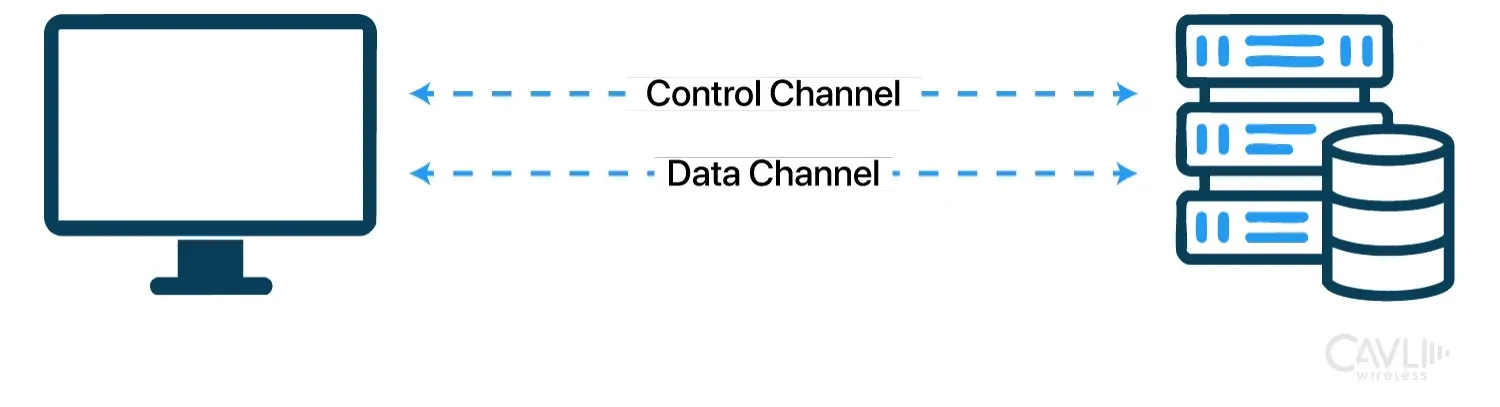
This version of FTP introduced control and data channels, a dual-channel structure that improved transfer efficiency by separating commands from data exchange.
Despite its popularity, traditional FTP faced a major security limitation: it transmitted data, including login credentials, in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception. This led to the development of secure variants of FTP:
- (FTP Secure):
Adds SSL/TLS encryption to FTP, securing data in transit by encrypting both control and data channels. - SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol):
A separate protocol that uses SSH (Secure Shell) for secure file transfers, providing robust encryption and better firewall compatibility than FTPS.
FTP continues to play a vital role in many industries, with a significant portion of IoT deployments relying on FTP or its secure variants for data exchange. The protocol's ability to work with both legacy systems and modern technology ensures its ongoing relevance in diverse environments.
How Does FTP Work?
The File Transfer Protocol (FTP) defines a set of rules and procedures for transferring files over TCP/IP networks. Think of FTP as a digital postal service that enables reliable and organized data exchange between an FTP client (the sender/requester) and an FTP server (the receiver/provider). FTP manages both commands and data transmission, ensuring files are uploaded, downloaded, and managed effectively across networked systems.
- The client acts like the sender, making requests to upload or download files.
- The server acts as the recipient (or sometimes sender), managing and storing files for retrieval.
FTP establishes standard procedures for these transfers, ensuring that both the client and server understand each other’s commands and responses, facilitating efficient file exchanges. Users can upload files from their local machines to a remote server or download files from a server to their devices. FTP protocol is crucial for efficient data management and sharing, particularly in IoT applications where large volumes of data need to be transferred reliably and securely.
