What Is Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT)?
Narrowband Internet of Things, generally referred to as NB-IoT, is a cellular technology focused on connecting everyday objects to the Internet, allowing the transfer of small amounts of data over more extended periods. This NB-IoT technology , developed by 3GPP, is a key component of the Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) radio technology standard. The development of NB-IoT technology addressed the lack of a standard that addresses a wide range of cellular devices and services. Narrowband IoT explained that at the time when the specification was frozen in 3GPP Release 13, NB-IoT technology was mainly focused on indoor coverage, low cost, long battery life, and high connection density. However, Narrowband IoT has also proved to be a sublime choice concerning other specifications as well.
NB-IoT was defined to adhere to the features of LTE. This has allowed NB-IoT technology to integrate into already prevalent LTE networks, demonstrating the versatility and applicability of NB-IoT in various IoT scenarios.
NB-IoT operates using a narrow bandwidth of 180 kHz, which enables efficient use of licensed spectrum and allows for better penetration in challenging environments such as deep indoors and underground locations. The technology can be deployed in three main modes:
- Standalone mode: Using dedicated spectrum such as refarmed GSM bands.
- Guard band mode: Utilizing unused resource blocks within LTE carriers.
- In-band mode: Operating within LTE carrier bandwidth without additional hardware changes.
These deployment options make NB-IoT flexible for mobile network operators and accelerate its global adoption.
Why Choose Narrowband IoT? Benefits & Advantages Explained
Generally, in the absence of proper coverage, it is a weary task “connecting” things, given considerations like the absolute necessity of high power to enable speedy transfer, which in turn is always a constant drain on the battery. Cellular IoT is traditionally designed for the transfer of high quantities of data and is considered ideal for sensor-based low-bandwidth-data projects. As a result, they are not precisely considered ideal for the transfer of small amounts of infrequent data.
NB-IoT, as the future driver of IoT, addresses all these inadequacies. This NB-IoT cellular technology is particularly focused on the interaction between devices that require the transfer of data in minimal quantities but over more extended periods. This NB-IoT data-driven technology can connect any stationary device to the Internet of Things, making it the ideal technology for static sensor applications. NB-IoT can co-exist with networks such as 2G, 3G, and 4G, and benefit from the security and privacy features of mobile networks. This is also why NB-IoT is considered a better alternative to license-free LPWAN technologies like SigFox and LoRa.
Technology Of The Future
As mentioned before, NB-IoT technology is designed to meet everything that traditional cellular technology has fallen short of, and that is precisely why it is recognized as a technology of the future. 3GPP has identified NB-IoT to be a less expensive option than LTE-M, with the added benefits of extensive range, longevity, and ability to support a large number of devices over just 200 kHz of the spectrum. This means that it is rapidly getting popular among a wide variety of devices, ranging from storage units and wind turbines to smoke detectors and smart parking systems. NB-IoT provides deeper building penetration than LTE-M, which is achieved by low bitrates. It also offers better link budgets for NB-IoT.
NB-IoT operates in the licensed spectrum and is considered highly secure. It bought in the much-needed economies of scale to the Internet of Things. The efficiency and cost-effectiveness associated with NB-IoT will drive the future popularity of this cellular technology.
Key advantages of NB-IoT include:
- Extensive coverage with up to 20 dB improved link budget for deep indoor penetration.
- Ultra-low power consumption enabling battery life of up to 10 years.
- Support for massive numbers of connected devices per cell (up to 50,000).
- Secure and reliable communication on licensed cellular spectrum.
- Cost-effective device modules due to simplified design.
- Seamless coexistence and integration with existing cellular networks.
These features position NB-IoT as a preferred choice for large-scale IoT deployments.
Key Benefits of Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Technology
NB-IoT technology offers numerous benefits that make it ideal for connecting a wide variety of IoT devices, especially where low power, extended coverage, and cost efficiency are critical. The key benefits include:
Higher Data Rates and Lower Power Consumption in NB-IoT
Narrowband IoT, or NB-IoT, operates on a 200KHz bandwidth, offering impressive data transmission speeds of up to 250kbps. This feature is particularly advantageous in IoT applications where small data packets are transmitted intermittently over short distances. NB-IoT's deliberate focus on lower data rates directly contributes to its exceptional energy efficiency and sustainability within IoT solutions.
