What Is Supply Chain Management (SCM)?
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is the strategic oversight of material, information, and financial flows from procurement of raw materials to delivery of products to consumers, aimed at enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction. It incorporates process optimization, cost reduction, and agility in responding to market demands. SCM leverages advanced technologies for data analytics, automation, and real-time communication, focusing on sustainability and ethical practices across the supply chain. Key aspects include logistics management, inventory optimization, demand forecasting, supplier relationship management, production planning, transportation management, supply chain analytics, digital supply chain solutions, and compliance with environmental and social governance standards. These components are crucial for achieving operational excellence and sustainable growth in a competitive landscape.
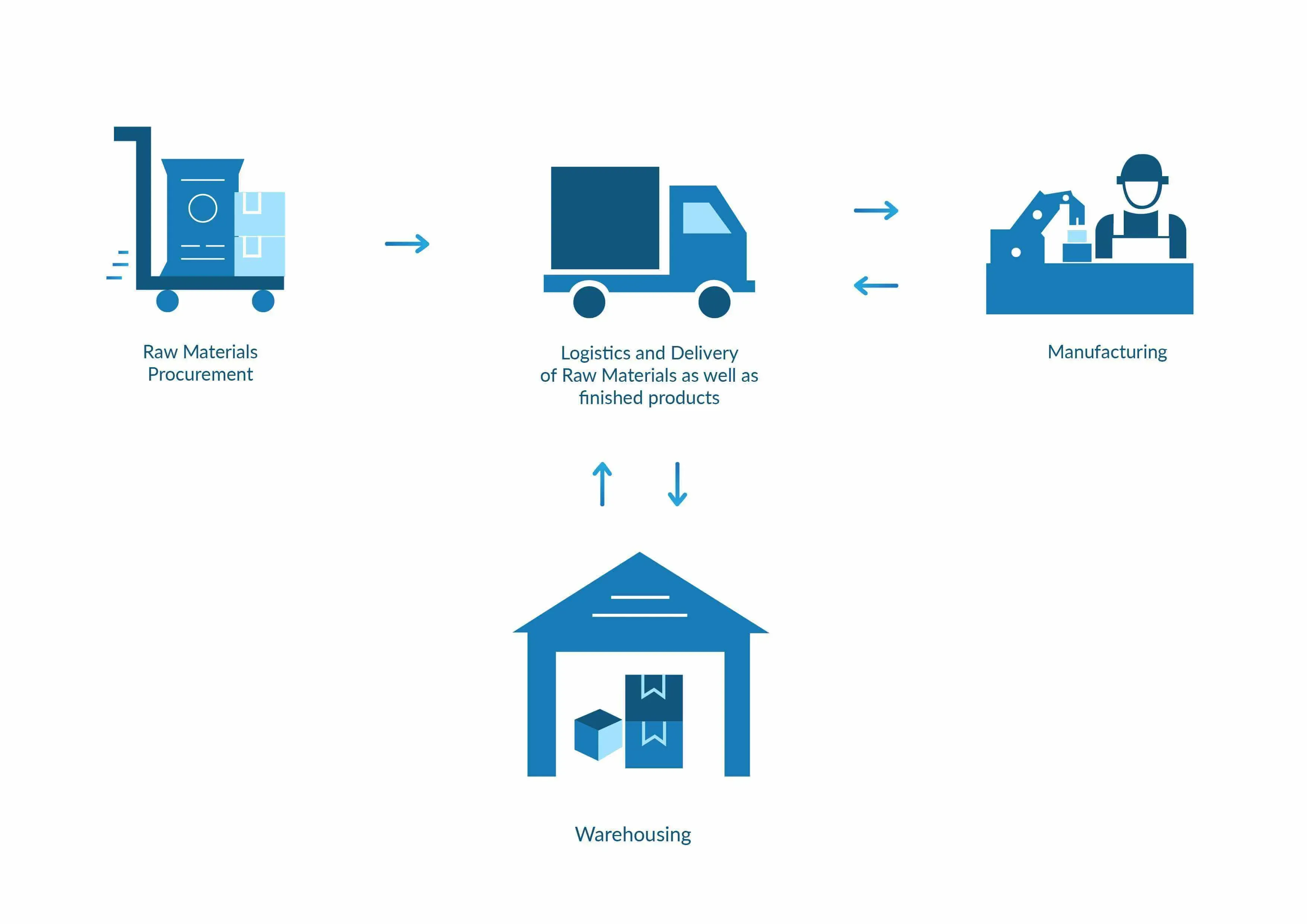
How does supply chain management work?