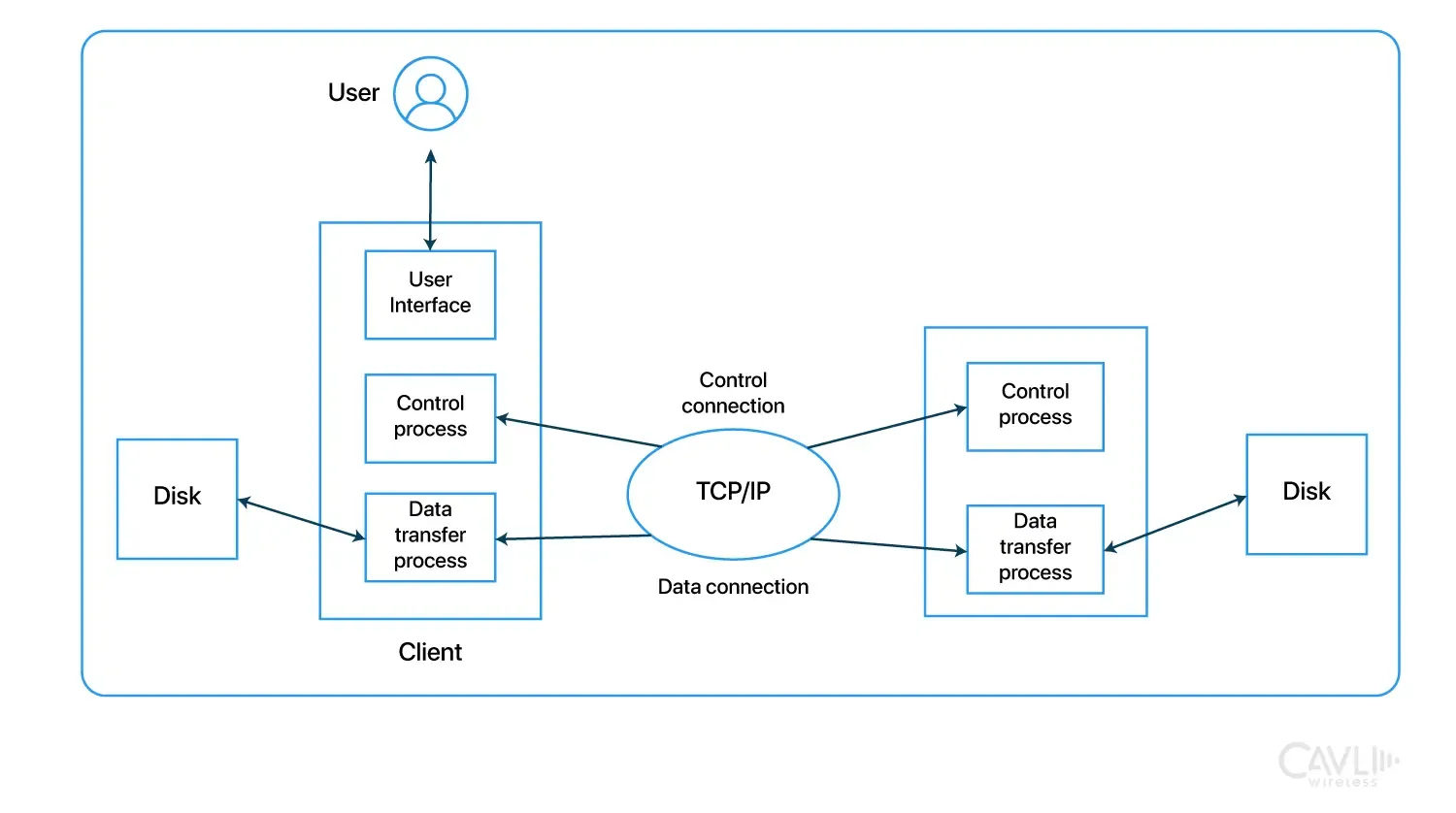
Basic FTP Architecture
The Basics of FTP Architecture
1. Client-Server Model
FTP uses a client-server architecture, where the FTP client initiates a connection to the FTP server to request file services. The server listens for connections on a specific port and responds to clients with the requested data or access to files. The FTP server is a central repository of files and directories, accessible to authorized clients. Each client can use an FTP client software or a command-line interface to interact with the server.
2. Two Connection Channels: Control and Data
Control Connection (Command Channel):
Established on port 21, this channel is used exclusively for exchanging FTP commands and responses between the client and server. Once the connection is open, the client sends commands, and the server responds with status codes and messages. This connection remains open throughout the session.