Advanced Power Optimization Techniques
NB-IoT employs two critical power-saving techniques: Power Saving Mode (PSM) and Extended Discontinuous Reception (eDRX). These innovative features play a crucial role in enhancing the energy efficiency of IoT devices. They significantly extend battery life and reduce maintenance costs, making NB-IoT an excellent choice for large-scale IoT deployments.
Adherence to Open Standards for Seamless Integration
By strictly adhering to global open standards, NB-IoT ensures interoperability and compatibility across a wide array of devices and networks. This compliance promotes the seamless integration of IoT solutions, facilitating the widespread adoption of NB-IoT technology within the Internet of Things ecosystem.
Utilization of Licensed Spectrum for Secure Connectivity
Operating on a licensed spectrum guarantees that NB-IoT networks remain secure, reliable, and free from interference. This is a pivotal factor for critical IoT applications that demand consistent and trustworthy connectivity.
Integration with Existing Cellular Networks for Cost Efficiency
NB-IoT leverages the existing cellular network infrastructure, providing a strategic advantage that allows for rapid and cost-effective deployment of IoT solutions. This eliminates the need for additional network investments, reducing both time and resources.
Coexistence with Multiple Cellular Technologies for Versatility
NB-IoT is meticulously designed to coexist harmoniously with a variety of existing cellular technologies. This versatility makes NB-IoT an excellent and flexible option for a wide range of IoT applications.
Superior Indoor Penetration for Urban and Indoor Settings
Thanks to its exceptional penetration capabilities, NB-IoT is highly effective in urban environments and indoor settings. It excels at transmitting signals through thick walls or reaching underground locations, ensuring reliable IoT connectivity.
Cost-Effective Components for Economical Solutions
The utilization of budget-friendly components in NB-IoT devices positions this technology as an economically viable choice for a diverse range of IoT applications. This cost-effectiveness lowers barriers to entry for businesses and consumers alike.
Enhanced Security and Reliability for Sensitive IoT Applications
NB-IoT offers robust security protocols and consistently reliable connectivity, making it an ideal choice for IoT applications that handle sensitive data or require uninterrupted online presence.