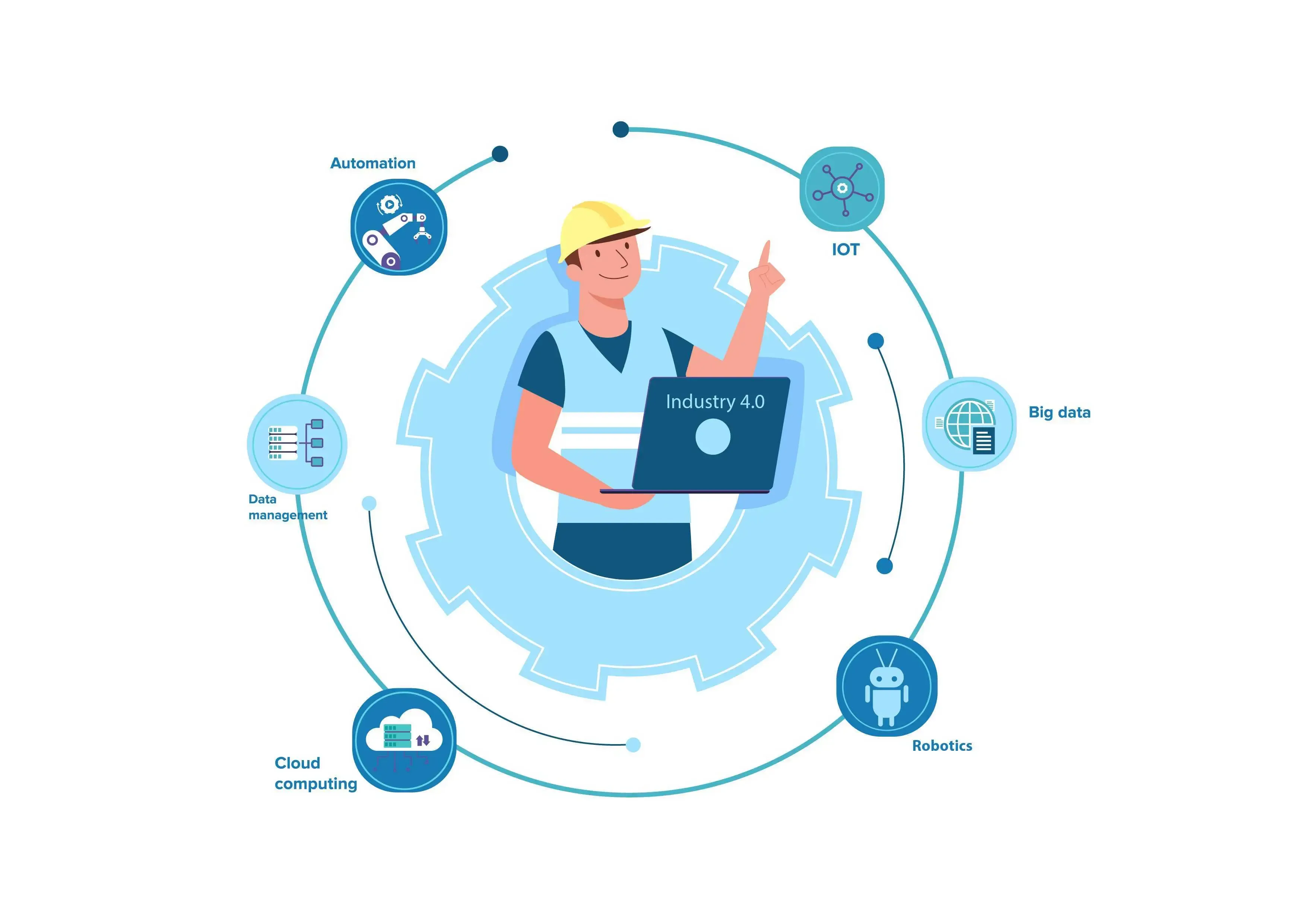
What is Industry 4.0 and its significance?
Industry 4.0, often referred to as the fourth industrial revolution, is a transformative phase in the industrial and manufacturing sectors characterized by the integration of digital technologies with physical production processes. Its significance lies in its potential to dramatically increase operational efficiency, productivity, and flexibility in manufacturing. By harnessing the power of advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and robotics, Industry 4.0 enables a smarter, more interconnected manufacturing environment. This integration facilitates the real-time collection and analysis of data across machines and systems, leading to more informed decision-making and optimized production processes.