Data Connection:
This channel is responsible for the actual transfer of files between client and server. The data connection can be on port 20 (in active mode) or a dynamically assigned port (in passive mode). The data connection opens and closes with each file transfer, allowing files to be transmitted independently of the control connection.
3. Operation Modes: Active vs. Passive
Active Mode
In Active mode, the client initiates the control connection to the server on port 21. The server then initiates the data connection back to the client from its data port (typically port 20) to a random port specified by the client.
Because the server initiates the data connection back to the client, this can lead to complications with firewalls and NAT (Network Address Translation). Firewalls typically block incoming connections by default, which means the data connection from the server might be rejected. NAT setups can also interfere, as they dynamically map external IPs and ports to internal ones, making it hard for the server to identify and connect to the correct client port.
Passive Mode
In Passive mode, the client initiates both the control and data connections. After the client establishes the control connection on port 21, the server opens a random port for the data connection and informs the client of this port. The client then connects to the server on this designated port to initiate the data transfer.
Since the client initiates both connections in Passive mode, it generally works better with firewalls and NAT configurations. Passive mode is commonly used for FTP connections over the Internet, where clients are often behind firewalls or NAT.
FTP Troubleshooting and Best Practices
Understanding the differences between active and passive FTP modes is crucial for troubleshooting firewall and NAT-related issues. Passive mode is typically preferred in firewall-restricted environments since the client initiates both control and data connections. Proper firewall configuration should include allowing ports 20, 21, and a range of passive ports. Regularly monitoring FTP server logs helps identify connection failures and unauthorized access attempts, enabling prompt resolution.
Commands and Responses
FTP sessions are controlled by a standardized set of commands and responses that regulate file transfers between client and server. Common FTP commands include:
- USER: Specifies the username to the FTP server for authentication.
- PASS: Provides the password for user verification..
- LIST (LS): Requests a list of files/directories on the server.
- RETR: Initiates the download of a specified file from the server.
- STOR: Uploads a file from the client to the server.
- CWD (Change Working Directory): Changes the current working directory on the server.
These commands form the core of the file transfer protocol, enabling precise and controlled file operations between devices.
A typical FTP session might look something like this:
Client: USER username
Server: 331 Password required for username.
Client: PASS password
Server: 230 User logged in, proceed.
Client: LIST
Server: (Lists files and directories)
Client: RETR file.txt
Server: (Transfers file.txt to the client)
Client: QUIT
Server: 221 Goodbye
Authentication and Access Control
FTP can require a username and password for access to secure areas, though it also supports anonymous access (often for public files). However, FTP transmits credentials in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception on open networks. Secure alternatives like FTPS (FTP Secure) or SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) add encryption to mitigate this risk.
FTP Security: Threats and Compliance
FTP servers remain common targets for cyberattacks, including brute-force attempts and ransomware. Secure FTP variants such as SFTP and FTPS encrypt data and credentials, significantly mitigating these risks. Compliance with regulatory frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS requires encryption and robust access controls, making secure FTP protocols essential for modern data protection.
Benefits of FTP for IoT
Efficient Handling of Large File Transfers
FTP enables reliable, high-volume data transfers, which is particularly beneficial in applications that rely on consistent, high-quality multimedia or sensor data. This ensures that IoT systems handling large file sets can maintain data flow without interruptions.
Consider a smart agriculture setup where numerous sensors across a large field collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and humidity. This data needs to be sent to a central server for analysis to optimize irrigation schedules. Using FTP, the data from each sensor can be reliably uploaded to the server, ensuring timely and accurate analysis. FTP’s robust architecture ensures these transfers are handled smoothly, minimizing the risk of data loss or corruption.
Reliable Data Transfer
FTP’s reliable data transfer capabilities are critical in IoT applications where accurate, uncorrupted data is essential. This ensures that IoT systems can depend on consistent, reliable inputs for analysis and decision-making, thereby supporting high-stakes operations in businesses.
Predictive maintenance is a significant advantage of IoT. Industrial IoT devices collect and send equipment diagnostics and performance logs to central servers for predictive maintenance. FTP’s robust protocol ensures that even large batches of data are transferred without corruption. This reliability is crucial for manufacturers to perform accurate analysis, anticipate failures, and schedule timely maintenance, thus avoiding unexpected downtimes and ensuring operational efficiency.