Prolonged Battery Life and Reduced Energy Usage
NB-IoT's dedication to minimizing energy consumption translates to significantly extended battery life for IoT devices. This reduces the need for frequent battery replacements, contributing to sustainable IoT practices and cost savings.
Extensive Coverage Range for Wide Geographical Reach
NB-IoT's impressive ability to cover vast areas, including remote and rural locations, makes it the ideal technology for IoT applications that require expansive geographical coverage. It opens up opportunities for innovative solutions in diverse geographical settings.
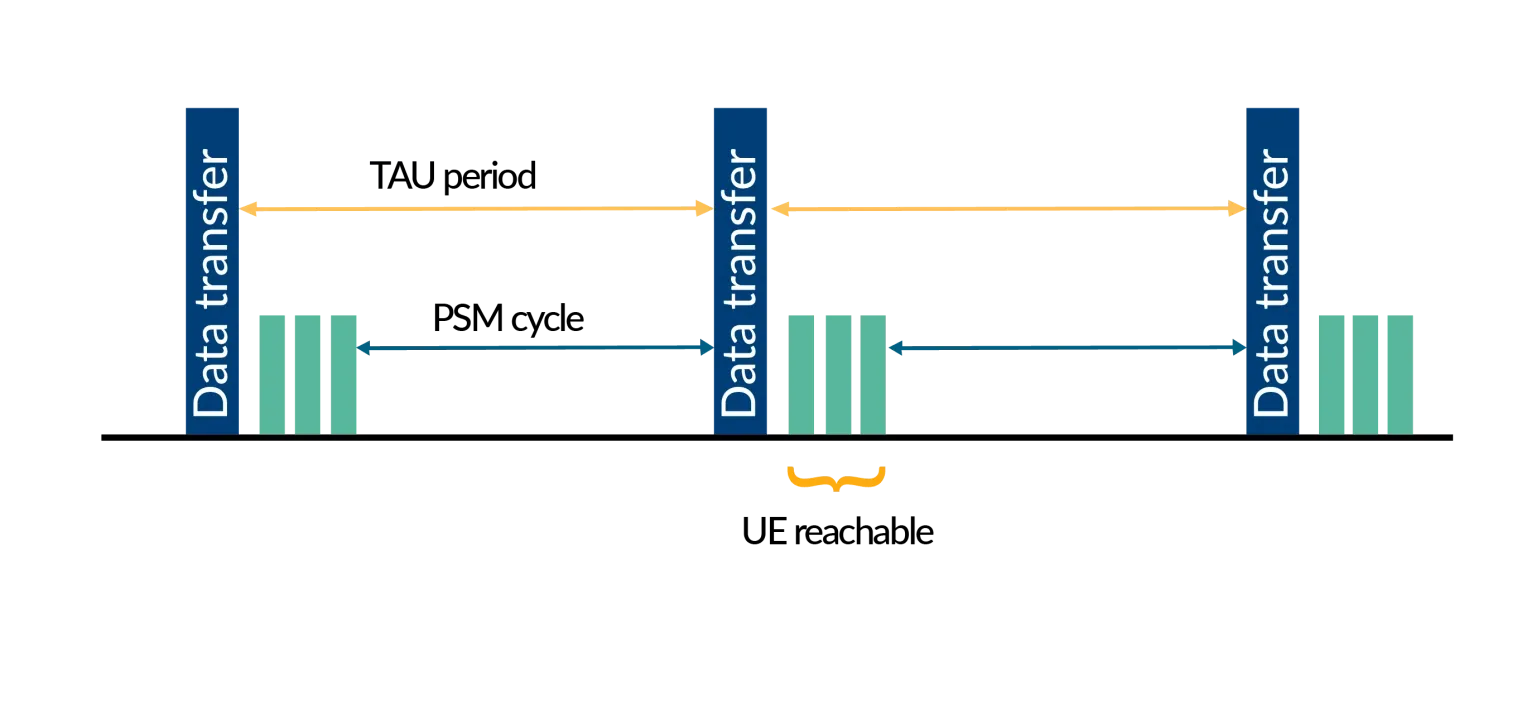
NB-IoT Power Saving Techniques: PSM and eDRX Explained
PSM (Power Save Mode)
Power Save Mode feature enables a cellular modem to turn off the radio communication and puts the device to sleep. PSM has the following key points:
- PSM mode is similar to off mode, but the UE remains registered with the network.
- There is no need to reattach itself to the network after it wakes up, which allows prolonged battery life.
- T3324 and T3412 are the two preferred timings when a device initiates PSM with the network
- A device can stay in the PSM cycle for a max of 12 hours on the T-Mobile NB network. A device is unreachable during this period.
- After MO access and data transfer has been completed, devices that are in PSM mode would start an active timer.
eDRX (Extended Discontinuous Reception)
Extended Discontinuous Reception, also termed as eDRX, benefits IoT devices to reduce power consumption. They can be used without PSM or in conjunction with PSM to obtain additional power savings. eDRX has the following key points:
- eDRX works by extending DRX cycles in order to allow devices to remain longer in power-saving states between “Paging Occasions.” This will consecutively minimize its energy consumption.
- The device keeps its receiver side switched off for a certain period of time, during which it does not capture pages or downlinks from control channels.
- When the UE (device) is active, the receiver will begin to listen to the physical control channel.
- The device sets itself available at certain intervals for MT services.
- Does not require to initially perform RAU or TAU to trigger a limited period of reachability.
- For a given triggering interval, eDRX performs better than PSM mode when shorter reachability is needed. PSM performs better than eDRX when the reachability requirement is in the same range as the trigger interval.