The revolution employs smart automation, data analytics, and robotics, starting with cyber-physical systems and digital twins for real-time system monitoring. The central role of IoT technologies creates networks of connected devices that enhance manufacturing with real-time data for better decision-making and quality control. IoT modules introduce precision to these operations, supporting advanced applications. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are pivotal, offering predictive analytics to foresee and address maintenance and efficiency issues, significantly boosting throughput. Industry 4.0 also integrates blockchain for supply chain transparency, cybersecurity to protect digital systems, and 5G technology for superior connectivity, driving manufacturing towards more efficient, sustainable, and customer-oriented outcomes.
Additionally, Industry 4.0 impacts the entire value chain, fostering a cooperative ecosystem for quicker adaptation to market shifts and customer demands. It encourages innovation and product customization, leveraging interconnected technologies to enhance both production efficiency and customer satisfaction. This strategic advantage positions businesses for improved global competitiveness.
What has slowed down innovations in the Supply Chain Management sector?
Geopolitical considerations
Innovations in Supply Chain management cannot be fully leveraged if the implementations are not cross-border. Industrialized countries like China or the US will have robust supply chain networks, spreading across the country. Facilities like railways, roadways, trucks, ports, will be available alongside a skilled workforce. This may not be true for other countries especially in Africa or developing nations in Asia. Even legal complexities and ease of doing business affect how innovations in Supply chain management are implemented.
For instance, for an original product manufacturer in a developing country, the promoters need to first sort fundamental problems in labour safety and logistics before they can consider optimization techniques like an ERP or Robotic Process Automation.
An instance of Geo-political considerations coming into play is when landlocked countries with potential for indigenous goods production have no coastline and hence no seaports of their own. Thus they are dependent on their neighbouring countries for access to sea routes.
Trade Wars between countries with huge Import-Export volumes also affect the smaller developing nations by forcing them to comply with Tariffs or Embargo which hurt their business interests. This leaves these countries with less room to explore the latest innovations to improve their supply chain sector as their primary focus is to ensure they secure effective trade routes which are commercially viable to their customers.
In 2003 the UN in collaboration with the World Bank had unveiled the Almaty Programme of Action which is a project aimed at helping landlocked nations improve their infrastructure and empower the supply chain. In July 2021, over 50 countries and 30 organizations came together in the Central and South Asia Conference to promote economic integration, cooperation, and improving multilateral trade between landlocked Central Asia and South Asia.
Risk of natural calamities, epidemics, or disasters
The risk of force majeure disruptions in the supply chain sector reached unprecedented levels with the onset of COVID-19. The pandemic must be a lesson not only to fill the gaps in the existing supply chain system but also to improve it through decentralization and automation.
Amidst the pandemic, we can see that shortage of chips affected the automotive industry thus hampering vehicle production. This is also when the world is seeing a surge in demand for private vehicles, electric cars etc. This shortage is expected to last even after the pandemic dies out.
Such disruptions have pushed developing nations further back as the goal of enterprises and manufacturers now is to survive & stabilize, before they put together a roadmap to budget for industry 4.0 practices, even though they realize that such forward-looking practices are what will help them brave later storms.
Slow adoption of robust data management practices & data visibility
Big Data analytics is getting popular across all industries and domains. Removing unwanted data, non-essential fields and noise is becoming ever more important to dramatically improving operational efficiency.
However, the adoption rates have been relatively slow which is expected to pick up in the next 5-year window.
The Supply Chain Big Data Analytics Market was valued at $3.55 B in 2020. SCM is expected to reach $ 9.28 B by 2026, at a CAGR of 17.31% for the period 2021-2026.
Impact of Industry 4.0 on Supply Chain Management
Revolutionizing Visibility and Accuracy Across Global Supply Chains
The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) has dramatically enhanced the transparency and precision of global supply chains. This digital transformation allows for real-time tracking of goods and inventory, significantly improving order accuracy and reducing the risk of supply chain disruptions. The ability to monitor the entire supply chain ecosystem in real-time is a hallmark of Industry 4.0's impact, ensuring a more efficient and reliable flow of goods worldwide.