Interoperability with Legacy Systems
FTP’s compatibility with legacy systems provides a cost-effective bridge between older infrastructure and modern IoT applications, allowing businesses to leverage existing systems while benefiting from the insights and efficiencies of IoT. This interoperability is particularly valuable in sectors with significant legacy investments, like utilities, logistics, and manufacturing.
For instance, shipment information from legacy GPS systems can be transferred to a central server, where it integrates with data from IoT devices on vehicle health or location, allowing comprehensive fleet management.
FTP in Modern Cloud and IoT Ecosystems
FTP remains integral in hybrid cloud and IoT environments, enabling reliable transfer of large datasets and firmware updates between edge devices and central servers. Integration with cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud allows FTP workflows to support automated DevOps pipelines and remote device management, maintaining FTP’s relevance alongside emerging technologies.
Best Practices for Implementing FTP Protocol in IoT
1. Using Secure Variants of FTP: SFTP or FTPS
For IoT applications dealing with sensitive or confidential data, secure variants such as SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) or FTPS (FTP Secure) are essential. These protocols encrypt data during transfer, protecting it from eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Configuring IoT systems to use SFTP or FTPS instead of standard FTP, ensure that all devices, including legacy devices, support these secure variants to maintain consistent data security across the network.
2. Implement Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Ensuring that only authorized devices and users can access FTP servers is critical in IoT, where unauthorized access could lead to data breaches or system compromises.
- Use strong and unique passwords for each IoT device.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Regularly update passwords.
- Avoid sharing credentials across devices or users.
- Implement role-based access control to restrict access based on user roles and responsibilities.
3. Enable Regular Software and Firmware Updates
Unpatched vulnerabilities in FTP servers and clients can expose the entire IoT network to cyber threats. Regular updates help protect against security exploits, improve performance, and maintain compatibility with other protocols.
4. Monitor Access to FTP Servers
Not all IoT devices and users require access to FTP servers. Implementing IP whitelisting to restrict server access to approved devices and networks can keep a check on unauthorized activities. Configure firewalls to allow only necessary connections.
Additionally, monitor FTP server access logs regularly for unusual activity, such as repeated failed login attempts or unexpected file transfers, and implement alerts for quick detection and response to potential security incidents.
5. Implement Logging and Audit Trails
Detailed logging allows for tracking FTP transactions, which is essential for troubleshooting, security audits, and ensuring data integrity.
Enabling detailed logging on FTP servers can capture transaction details, including login attempts, file transfers, and command usage. Store logs securely and review them periodically to identify and respond to unusual patterns, which can indicate potential security threats or operational issues.
6. Ensure Data Integrity with Checksum Verification
In IoT applications, data integrity is essential, especially for critical applications like predictive maintenance or medical monitoring. Using checksums verifies that data arrives intact, free from corruption during transfer.
Implementing checksum mechanisms (such as MD5 or SHA-256) to verify file integrity after transfer. Checksum verification is a method used to ensure data integrity during storage or transmission. It involves generating a unique, fixed-length string of characters from a data file or message using a mathematical algorithm.
7. Establish Robust Backup and Recovery Procedures
IoT systems may experience hardware failures, network interruptions, or accidental data loss, which can disrupt data transfers or impact critical IoT applications. Establishing a data backup system that frequently backs up files transferred via FTP.
Ensure that backup processes include both data and configuration files for FTP servers, allowing for rapid recovery in case of unexpected failures or data loss.