NB-IoT Operating Modes: Standalone, Guard Band & In-Band
1. Stand-alone
The stand-alone mode utilizes a standalone carrier, e.g., spectrum currently used by GSM EDGE Radio Access Network (GERAN) systems as a replacement for one or more GSM carriers. It is employed for instances where cellular services are not present or are decommissioned to make a narrowband spectrum available, as in the case of cellular GSM. Restructuring one or more GSM carriers to enable NB-IoT traffic ensures a smooth transition to LTE for massive machine type communication with NB-IoT.
2. Guard Band
This mode utilizes unused resource blocks within an LTE carrier’s guard-band. It is employed in cases where cellular services are available, and NB-IoT is present in the guard band of LTE. Utilizing NB-IoT in the guard band allows for efficient use of available spectrum.
3. In-band
This mode utilizes resource blocks within a normal LTE carrier. It is employed in cases where cellular services are available, and NB-IoT is present in the guard band of LTE. This mode of operation is cost-effective and seamless for mobile operators as it does not require any hardware changes and efficiently uses spectrum resources for LTE or NB-IoT services based on demand from mobile users or devices. NB-IoT's in-band mode ensures optimal use of spectrum for both LTE and NB-IoT services.
Why NB-IoT Is Poised to Dominate LPWAN Networks in 2025
NB-IoT has an impressive battery life of 10 years, made possible using power optimization techniques such as eDRX and PSM. But impressive battery life will be of no use if the technology decides to give in before the so proclaimed ten years. So developing a technology that delivers uninterrupted connectivity, seamlessly and efficiently on the same battery for a full decade, is a major challenge associated with NB-IoT.
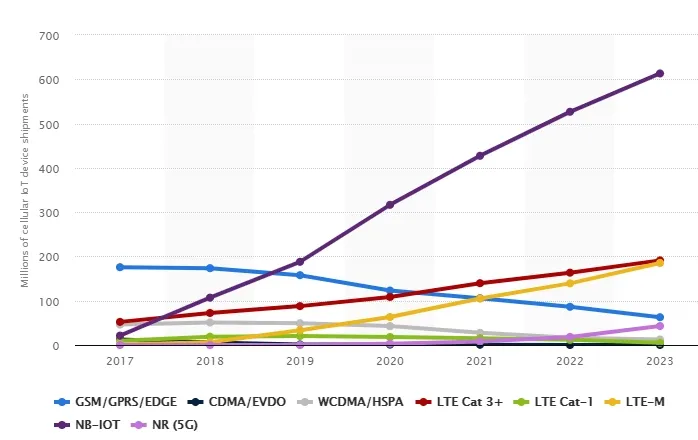
NB-IoT is rapidly getting popular with telecom operators, equipment manufacturers, and industry pioneers. According to the latest GSMA report in 2023, over 200 operators across more than 90 countries have launched NB-IoT networks, reflecting rapid global adoption. NB-IoT deployments are strongest in Europe, Asia Pacific, and North America, with increasing rollout in Latin America and the Middle East. Furthermore, NB-IoT is evolving alongside 5G technology, with 3GPP Release 16 introducing features for NB-IoT integration within 5G networks, ensuring its relevance and performance in the future of IoT connectivity.
NB-IoT and 5G: How Narrowband IoT Fits into the 5G Ecosystem
Is NB-IoT 5G? NB-IoT and LTE-M, originally developed for the 4G LTE standard, have evolved to become integral components of the 5G framework, including their integration into 5G IoT modules. 3GPP, the organization responsible for major mobile telecommunications standards, including 5G NR and earlier technologies like NB-IoT and LTE-M, has officially incorporated NB-IoT and LTE-M into the 5G standard. This inclusion marks a significant advancement in 5G technology, particularly for Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) applications. Contrary to the earlier perception of NB-IoT as a technology exclusive to 4G, it is now recognized as a critical element of the 5G system, aligning with the capabilities of 5G NR. As a part of the 5G IoT module ecosystem, NB-IoT is expected to become a prominent solution, connecting a wide range of low-power IoT devices. The 3GPP Standards have acknowledged the role of NB-IoT in 5G and are exploring methods to integrate NB-IoT devices with the 5G core network, facilitated by 5G NR technology. This progress allows mobile operators to align their LPWAN strategies with the advancements in 5G, including the deployment of 5G IoT modules. The acknowledgment of NB-IoT under the 3GPP and its compatibility with 5G NR underscore its significance in the ongoing evolution of 5G technology. In particular, 3GPP Release 16 is anticipated to detail the in-band deployment of NB-IoT alongside 5G NR within the 5G spectrum, meeting the IMT-2020 5G requirements.