Driving Efficiency with Predictive Analytics and IoT Data
Predictive analytics, powered by IoT data, is a key benefit of Industry 4.0, enabling companies to forecast demand with unprecedented accuracy. This advanced approach to demand planning reduces forecasting errors, optimizes inventory management, and leads to significant cost savings. The use of data analytics in this context demonstrates how Industry 4.0 technologies can transform supply chain operations by making them more responsive and cost-effective.
Enhancing Collaboration through Digital Supply Chain Integration
Industry 4.0 facilitates unparalleled collaboration within the supply chain through the use of digital platforms and IoT technologies. This seamless connectivity between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers breaks down traditional silos and fosters a more integrated and efficient supply chain ecosystem. The result is a more agile and resilient supply chain capable of responding quickly to changes and challenges.
Optimizing Warehouse Operations with Smart Technology
The application of IoT and smart technologies under Industry 4.0 greatly improves warehouse management and logistics. From real-time goods tracking to automated inventory management, these technologies enhance operational efficiency and reduce costs. The ability to precisely monitor and control inventory in real time is a clear indication of how Industry 4.0 is reshaping warehouse operations for the better.
Creating Adaptive and Intelligent Supply Chains
Industry 4.0 introduces the concept of intelligent supply chains, which can autonomously learn and adapt to risks and changes. This self-optimizing capability, supported by IoT data analysis and machine learning, ensures that supply chains are more resilient and efficient, capable of handling complexities with minimal human intervention.
Boosting Supply Chain Agility with Integrated Technologies
The convergence of cloud computing, IoT, and other Industry 4.0 technologies significantly increases the agility of supply chain management. This technological synergy ensures that all stakeholders have access to consistent, real-time information, enabling rapid adaptation to market changes and disruptions. The agility afforded by these integrated technologies is essential for maintaining competitiveness in a volatile market.