Comparison Between Protocols: FTP vs HTTPS vs MQTT vs CoAP
| Protocol | Common Use in IoT | Security | Transport Layer | Data Transfer Method | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTP | File transfers, large data | Low; plain text (unless FTPS) | TCP | Direct file transfer | Simple, widely supported | Unencrypted, unsuitable for sensitive data |
| SFTP | Secure file transfers, logging | High; SSH encryption | TCP | Encrypted transfer | Secure file transfer, ideal for sensitive data | More resource-intensive than FTP |
| FTPS | Secure FTP file transfers | High; SSL/TLS encryption | TCP | Encrypted transfer | Encrypts traditional FTP, good for compliance | Complex setup |
| HTTP/HTTPS | Web access, APIs, data streams | High (HTTPS with TLS) | TCP | Request-response | Universally supported, encryption for HTTPS | Overhead may affect performance |
| MQTT | Lightweight messaging for sensors | Medium (TLS optional) | TCP | Publish-subscribe | Lightweight, low power, good for constrained devices | Limited security without TLS |
| CoAP | Constrained data transfer | Medium (DTLS optional) | UDP | Request-response | Lightweight, efficient for low-power devices | Limited functionality without DTLS |
Closing Notes
FTP has proven to be a foundational technology, crucial for the reliable and secure transfer of large files, especially in the context of IoT. Its robust architecture, combined with secure versions like SFTP and FTPS, ensures that it meets the stringent demands of modern data transfer needs. While newer technologies and cloud services offer convenience, FTP's ability to handle massive datasets with fine-grained control remains unmatched.
As the IoT landscape continues to evolve, embracing advancements in FTP, such as integration with cloud platforms and enhanced security protocols, will ensure its continued relevance and utility. Understanding and leveraging FTP empowers IoT applications to function efficiently, securely, and effectively in our interconnected world. FTP will continue to coexist with newer technologies, each serving specific needs in data transfer.
Amusing Tech Chronicles
Facts and Anecdotes Related to this Edition of Wireless By Design
The Warehouse Dispatch System
Just like a warehouse shipping out products to various retail locations, FTP enables users to pack (or batch) files and transfer them in one go, much like a warehouse dispatch system. This approach is particularly useful in industries where large volumes of files, such as daily log reports or multimedia content, need to be transferred at once, ensuring all data is received intact and ready for processing. FTP is one of the oldest internet protocols still in use today!
The Logistics Hub
In a logistics hub, packages are sorted and routed according to their destinations. The facility has separate lanes and areas for different delivery regions. Likewise in FTP, the server reaches out to the client, and sends data packages to different network environments, just as logistics hubs adapt to manage efficient delivery across a geographical area.
The Pizza Delivery of File Transfers
When you order pizza, you specify what you want, and the restaurant prepares it and delivers it to you. Similarly, in FTP, the client requests files, and the server prepares and "delivers" the data back to the client. FTP allows you to "order" data from a server and get it delivered to your computer. This simple analogy helps many understand the client-server model of FTP.
Go Beyond and Explore
What does FTP stand for?
What are the disadvantages of FTP Protocol?
- Lack of Encryption: FTP’s biggest disadvantage is its lack of encryption. Data, including usernames and passwords, is sent in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception. This poses a significant security risk, particularly for transferring sensitive information.
- Incompatibility with Secure Networks: FTP’s reliance on plaintext data transfer means it’s unsuitable for networks requiring high security standards. Its lack of security protocols makes it a poor choice for modern secure applications, especially over public or shared networks.
- Complex Firewall and NAT Configuration: FTP uses two channels (control and data), making it harder to configure with firewalls and NAT. This can lead to connectivity issues and requires extra setup steps, particularly in environments where security protocols tightly control network traffic.
- Availability of Secure Alternatives: With the development of secure alternatives like SFTP and FTPS, there’s little reason to use FTP when more secure options exist. These alternatives provide encryption and stronger authentication, addressing FTP’s primary shortcomings.
What is the difference between FTP and HTTP/HTTPS?
- FTP: FTP is designed specifically for transferring files between a client and server, typically for uploading or downloading files.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Designed to deliver web pages and content (like HTML, images, videos) over the internet. HTTPS is an encrypted version of HTTP, commonly used to secure online transactions and protect user data on websites.
- Connections: FTP uses two separate connections—one for control (commands) and another for data transfer. This dual-channel setup, often using ports 21 (control) and 20 (data), can make FTP harder to configure with firewalls. HTTP/HTTPS uses a single connection (usually on port 80 for HTTP and port 443 for HTTPS) to request and transfer web content.
Can FTP be integrated with modern cloud services for enhanced functionality?
Hybrid solutions allow businesses to leverage FTP for large, bulk transfers while taking advantage of the cloud for storage, sharing, and real-time collaboration, combining the strengths of both technologies.