How Secure Is Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT)? Security Features Explained
NB-IoT uses secure dedicated communication channels, the use which ensures confidentiality and data integrity. The encryption of data further adds to the security of this technology. NB-IoT follows the UDP protocol, which caters to the security concerns in communication. Furthermore, the mobile operators can manage secure connections by the use of a secure Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection to the operators’ platform, creating a path from the device to the customers’ cloud server.
Key security features of NB-IoT include:
- SIM-based authentication ensuring device legitimacy.
- LTE-grade encryption protecting data confidentiality.
- Secure VPN tunnels between devices and cloud servers.
- Robust network access control preventing unauthorized access.
- Integrity protection ensuring data is not tampered during transmission.
NB-IoT Performance Specifications and Network Coverage
| Spectrum | Licensed |
|---|---|
| Bandwidth | 200 kHz |
| Deployment | In-band & Guard band LTE, standalone |
| Peak rate (DL/UL) | DL ~250 kbpsUL ~250 for multitone, ~20kbps for single tone |
| Power saving | eDRX, PSM-Power Saving Mode |
| Expected battery life | 10 years |
| Coverage | Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, Latin America and ME |
NB-IoT vs LTE-M: Comparing the Leading LPWAN Technologies
| NB-IoT | LTE-M |
|---|---|
| Peak data rate < 100 kbps | Peak data rate- 384 kbps |
| Latency 1.5 – 10 seconds | Latency 50 – 100 ms |
| Particularly focused on low data rates. | Particularly focused on maintaining a high bandwidth. |
| Ideal for static sensor application cases. | Ideal for mobile application uses. |
| No voice support. | Supports voice in areas of standard coverage. |
| Cost per module 5-10 dollars | 10-15 dollars |
In summary, NB-IoT is best suited for static devices that require deep coverage and low data rates with long battery life, such as smart meters and environmental sensors. LTE-M, on the other hand, supports higher data rates, lower latency, and mobility, making it suitable for applications like wearables and asset tracking with moderate movement.
GSM vs Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT): Key Differences Explained
In the context of cellular network technology, specifically comparing Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM) with Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoT), there is a notable difference in uplink transmission power and spectral efficiency. NB-IoT, a key player in the IoT connectivity landscape, exhibits a maximum transmit power for its uplink terminal that is 10dB lower than GSM, a traditional cellular communication standard. Despite this lower transmit power, NB-IoT's smaller minimum scheduling bandwidths, either 3.75K or 15K, result in its uplink power spectral density being higher by 0.8 to 6.9dB compared to GSM. This aspect highlights the efficiency and specialized design of NB-IoT for IoT applications, offering enhanced performance in terms of spectral usage compared to the conventional GSM network.
What is the NB-IoT standard?
NB-IoT, or Narrowband Internet of Things, is a specialized wireless telecommunications standard crafted by 3GPP, the globally recognized authority in mobile telecommunications standards, encompassing both 4G, like LTE, and 5G technologies, such as 5G NR.
Operating within the same sub-6 GHz frequency band utilized by 4G LTE, NB-IoT distinguishes itself by being tailored specifically for IoT applications, unlike its 4G LTE counterpart and earlier wireless technologies. This focus on IoT is shared with LTE-M, another standard developed for IoT purposes. NB-IoT's design prioritizes aspects crucial for IoT connectivity, such as efficient power usage, extended coverage, and the ability to support a large number of low-bandwidth devices, making it an ideal solution for various IoT scenarios. This unique approach positions NB-IoT as a pivotal element in the expanding landscape of IoT networks, contributing to the growth of IoT ecosystems globally.
NB-IoT for Fixed Devices: Use Cases and Limitations
NB-IoT does not fully support mobility (LTE-M also supports voice) as opposed to LTE-M since the 3GPP Release 13 (Release 14 has some improvements as in many characteristics of NB-IoT).