The tangible impact in Manufacturing Operations
Industry 4.0 will impact the supply chain in a way beyond our imagination. Interconnectedness and interoperability will be the primary focus. Before the introduction of automation technologies, the product supply chains were fully manually operated. This meant feedback loops and data analysis was not easy to perform which resulted in long cycles for process improvement.
The concept of Smart factories & Industrial IoT is getting massive attention across the developed world. Innovative technologies consisting of sensors, IoT, 3D visualization and printing, Data analytics, embedded systems are now energizing & fixing the supply chain holes.
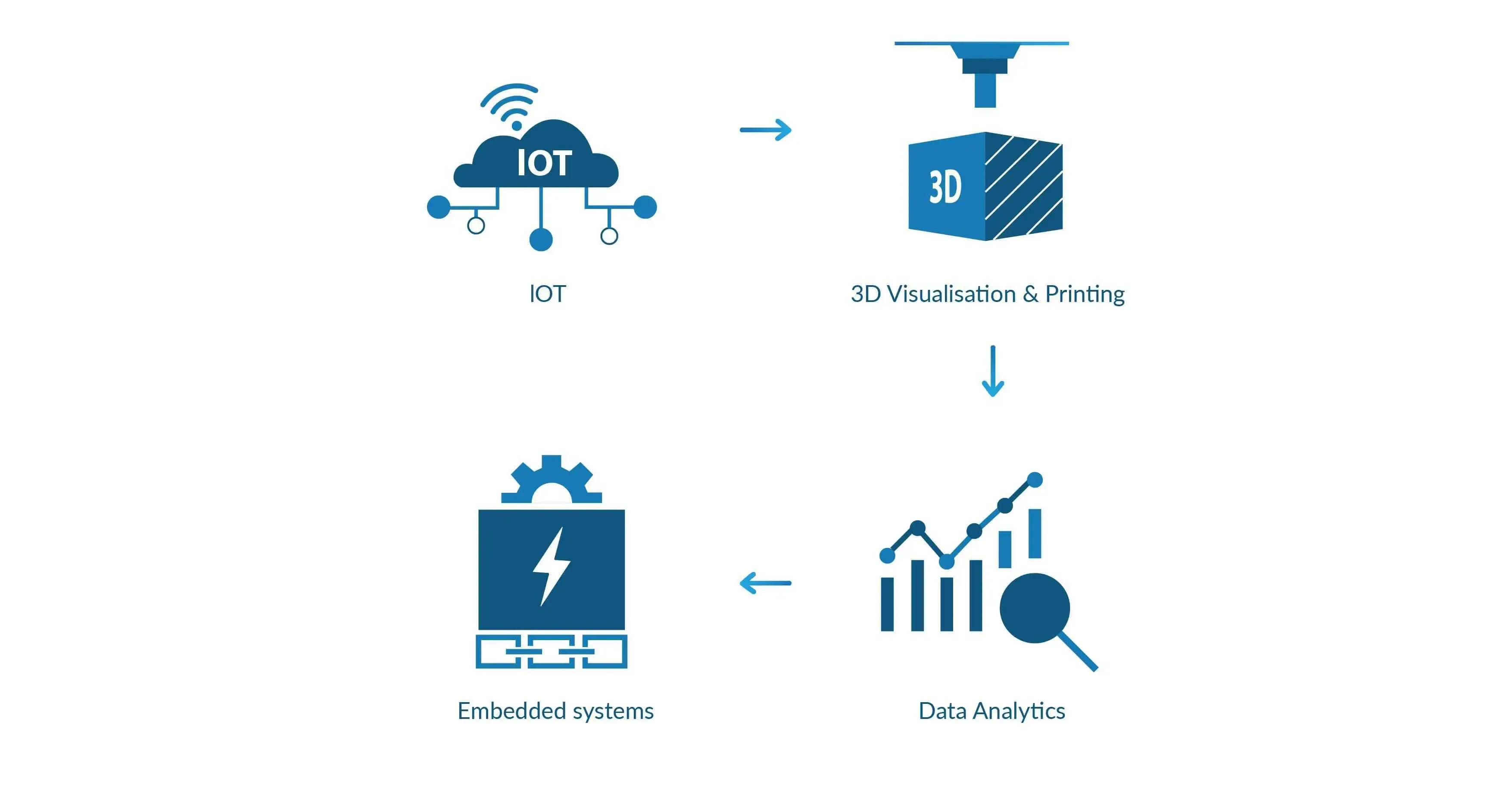
Data feedback loops powered by sensor-based systems are enabling organizations and businesses to better understand what is working and what needs improvement in their own backyards.
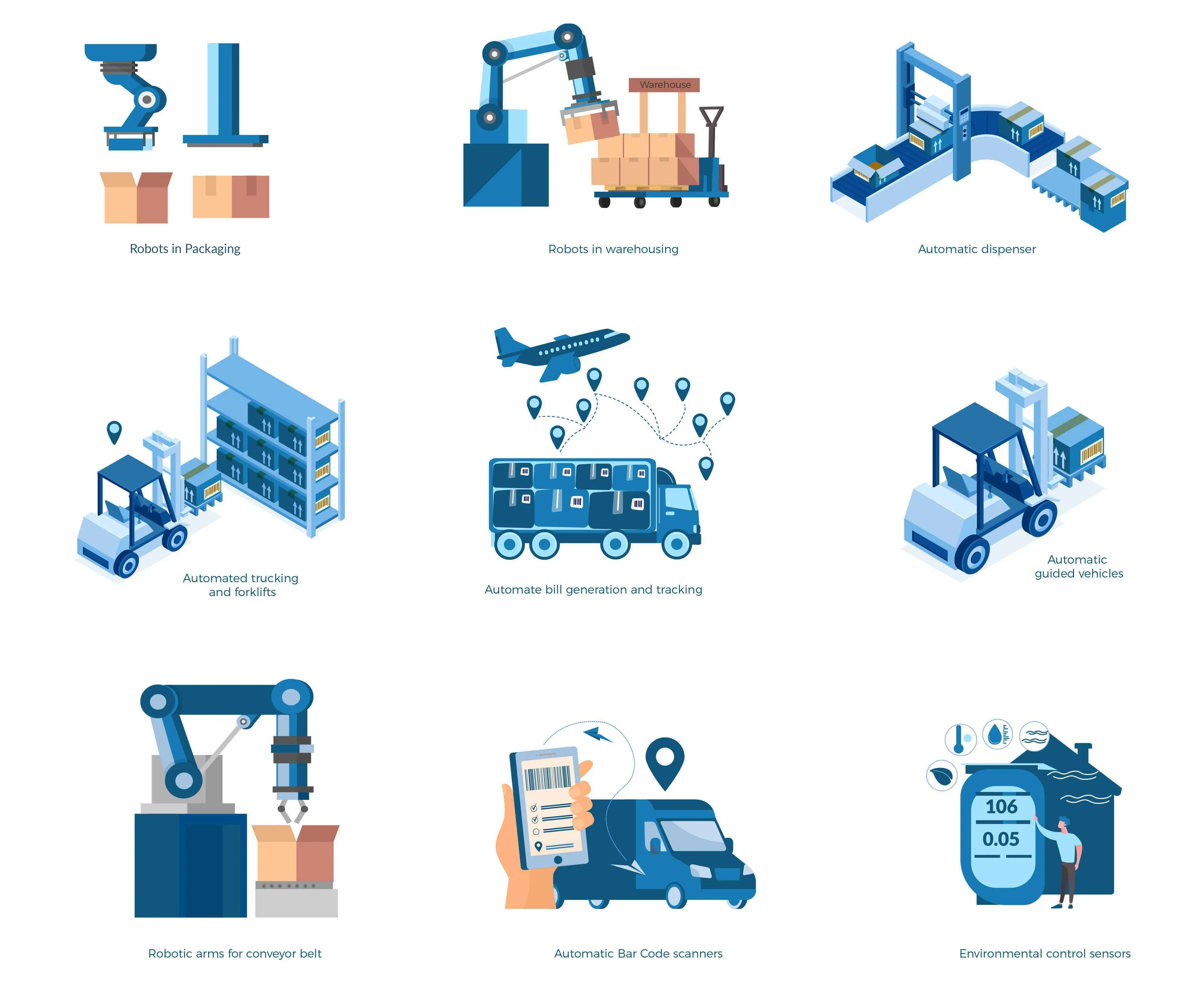
A few instances of how industry 4.0 practices are changing the face of manufacturing & logistics operations are captured below
Getting the Supply Chain Operations workforce skill ready to embrace the change.
Along with the automation of the system, we need to ensure that the employees or workers associated with the same should be able to adapt themselves.
When an existing industry turns smart we need to ensure that employees are taught to work with these technologies. The workforce must be given appropriate training, online courses, upskilling in IoT, software applications used, simulators used, web-based technologies. Along with technical skills, soft skills also need to be given due importance in the 21st century when communication is given utmost priority.
Supply Chain Management Trends in 2024
As Industry 4.0 continues to reshape industries, the realm of supply chain management undergoes a profound transformation, prompting organizations to reevaluate their operational strategies in response to shifting paradigms. With the emergence of disruptive technologies and the convergence of mega-trends alongside evolving consumer expectations, supply chains are presented with both challenges and opportunities to optimize their performance and embrace innovative digital frameworks.
Harnessing Technological Innovations for Enhanced Operational Agility