NB-IoT is mainly used in applications and use cases with fixed (stationary) assets and devices but doesn’t always mean that they can’t be used for devices that aren’t stationary. There are certain applications such as real-live NB-IoT applications with trackers, shared bicycle applications, environmental applications with moving components, smart logistics, etc.
With NB-IoT, the device needs to reselect cells as it travels; but with LTE-M, that isn’t the case. So, it’s far less suited for mobile (and the reselection of cells has an impact on battery life as it consumes power). In general, fixed assets such as those smart meters or point of sales terminals, to add another, are the typical area of NB-IoT but not the sole – and for ‘real seamless mobility’ it’s LTE-M.
Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) Applications & Industry Use Cases
- This low power wide area cellular technology works from anywhere, some location right in the heart of the city where the network connectivity is as reliable as it gets, to deep underground tunnels where it is much harder to penetrate. NB-IoT’s unique combination of wide coverage, low power consumption, and low cost makes it suitable for a diverse set of IoT applications across industries. Here are some of the most common and impactful use cases:
Smart Metering
NB-IoT can be utilized in the employment of advanced metering infrastructure, which enables two-way communication between the meter and the user, without the involvement of the physical presence of a monitor. NB-IoT can facilitate direct controlling and monitoring of devices from any specific location as per the convenience of the owner of the equipment.
Smart Cities
The scope of NB-IoT is unlimited when the application involves smart cities. From Automatic Street Lighting to Smart Waste Management to Smart Parking, the opportunities opened up to employ NB-IoT are innumerous. Other applications include connected emergency services, weather monitoring, and traffic monitoring.
Smart Homes And Commercial Properties
NB-IoT can be connected to sensors that are designed to alert the users whenever there are disruptions in the optimally set parameters, like access control & identity management, room temperature, smoke detectors, lighting controls, oxygen levels in confined rooms, intruder alerts, and fire alarms.
Healthcare/E-health
NB-IoT technology can materialize the idea of connected personal appliances that measure health parameters. These appliances, mostly in the form of wearables, are proving to be a great boon for the elderly, who require constant monitoring of their health parameters. NB-IoT is the most reliable and feasible option when parameters such as Blood Pressure and Heart rate are to be measured and analyzed at regular intervals.
Industries
NB-IoT as an underlying technology is used in industrial appliances ranging from precision farming tools in the agriculture sector to smart shelves in the connected retail sector. NB-IoT enables automation in manufacturing and real-time monitoring of equipment. This technology’s advanced performance can enable factories and warehouses to achieve efficient integration of processes and equipment through real-time decision making and enhanced efficiency.
Energy And Utilities
With NB-IoT technology, you can easily rein in the overconsumption of power and water resources, thereby cutting short any wastage involved. This technology proves exceptionally useful when the apparatuses are set up in underground tunnels, cellars, and excavated locations. NB-IoT has the ability to decipher meter readings easily, giving away any obscure information related to wastage or obstruction of flow.
Agricultural Industry
In Agricultural Industry, NB-IoT can help you constantly monitor the growth status of your crops and livestock health through data-driven decision-making. NB-IoT enabled smart soil sensors, and analytics can help automate farm processes like irrigation and manuring through precision farming, by providing regular updates about the set conditions.
Retail Industry
From Supply Chain management to logistics, NB-IoT has brought in the optimization of multiple aspects of the retail sector. NB-IoT can facilitate easy tracking of assets of the organization, provided the tracking is of non-continuous nature. This technology is considered ideal in cases when the tracking involved is long-range and low power consuming.
- NB-IoT has grown to be a key technology enabler that supports wireless connectivity in a licensed spectrum to devices (static or mobile). IoT devices will transform wireless network capacity and leverage the demand for coverage as their range of applications emerge from static sensors to mobile sensors with latency constraints. Furthermore, Strategy Analytics estimates that over 3 billion connected devices will be deployed in 2020. The necessity of The ability to evolve the radio access network and implement NB-IoT services is critical for mobile operators and consumers who employ IoT.