The advent of Industry 4.0 has ushered in an era of unprecedented technological advancements, with IoT modules and connectivity platforms at the forefront of revolutionizing supply chain dynamics. These cutting-edge solutions offer unparalleled visibility and control, empowering businesses to optimize processes, mitigate risks, and adapt swiftly to fluctuating market demands with precision and efficiency.
Navigating Macro-Economic Trends for Sustainable Supply Chain Practices
Supply chain strategies are increasingly influenced by macro-economic shifts, including the rapid expansion of rural economies and the redistribution of wealth on a global scale. Concurrently, imperatives to reduce carbon emissions and comply with evolving regulatory frameworks pose significant challenges for logistics operations. Moreover, demographic changes, such as labor shortages and evolving workforce demographics, underscore the importance of implementing agile and sustainable solutions to ensure operational resilience and longevity.
Meeting Heightened Customer Expectations in the Digital Age
In today's digital landscape, consumer expectations are continually evolving, driven by the convenience and personalization afforded by online commerce. This necessitates supply chains to not only adapt to the granularization of orders and expanding SKU portfolios but also to prioritize agility and responsiveness to cater to the diverse needs and preferences of modern consumers. Furthermore, the proliferation of online platforms heightens competition, emphasizing the importance of leveraging data-driven insights and innovative strategies to maintain a competitive edge and drive customer satisfaction.
Cavli Wireless for applications in Supply Chain & Logistics that require Smart-Connectivity
Cavli Wireless provides Connectivity at the Edge & Connectivity as a Service with its own range of Cellular modules & eSIM solutions which are integrated with our proprietary Global Data Subscription & Device Management Platform. Our solutions have applications across industries like logistics & transportation, industrial IoT & smart manufacturing, smart city, safety & monitoring and others.
A few use cases for which Cavli takes care of IoT connectivity management include
Please scan through our IoT applications page to learn more about use cases we power in Supply chain & logistics management
